Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Basic Authentication
1. Objective of Example
This document is based on:
Spring Boot 2.x (Or >= 1.5.9)
Eclipse 4.7 Oxygen
In this post, I am going to show you how to create a RESTful Web Service application and secure it with the Basic Authentication. This means that your application will provide data resources but the user that wants to use this data resource have to be authenticated with the Basic Authentication method.
Basic Authentication
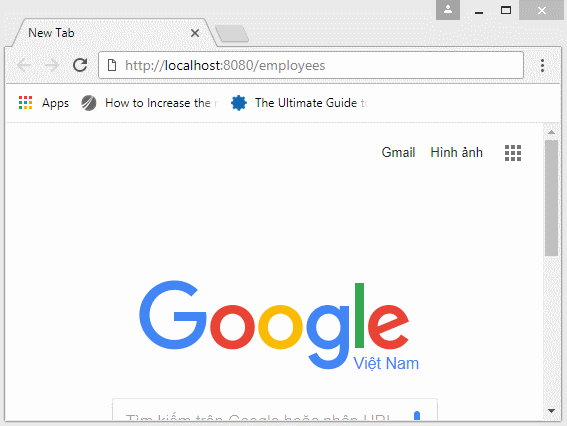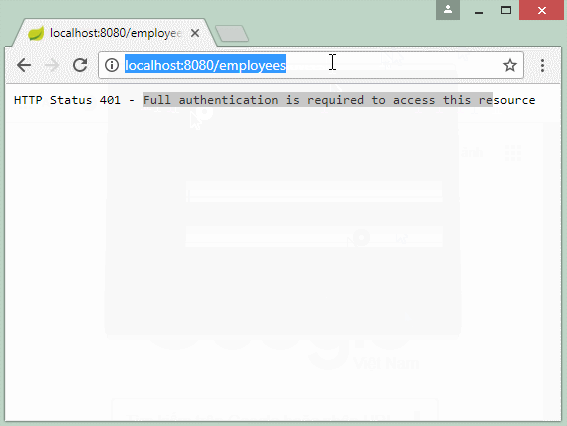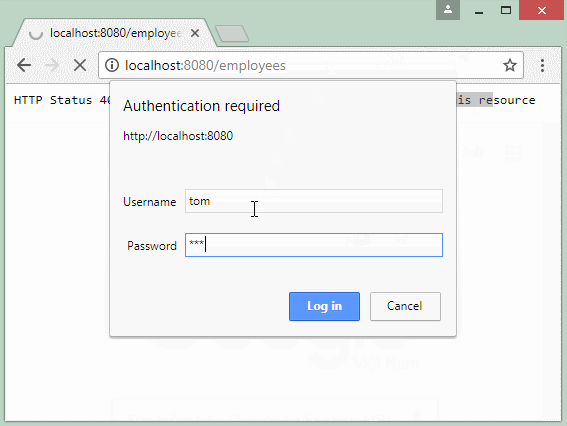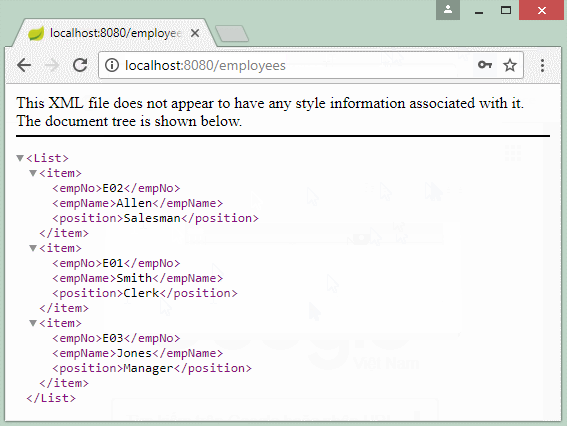
To visit the data resource secured by the Basic Authentication, an user has to give a request and that request contains the username/password information attached on the Header.
You can use a a browser to access a data resource secured by the Basic Authentication, in which case a dialog box will be displayed allowing you to enter the username/password. This information will be attached with the request to send to REST Server.
2. Create Spring Boot project
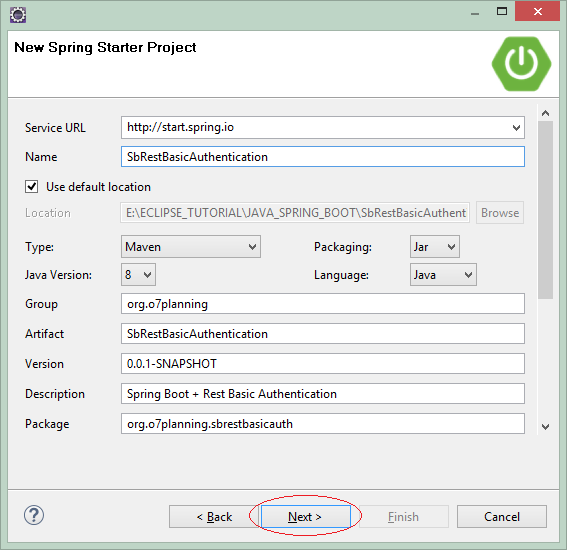
On Eclipse, create Spring Boot project.
Enter:
- Name: SbRestBasicAuthentication
- Group: org.o7planning
- Package: org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth
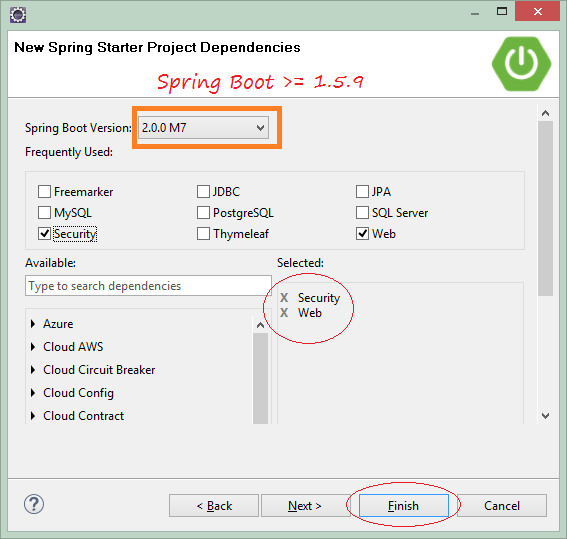
In the next step, you need to select the technologies to be used.
SbRestBasicAuthenticationApplication.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SbRestBasicAuthenticationApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SbRestBasicAuthenticationApplication.class, args);
}
}3. Configure pom.xml
In this example, we need a library to convert the XML object into a Java one and vice versa and another library to convert JSON into Java and vice versa.
JSON <==> Java
The spring-boot-starter-web has built in jackson-databind, which helps to convert JSON into Java object and vice versa.
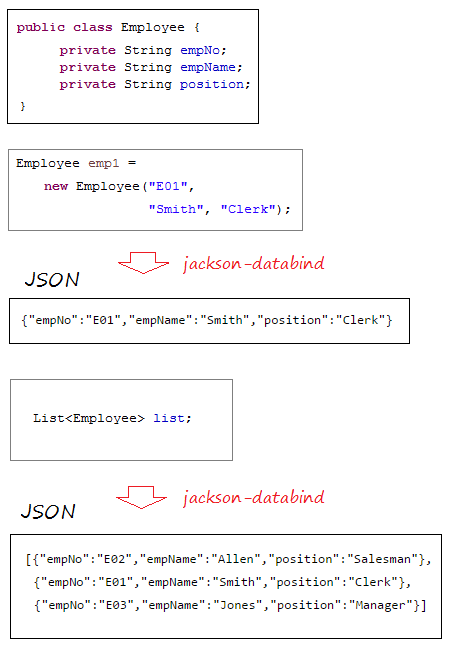
XML <==> Java
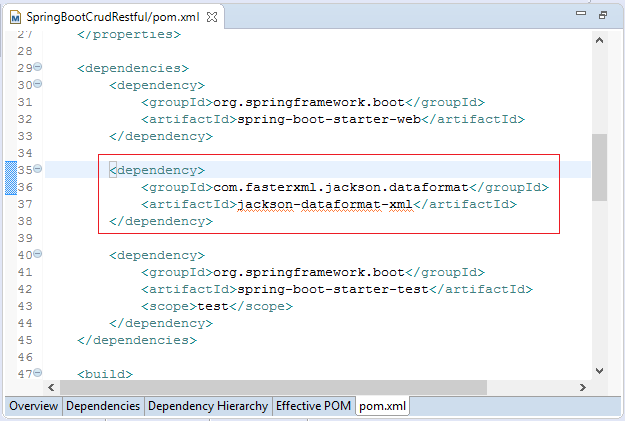
The Spring Boot uses JAXB (available in JDK) as a default library to convert XML and Java. However, your Java classes need to be annotated by @XmlRootElement,... Therefore, my advice is that you should use the jackson-dataformat-xml as a library to convert XML and Java. To use the jackson-dataformat-xml, you need to declare it in the pom.xml file:
** pom.xml **
...
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
...

pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SbRestBasicAuthentication</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SbRestBasicAuthentication</name>
<description>Spring Boot +Rest + Basic Authentication</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4. Security & AuthenticationEntryPoint
The security configurations will be written in the WebSecurityConfig class. In this post, I don't focus on "How to obtain usernames in database", therefore, we create 2 fixed UserNames and store them in the memory. The user visiting the data resource of the REST Service will log in with one of these username.
WebSecurityConfig.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.configurers.provisioning.InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;
import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
import org.springframework.security.web.AuthenticationEntryPoint;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class WebSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationEntryPoint authEntryPoint;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable();
// All requests send to the Web Server request must be authenticated
http.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
// Use AuthenticationEntryPoint to authenticate user/password
http.httpBasic().authenticationEntryPoint(authEntryPoint);
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
return bCryptPasswordEncoder;
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
String password = "123";
String encrytedPassword = this.passwordEncoder().encode(password);
System.out.println("Encoded password of 123=" + encrytedPassword);
InMemoryUserDetailsManagerConfigurer<AuthenticationManagerBuilder> //
mngConfig = auth.inMemoryAuthentication();
// Defines 2 users, stored in memory.
// ** Spring BOOT >= 2.x (Spring Security 5.x)
// Spring auto add ROLE_
UserDetails u1 = User.withUsername("tom").password(encrytedPassword).roles("USER").build();
UserDetails u2 = User.withUsername("jerry").password(encrytedPassword).roles("USER").build();
mngConfig.withUser(u1);
mngConfig.withUser(u2);
// If Spring BOOT < 2.x (Spring Security 4.x)):
// Spring auto add ROLE_
// mngConfig.withUser("tom").password("123").roles("USER");
// mngConfig.withUser("jerry").password("123").roles("USER");
}
}The AuthenticationEntryPointImpl class is extended from the BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint class. It is used to check whether the username/password attached with the request is valid or not.
AuthenticationEntryPointImpl.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.auth;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.www.BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class AuthenticationEntryPointImpl extends BasicAuthenticationEntryPoint {
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authEx)
throws IOException, ServletException {
response.addHeader("WWW-Authenticate", "Basic realm=" + getRealmName());
response.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_UNAUTHORIZED);
PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter();
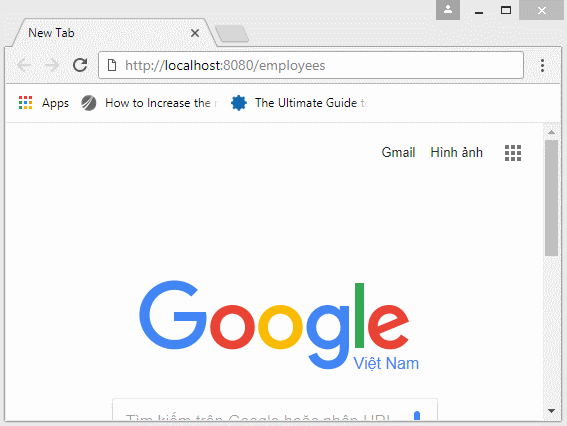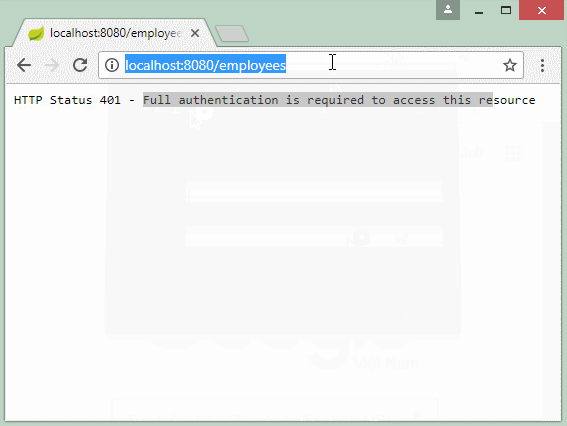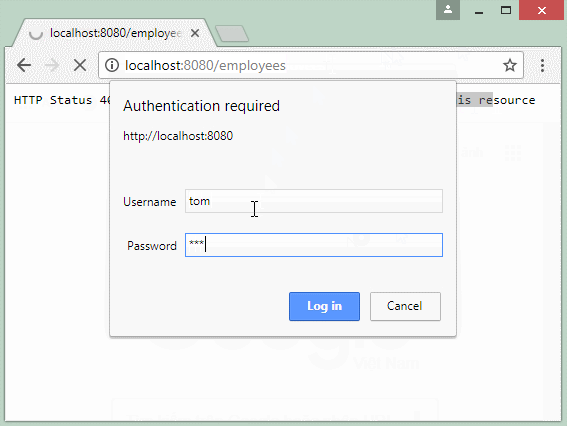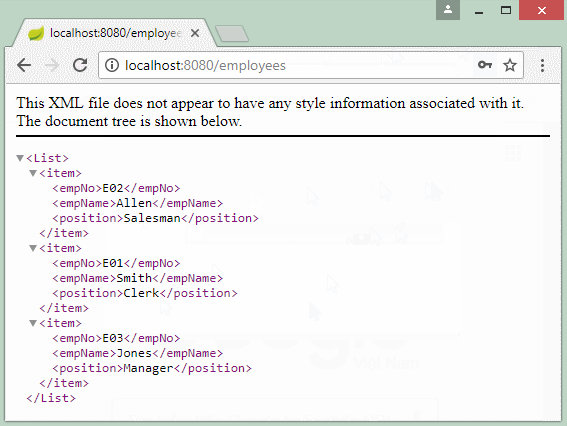
writer.println("HTTP Status 401 - " + authEx.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// RealmName appears in the login window (Firefox).
setRealmName("o7planning");
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
}5. Model, DAO, Controller
Employee class represents for an employee.
Employee.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.model;
public class Employee {
private String empNo;
private String empName;
private String position;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String empNo, String empName, String position) {
this.empNo = empNo;
this.empName = empName;
this.position = position;
}
public String getEmpNo() {
return empNo;
}
public void setEmpNo(String empNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
}
public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
}
public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
}
public String getPosition() {
return position;
}
public void setPosition(String position) {
this.position = position;
}
}The EmployeeDAO class is annotated by @Repository to notify to the Spring that it is a Spring BEAN. This class includes the methods helping query a list of employees, create employees, update employee's information, and delete employees.
EmployeeDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.dao;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.o7planning.sbrestbasicauth.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class EmployeeDAO {
private static final Map<String, Employee> empMap = new HashMap<String, Employee>();
static {
initEmps();
}
private static void initEmps() {
Employee emp1 = new Employee("E01", "Smith", "Clerk");
Employee emp2 = new Employee("E02", "Allen", "Salesman");
Employee emp3 = new Employee("E03", "Jones", "Manager");
empMap.put(emp1.getEmpNo(), emp1);
empMap.put(emp2.getEmpNo(), emp2);
empMap.put(emp3.getEmpNo(), emp3);
}
public Employee getEmployee(String empNo) {
return empMap.get(empNo);
}
public Employee addEmployee(Employee emp) {
empMap.put(emp.getEmpNo(), emp);
return emp;
}
public Employee updateEmployee(Employee emp) {
empMap.put(emp.getEmpNo(), emp);
return emp;
}
public void deleteEmployee(String empNo) {
empMap.remove(empNo);
}
public List<Employee> getAllEmployees() {
Collection<Employee> c = empMap.values();
List<Employee> list = new ArrayList<Employee>();
list.addAll(c);
return list;
}
}The MainRESTController class is annotated by @RestController to inform to the Spring that it is a Spring Restful Controller,
MainRESTController.java
package org.o7planning.sbcrudrestful.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbcrudrestful.dao.EmployeeDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbcrudrestful.model.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.MediaType;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class MainRESTController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeDAO employeeDAO;
@RequestMapping("/")
@ResponseBody
public String welcome() {
return "Welcome to RestTemplate Example.";
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employees
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employees.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employees.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employees", //
method = RequestMethod.GET, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public List<Employee> getEmployees() {
List<Employee> list = employeeDAO.getAllEmployees();
return list;
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{empNo}", //
method = RequestMethod.GET, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public Employee getEmployee(@PathVariable("empNo") String empNo) {
return employeeDAO.getEmployee(empNo);
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee", //
method = RequestMethod.POST, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public Employee addEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
System.out.println("(Service Side) Creating employee: " + emp.getEmpNo());
return employeeDAO.addEmployee(emp);
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.xml
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee.json
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee", //
method = RequestMethod.PUT, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, //
MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public Employee updateEmployee(@RequestBody Employee emp) {
System.out.println("(Service Side) Editing employee: " + emp.getEmpNo());
return employeeDAO.updateEmployee(emp);
}
// URL:
// http://localhost:8080/SomeContextPath/employee/{empNo}
@RequestMapping(value = "/employee/{empNo}", //
method = RequestMethod.DELETE, //
produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE })
@ResponseBody
public void deleteEmployee(@PathVariable("empNo") String empNo) {
System.out.println("(Service Side) Deleting employee: " + empNo);
employeeDAO.deleteEmployee(empNo);
}
}Explain:
- produces = { MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE, MediaType.APPLICATION_XML_VALUE }
- produces = { "application/json" , "application/xml" }
The produces attribute is used to specify an URL that will only create (return to the user) the data in which format, for example, "application / json", "application / xml".
Java Web Services Tutorials
- What are RESTful Web Services?
- Java RESTful Web Services Tutorial for Beginners
- Simple CRUD example with Java RESTful Web Service
- Create Java RESTful Client with Jersey Client
- RESTClient A Debugger for RESTful Web Services
- Simple CRUD example with Spring MVC RESTful Web Service
- CRUD Restful Web Service Example with Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Restful Client with RestTemplate Example
- Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Basic Authentication
Show More
Spring Boot Tutorials
- Install Spring Tool Suite for Eclipse
- Spring Tutorial for Beginners
- Spring Boot Tutorial for Beginners
- Spring Boot Common Properties
- Spring Boot and Thymeleaf Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and FreeMarker Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Groovy Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Mustache Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and JSP Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP Tutorial with Examples
- Use Logging in Spring Boot
- Application Monitoring with Spring Boot Actuator
- Create a Multi Language web application with Spring Boot
- Use multiple ViewResolvers in Spring Boot
- Use Twitter Bootstrap in Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Interceptors Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Spring JDBC and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Spring JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, JPA and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Spring Data JPA Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Hibernate and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Integrating Spring Boot, JPA and H2 Database
- Spring Boot and MongoDB Tutorial with Examples
- Use Multiple DataSources with Spring Boot and JPA
- Use Multiple DataSources with Spring Boot and RoutingDataSource
- Create a Login Application with Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Create a Login Application with Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Create a User Registration Application with Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Example of OAuth2 Social Login in Spring Boot
- Run background scheduled tasks in Spring
- CRUD Restful Web Service Example with Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Restful Client with RestTemplate Example
- CRUD Example with Spring Boot, REST and AngularJS
- Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Basic Authentication
- Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Auth0 JWT
- Spring Boot File Upload Example
- Spring Boot File Download Example
- Spring Boot File Upload with jQuery Ajax Example
- Spring Boot File Upload with AngularJS Example
- Create a Shopping Cart Web Application with Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Spring Email Tutorial with Examples
- Create a simple Chat application with Spring Boot and Websocket
- Deploy Spring Boot Application on Tomcat Server
- Deploy Spring Boot Application on Oracle WebLogic Server
- Install a free Let's Encrypt SSL certificate for Spring Boot
- Configure Spring Boot to redirect HTTP to HTTPS
- Fetch data with Spring Data JPA DTO Projections
Show More