Amazon S3 Bucket policies
S3 Bucket Policy is a resource-based policy that allows you to manage access to resources stored on an S3 Bucket of yours. You can assign permissions to each resource to allow or deny actions requested by a principal (user or role).
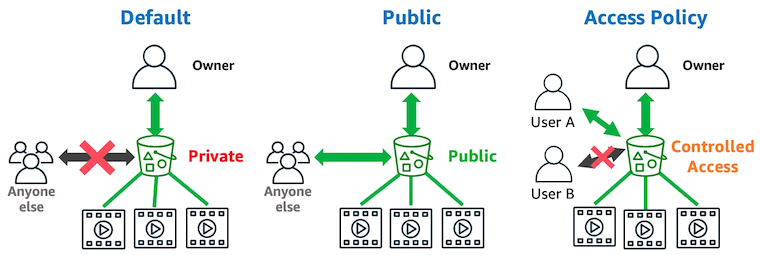
In this article, I will guide you through creating a few common S3 Bucket policies. To create more advanced policies, you should refer to the official Amazon S3 documents.
To assist in creating a Bucket policy quickly and accurately you can use the "policygen" tool below:
1. Where to change Bucket policy?
First, login to Amazon S3 Console.
Next, click on a Bucket you are interested in.
- [Selected Bucket] > Permissions > Bucket policy > Edit
2. Minimum public policy
Action | Description |
s3:GetObject | This permission allows the user to access the object. In case Bucket has the "Static website hosting" feature enabled, this permission will allow users to download objects. |
s3:ListBucket | Allows users to list objects in Bucket. Note: If you access an object that does not exist in the Bucket, there will be two situations:
|
s3:GetObject and s3:ListObject are the two minimum permissions for public users.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "Stmt-GetObject",
"Action": [
"s3:GetObject"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*",
"Principal": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "Stmt-ListBucket",
"Action": [
"s3:ListBucket"
],
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name",
"Principal": "*"
}
]
}3. Allow all permissions
This Bucket Policy grants all permissions.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "S3PolicyId1",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowAll",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name",
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*"
],
}
]
}4. Allow all Get and List permissions
This Bucket policy allows all permissions with the prefix "Get" or "List".
- s3:GetObject, s3:ListBucket, s3:GetBucketLocation, s3:GetBucketLocation,...
{
"Version":"2012-10-17",
"Id":"S3PolicyId1",
"Statement":[
{
"Sid":"AllowAll_GET_LIST",
"Effect":"Allow",
"Principal":"*",
"Action":[
"s3:Get*",
"s3:List*"
],
"Resource":[
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name",
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*"
]
}
]
}5. IP-based policy
- IPv4 and IPv6
IPv4
The policy below denies all users from performing any action on the Bucket, except users whose IPv4 falls within the specified range.
Warning:Before using this policy, replace the IPv4 address range (192.0.2.0/24) in this example with an appropriate value for your use case. Otherwise, you will lose the ability to access your Bucket.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Id": "S3PolicyId1",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "IPAllow",
"Effect": "Deny",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name",
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*"
],
"Condition": {
"NotIpAddress": {
"aws:SourceIp": "192.0.2.0/24"
}
}
}
]
}IPv4 & IPv6
The following example Bucket Policy shows how to mix IPv4 and IPv6 address ranges to cover all of your organization's valid IP addresses.
Note: IPv6 must conform to the CIDR standard format. :0000: can be replaced by ::
{
"Id": "PolicyId2",
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowIPmix",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": "*",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name",
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*"
],
"Condition": {
"IpAddress": {
"aws:SourceIp": [
"192.0.2.0/24",
"2001:DB8:1234:5678::/64"
]
},
"NotIpAddress": {
"aws:SourceIp": [
"203.0.113.0/24",
"2001:DB8:1234:5678:ABCD::/80"
]
}
}
}
]
}Result:
Allowed | 192.0.2.1 & 2001:DB8:1234:5678::1 |
Denied | 203.0.113.1 & 2001:DB8:1234:5678:ABCD::1 |
6. Policy based on HTTP/HTTPS
This policy denies HTTP requests (allows HTTPS requests).
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [{
"Sid": "RestrictToTLSRequestsOnly",
"Action": "s3:*",
"Effect": "Deny",
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name",
"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*"
],
"Condition": {
"Bool": {
"aws:SecureTransport": "false"
}
},
"Principal": "*"
}]
}HTTP Referer example:
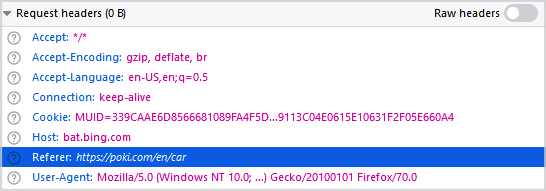
A policy that allows the actions s3:GetObject and s3:GetObjectVersion from a specific website, the requests need to include "Header referer" information. Note: Attackers can also forge "Header referer" information if they know you are using this policy.
{
"Version":"2012-10-17",
"Id":"HTTP referer policy example",
"Statement":[
{
"Sid":"Allow only GET requests originating from www.example.com and example.com.",
"Effect":"Allow",
"Principal":"*",
"Action":["s3:GetObject","s3:GetObjectVersion"],
"Resource":"arn:aws:s3:::your_bucket_name/*",
"Condition":{
"StringLike":{"aws:Referer":["http://www.example.com/*","http://example.com/*"]}
}
}
]
}Amazon Web Services Tutorials
- Introduction to Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Introduction to Amazon S3
- Introduction to Amazon Cloudfront and its architecture
- How to reduce Amazon Cloudfront Costs?
- Amazon CloudFront Invalidation
- Introduction to DigitalOcean Spaces
- Create DigitalOcean Spaces Bucket
- Introduction to Amazon ACM
- Java Awssdk S3 S3Client Upload object
- Create AWS accessKeyId/secretAccessKey
- Java Awssdk S3 List objects
- Host a static website on Amazon S3
- Java Awssdk CloudFront Invalidation
- DigitalOcean Spaces Create Access Key
- Java Awssdk Common Credentials Providers
- Java Awssdk ProfileCredentialsProvider
- Java Awssdk Creating and using EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider
- Java Awssdk Creating and using SystemPropertyCredentialsProvider
- Java Awssdk S3 Upload object with S3TransferManager
- Java Awssdk S3 S3TransferManager download object
- Java Manipulate DigitalOcean Spaces using S3TransferManager
- Java Create, list and delete S3 Bucket
- Aws Console create IAM User
- Create Amazon S3 Bucket
- Configure custom domain for Amazon S3 static website
- Create a CloudFront distribution for S3 Bucket
- Configure Amazon CloudFront Error Pages
- Amazon S3 Bucket policies
- Amazon AWS Policy Generator - policygen
- Migrate DNS service to Amazon Route 53
- Transfer domain registration to Amazon Route 53
- Request an SSL certificate from Amazon ACM
Show More