Flutter LinearProgressIndicator Tutorial with Examples
1. LinearProgressIndicator
LinearProgressIndicator is a subclass of ProgressIndicator. It creates a horizontal progress bar indicator, but you can also create a vertical progress bar indicator if you place it in a RotatedBox rotating 90 degrees.


- CircularProgressIndicator
- ProgressIndicator
LinearProgressIndicator is divided into two types:
Determinate
Determinate: a progress indicator that shows the user the percentage of work completed based on the value of the value property (in the range of 0 and 1).
Indeterminate
Indeterminate: a progress indicator that neither identifies the percentage of work completed nor indicates the end time.
LinearProgressIndicator Constructor:
LinearProgressIndicator constructor
const LinearProgressIndicator(
{Key key,
double value,
Color backgroundColor,
Animation<Color> valueColor,
double minHeight,
String semanticsLabel,
String semanticsValue}
)2. Example: Indeterminate
Let's begin with the simplest example, a LinearProgressIndicator simulates an active process but does not know the percentage of work that has been completed and does not know when to finish.
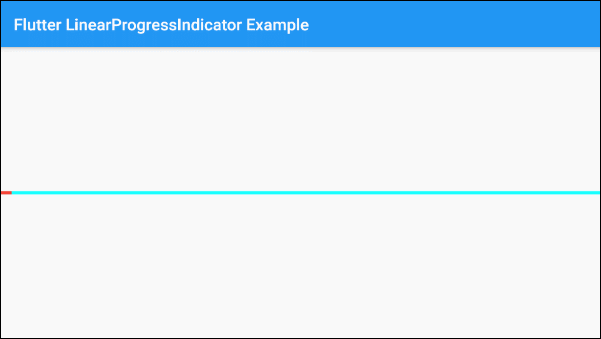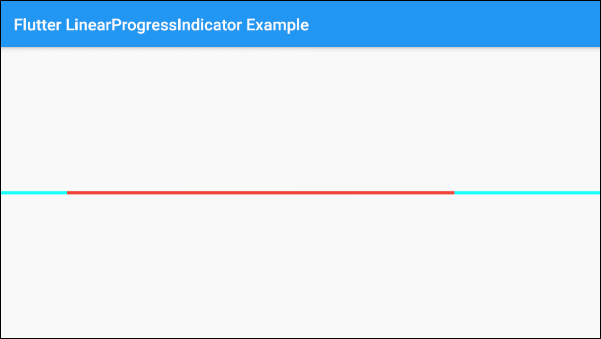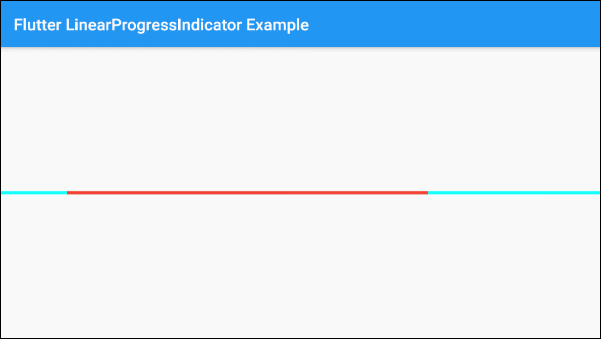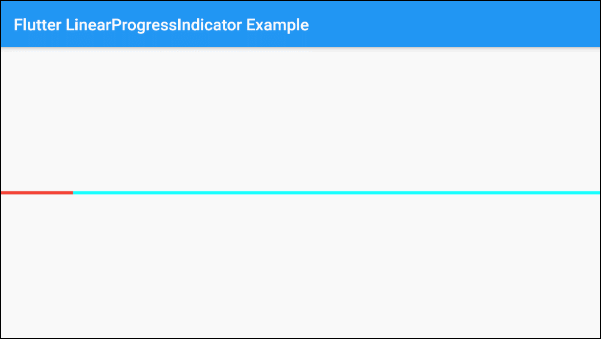
main.dart (ex 1)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'o7planning.org',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
home: HomePage(),
);
}
}
class HomePage extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter LinearProgressIndicator Example'),
),
body: Center(
child: LinearProgressIndicator(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyan[100],
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.green),
),
),
);
}
}By default, LinearProgressIndicator has a fairly small size, but if you want to customize its size, let's put it in a SizedBox.
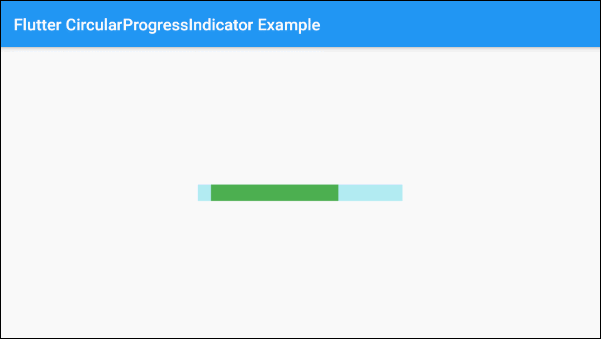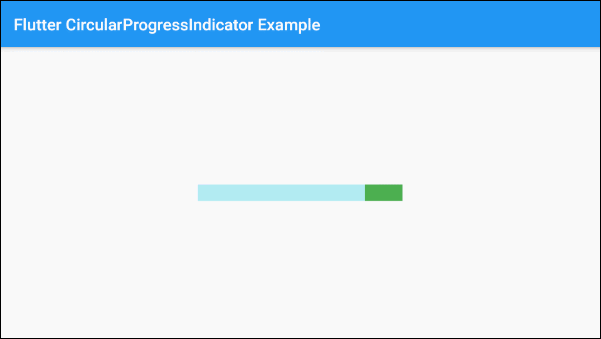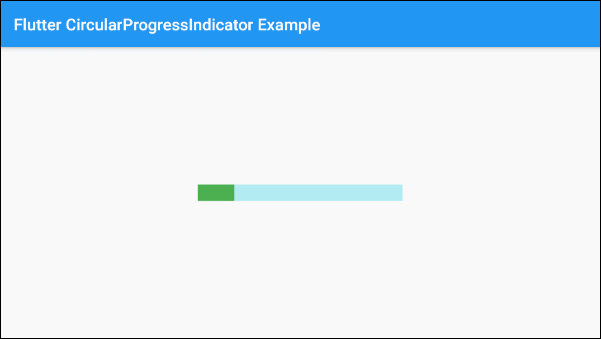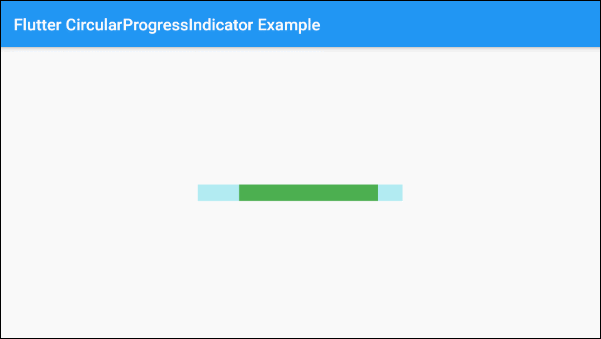
SizedBox(
width: 250,
height: 20,
child: LinearProgressIndicator(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyan[100],
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.green),
),
)The valueColor parameter is used to specify a color animation to the progress of LinearProgressIndicator, for example:
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.red)AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color> will always stop the animation of LinearProgressIndicator if the value parameter is a specific value and not a null value.
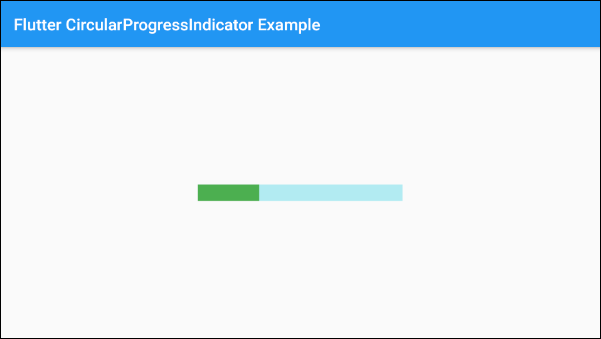
SizedBox(
width: 250,
height: 20,
child: LinearProgressIndicator(
value: 0.3,
backgroundColor: Colors.cyan[100],
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.green),
),
)
Based on the aforementioned characteristics of the value and valueColor parameters you can control the behavior of LinearProgressIndicator, let's see an example:
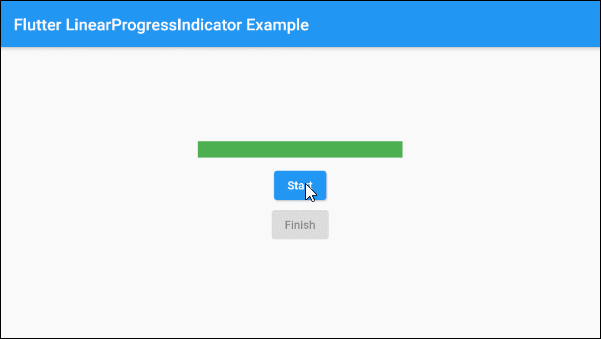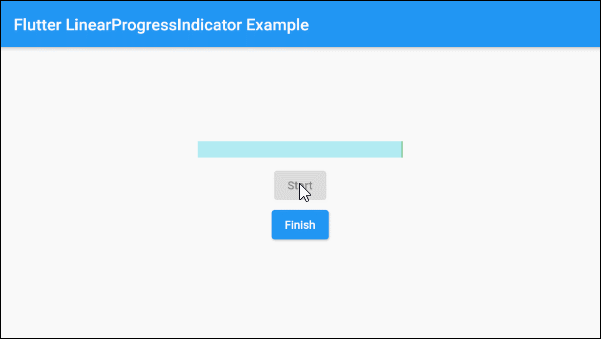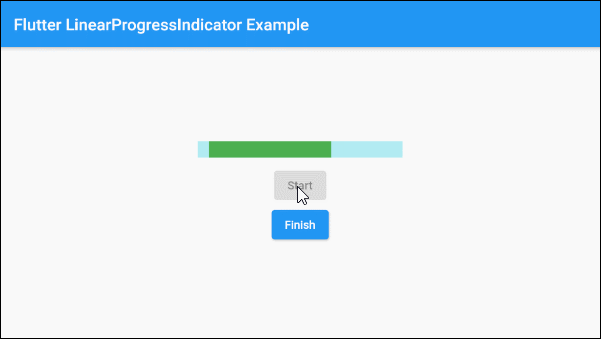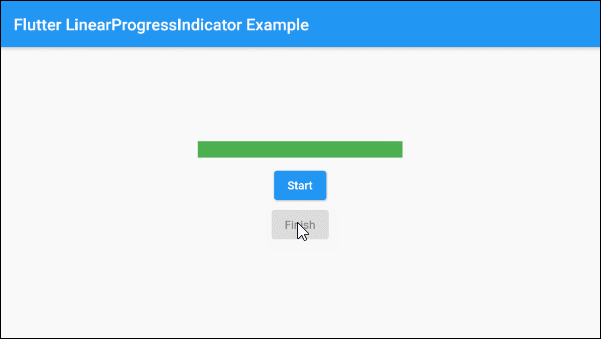
main.dart (ex 1d)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'o7planning.org',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
home: HomePage(),
);
}
}
class HomePage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return _HomePageState();
}
}
class _HomePageState extends State<HomePage> {
bool _working = false;
void startWorking() async {
this.setState(() {
this._working = true;
});
}
void finishWorking() {
this.setState(() {
this._working = false;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter LinearProgressIndicator Example'),
),
body: Center(
child: Column (
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
SizedBox(
width: 250,
height: 20,
child: LinearProgressIndicator(
value: this._working? null: 1,
backgroundColor: Colors.cyan[100],
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.green),
),
),
SizedBox(width:10, height:10),
ElevatedButton(
child: Text("Start"),
onPressed: this._working? null: () {
this.startWorking();
}
),
ElevatedButton(
child: Text("Finish"),
onPressed: !this._working? null: () {
this.finishWorking();
}
)
]
)
),
);
}
}3. Example: Determinate
The following example uses LinearProgressIndicator to present a progress with the percentage of work completed. The value parameter has a value from 0 to 1.
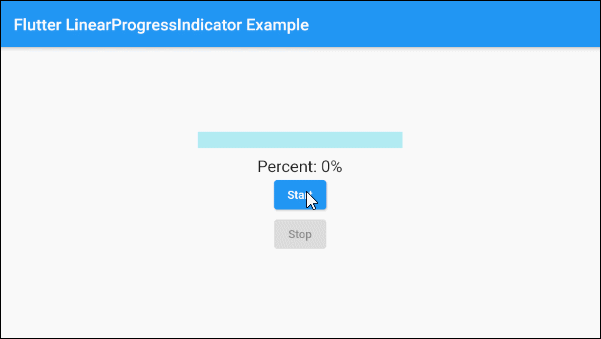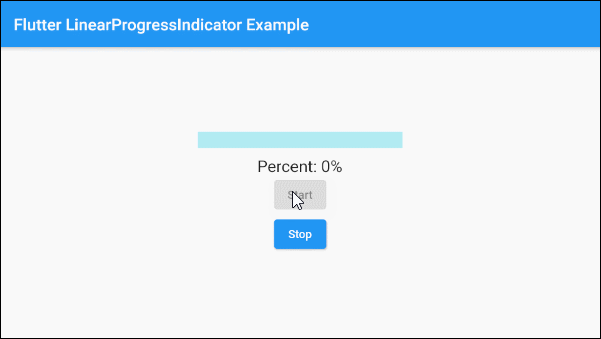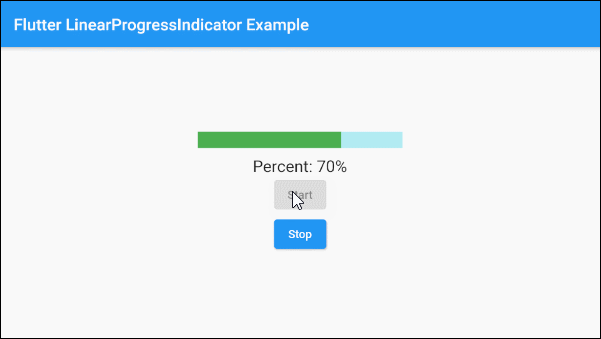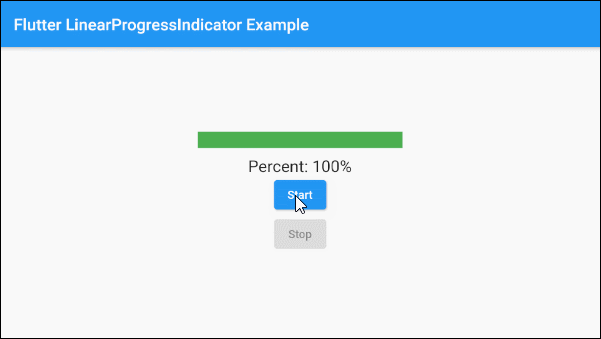
main.dart (ex 2)
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'o7planning.org',
debugShowCheckedModeBanner: false,
home: HomePage(),
);
}
}
class HomePage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
return _HomePageState();
}
}
class _HomePageState extends State<HomePage> {
double _value = 0;
bool _working = false;
void startWorking() async {
this.setState(() {
this._working = true;
this._value = 0;
});
for(int i = 0; i< 10; i++) {
if(!this._working) {
break;
}
await Future.delayed(Duration(seconds: 1));
this.setState(() {
this._value += 0.1;
});
}
this.setState(() {
this._working = false;
});
}
void stopWorking() {
this.setState(() {
this._working = false;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Flutter LinearProgressIndicator Example'),
),
body: Center(
child: Column (
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
SizedBox(
width: 250,
height: 20,
child: LinearProgressIndicator(
value: this._value,
backgroundColor: Colors.cyan[100],
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.green),
),
),
SizedBox(width:10, height: 10),
Text(
"Percent: " + (this._value * 100).round().toString()+ "%",
style: TextStyle(fontSize: 20),
),
ElevatedButton(
child: Text("Start"),
onPressed: this._working? null: () {
this.startWorking();
}
),
ElevatedButton(
child: Text("Stop"),
onPressed: !this._working? null: () {
this.stopWorking();
}
)
]
)
),
);
}
}4. Example: Vertical Progress
LinearProgressIndicator basically does not support the vertical direction. However, if you want a vertical progress bar indicator, you can place it in a RotatedBox with a 90 degree rotation.
For example:
RotatedBox(
quarterTurns: -1,
child: SizedBox(
width: 250,
height: 25,
child : LinearProgressIndicator(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyan[100],
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.green),
)
)
)- The quarterTurns = 1 parameter means 90 degrees clockwise rotation.
- Otherwise, quarterTurns = -1 means 90 degrees counterclockwise rotation.
5. backgroundColor
backgroundColor is used to set the background color of LinearProgressIndicator.
Color backgroundColor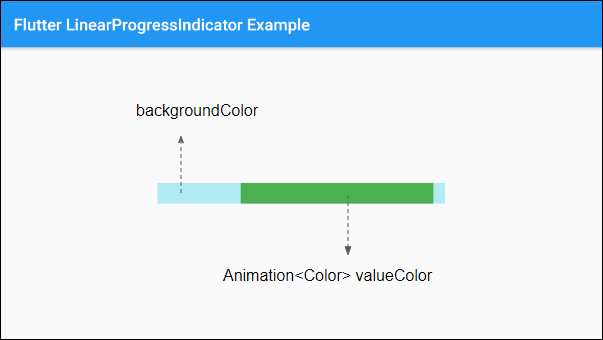
7. valueColor
valueColor is used to specify a color animation to the progress.
Animation<Color> valueColor
For example:
LinearProgressIndicator(
backgroundColor: Colors.cyanAccent,
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.red),
)- Flutter Animation
9. semanticsLabel
semanticsLabel is used to describe the intended use of LinearProgressIndicator, which is completely hidden on the interface and is purposeful for Screen readers, such as screen readers for the blind.
String semanticsLabel10. semanticsValue
semanticsValue is completely hidden on the screen. Its purpose is to provide information about the current progress for screen readers.
By default, the value of the semanticsValue is the percentage of the work completed, for example, the value of the value property is 0.3 meaning that the semanticsValue is "30%".
String semanticsValueExample:
LinearProgressIndicator(
value: this._value,
backgroundColor: Colors.cyanAccent,
valueColor: new AlwaysStoppedAnimation<Color>(Colors.red),
semanticsLabel: "Downloading file abc.mp3",
semanticsValue: "Percent " + (this._value * 100).toString() + "%",
)Flutter Programming Tutorials
- Flutter Column Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Stack Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter IndexedStack Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Spacer Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Expanded Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter SizedBox Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Tween Tutorial with Examples
- Install Flutter SDK on Windows
- Install Flutter Plugin for Android Studio
- Create your first Flutter app - Hello Flutter
- Flutter Scaffold Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter AppBar Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter BottomAppBar Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter TextButton Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter ElevatedButton Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter EdgeInsetsGeometry Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter EdgeInsets Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter CircularProgressIndicator Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter LinearProgressIndicator Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Center Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Align Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Row Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter SplashScreen Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Alignment Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Positioned Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter SimpleDialog Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter AlertDialog Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Navigation and Routing Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter TabBar Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Banner Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter BottomNavigationBar Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter FancyBottomNavigation Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Card Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Border Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter ContinuousRectangleBorder Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter RoundedRectangleBorder Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter CircleBorder Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter StadiumBorder Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter Container Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter RotatedBox Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter CircleAvatar Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter IconButton Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter FlatButton Tutorial with Examples
- Flutter SnackBar Tutorial with Examples
Show More