Spring Boot and Spring Data JPA Tutorial with Examples
1. Create Spring Boot project
On the Eclipse, create a Spring Boot project.
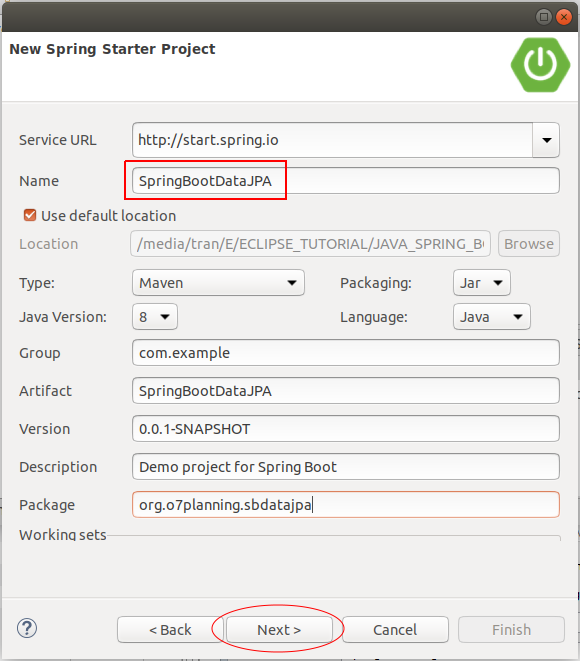
Select the technologies to be used in this project, including JPA and a database that you are familiar with.
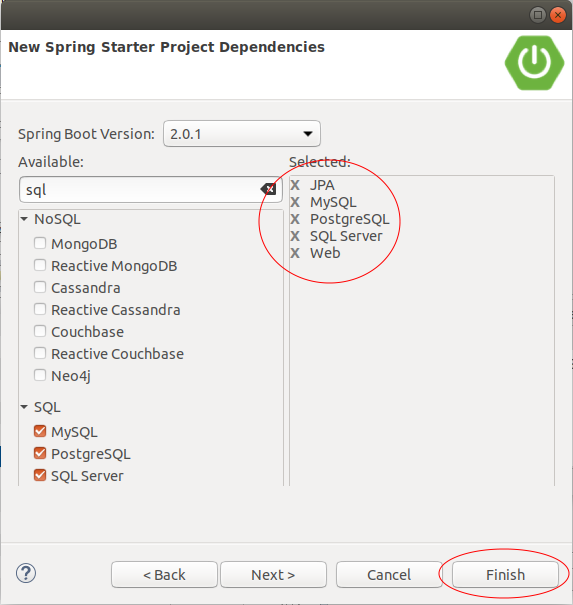
Add the following configuration snippetto the pom.xml file if you want to work with the Oracle database:
** Oracle **
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc7</artifactId>
<version>12.1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<repositories>
<!-- Repository for ORACLE ojdbc6. -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
</repositories>The full content of pom.xml file:
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootDataJPA</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SpringBootDataJPA</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc7</artifactId>
<version>12.1.0.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<repositories>
<!-- Repository for ORACLE ojdbc6. -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>SpringBootDataJpaApplication.java
package org.o7planning.sbdatajpa;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDataJpaApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDataJpaApplication.class, args);
}
}2. Configure Spring Boot & JPA
For the Spring Boot to be able to connect to a database, you need to configure in the applications.properties file. You can use any database with which you are familiar. Below are 4 configurations corresponding to 4 most common kinds of databases (MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, PostGres).
In practice, let's create a empty schema named "mydatabase". The JPA will create tables corresponding to the Entities included in the application.
application.properties (MySQL)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydatabase
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialectapplication.properties (Oracle)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
spring.datasource.username=mydatabase
spring.datasource.password=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.Oracle10gDialectapplication.properties (SQL Server)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:sqlserver://localhost\\SQLEXPRESS:1433;databaseName=mydatabase
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.SQLServer2012Dialectapplication.properties (PostGres)
# ===============================
# DATABASE CONNECTION
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydatabase
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=12345
# ===============================
# JPA / HIBERNATE
# ===============================
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.PostgreSQLDialect
# Fix Postgres JPA Error:
# Method org.postgresql.jdbc.PgConnection.createClob() is not yet implemented.
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.temp.use_jdbc_metadata_defaults=false3. Spring Data JPA (Quick Start)
In the JPA, each Entity class will correspond to one table in the database. There are very many tables in the database, therefore, there will be a lot of entity classes. You frequently have to work with Entities, and write DAO classes (Data Access Object) to manipulate data through these Entities. This is actually a boring job.
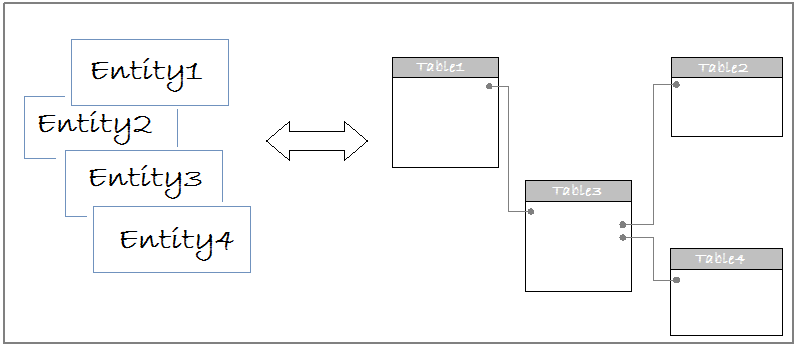
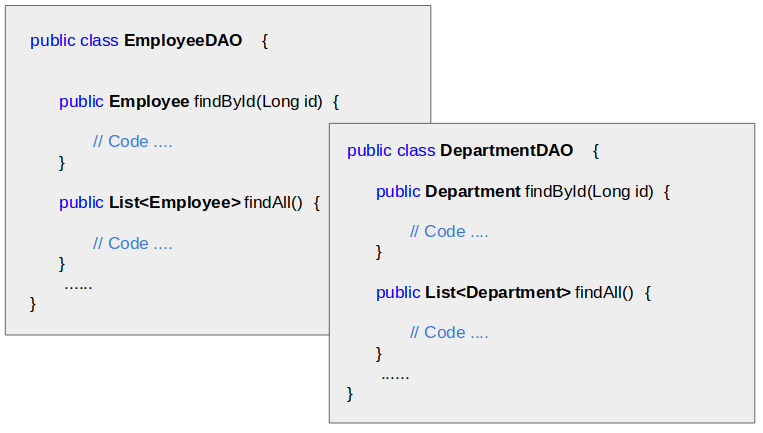
OK, I will tell you why it is boring. Let's imagine that you have 2 tables in the database such as EMPLOYEE & DEPARTMENT, and you have 2 corresponding Entity classes such as Employee & Department.
To manipulate with Employee, you write aDAO class including similar methods as follows:
- Employee findById(Long id)
- List<Employee> findAll()
- List<Employee> findByName(String likeName)
- .....
Certainly, to manipulate with the Department, you also do the same thing and if Entities are too many, it will take you so much time.
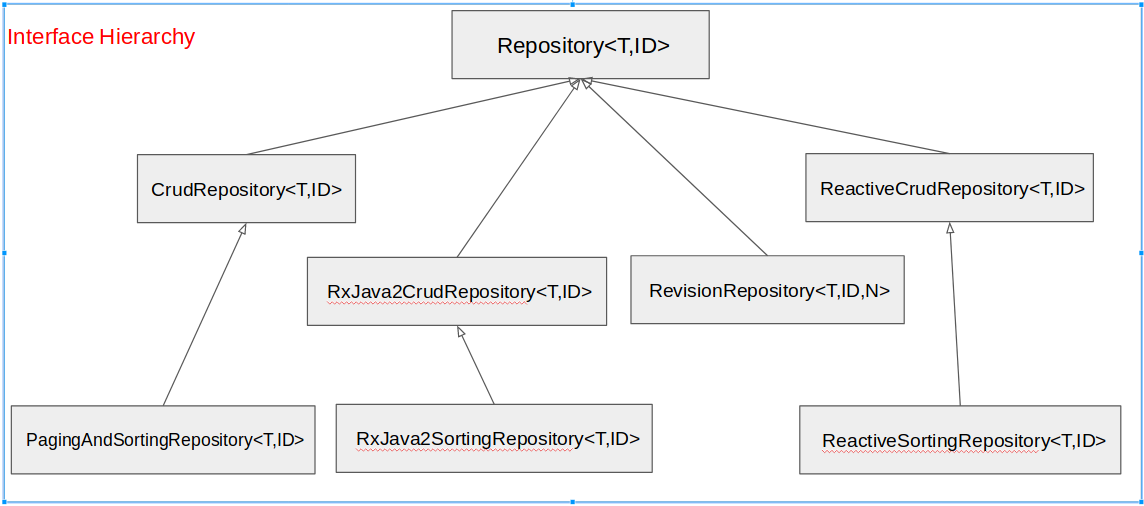
Spring Data JPA is a library of Spring. According to the rule of the Spring Data JPA, you just need to define an extended interface- Repository<T,ID> interface, and declare methods to manipulate with the data of this Entity. The Spring Data JPA will create a class that implements that interface for you.
Employee.java
package org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.entity;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
@Entity
@Table(name = "EMPLOYEE")
public class Employee {
@Id
private Long id;
@Column(name = "Emp_No", length = 30, nullable = false)
private String empNo;
@Column(name = "Full_Name", length = 128, nullable = false)
private String fullName;
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
@Column(name = "Hire_Date", nullable = false)
private Date hireDate;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getEmpNo() {
return empNo;
}
public void setEmpNo(String empNo) {
this.empNo = empNo;
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
public void setFullName(String fullName) {
this.fullName = fullName;
}
public Date getHireDate() {
return hireDate;
}
public void setHireDate(Date hireDate) {
this.hireDate = hireDate;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.getEmpNo() + ", " + this.getFullName();
}
}EmployeeRepository Interface extends CrudRepository<Employee, Long> interface.It has methods to manipulate with the Employee entity. The Spring Data JPA will automatically create a class that implements this interface at the time of running the application.
EmployeeRepository.java
package org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.repository;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.entity.Employee;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
// This is an Interface.
// No need Annotation here.
public interface EmployeeRepository extends CrudRepository<Employee, Long> { // Long: Type of Employee ID.
Employee findByEmpNo(String empNo);
List<Employee> findByFullNameLike(String fullName);
List<Employee> findByHireDateGreaterThan(Date hireDate);
@Query("SELECT coalesce(max(e.id), 0) FROM Employee e")
Long getMaxId();
}The Spring Data JPA will write code for your abstract methods, therefore, you need to tell the Spring Data JPA what you want through the name of method.
Keyword | Method | JPA Query |
GreaterThan | findByAgeGreaterThan(int age) | Select e from Person e where e.age > :age |
LessThan | findByAgeLessThan(int age) | Select e from Person e where e.age < :age |
Between | findByAgeBetween(int from, int to) | Select e from Person e where e.age between :from and :to |
IsNotNull, NotNull | findByFirstnameNotNull() | Select e from Person e where e.firstname is not null |
IsNull, Null | findByFirstnameNull() | Select e from Person e where e.firstname is null |
Like | findByFirstnameLike(String name) | Select e from Person e where e.firstname like :name |
(No keyword) | findByFirstname(String name) | Select e from Person e where e.firstname = :name |
Not | findByFirstnameNot(String name) | Select e from Person e where e.firstname <> :name |
..... |
You can also create interfaces with custom methods. In this case, you have to write the class to implement such interface.
EmployeeRepositoryCustom.java
package org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.repository;
import java.util.Date;
public interface EmployeeRepositoryCustom {
public Long getMaxEmpId();
public long updateEmployee(Long empId, String fullName, Date hireDate);
}EmployeeRepositoryCustomImpl.java
package org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.repository;
import java.util.Date;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.NoResultException;
import javax.persistence.Query;
import org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.entity.Employee;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class EmployeeRepositoryCustomImpl implements EmployeeRepositoryCustom {
@Autowired
EntityManager entityManager;
@Override
public Long getMaxEmpId() {
try {
String sql = "SELECT coalesce(max(e.id), 0) FROM Employee e";
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(sql);
return (Long) query.getSingleResult();
} catch (NoResultException e) {
return 0L;
}
}
@Override
public long updateEmployee(Long empId, String fullName, Date hireDate) {
Employee e = entityManager.find(Employee.class, empId);
if (e == null) {
return 0;
}
e.setFullName(fullName);
e.setHireDate(hireDate);
entityManager.flush();
return 1;
}
}4. Controller
MainController.java
package org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.controller;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.entity.Employee;
import org.o7planning.sbdatajpa.repository.EmployeeRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
private static final String[] NAMES = new String[] { "Tom", "Jerry", "Donald" };
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/")
public String home() {
String html = "";
html += "<ul>";
html += " <li><a href='/testInsert'>Test Insert</a></li>";
html += " <li><a href='/showAllEmployee'>Show All Employee</a></li>";
html += " <li><a href='/showFullNameLikeTom'>Show All 'Tom'</a></li>";
html += " <li><a href='/deleteAllEmployee'>Delete All Employee</a></li>";
html += "</ul>";
return html;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/testInsert")
public String testInsert() {
Long empIdMax = this.employeeRepository.getMaxId();
Employee employee = new Employee();
int random = new Random().nextInt(3);
long id = empIdMax + 1;
String fullName = NAMES[random] + " " + id;
employee.setId(id);
employee.setEmpNo("E" + id);
employee.setFullName(fullName);
employee.setHireDate(new Date());
this.employeeRepository.save(employee);
return "Inserted: " + employee;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/showAllEmployee")
public String showAllEmployee() {
Iterable<Employee> employees = this.employeeRepository.findAll();
String html = "";
for (Employee emp : employees) {
html += emp + "<br>";
}
return html;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/showFullNameLikeTom")
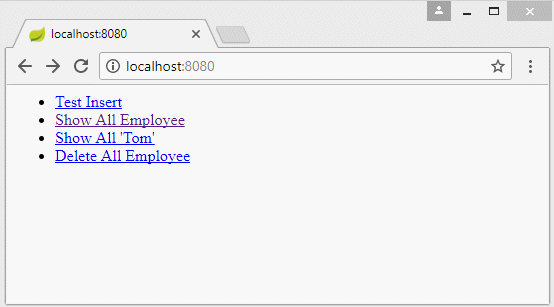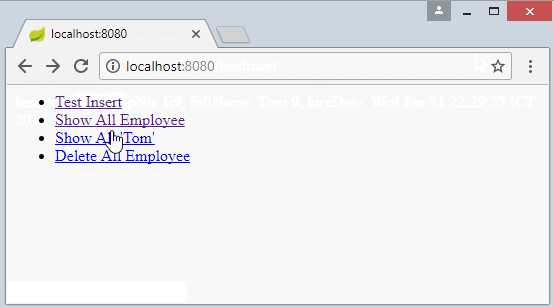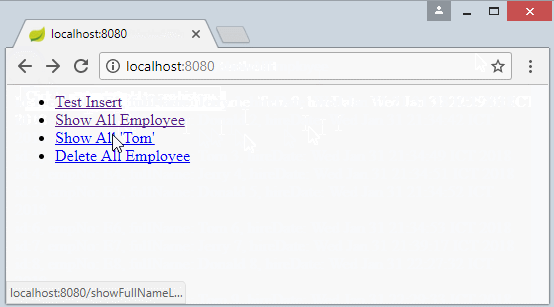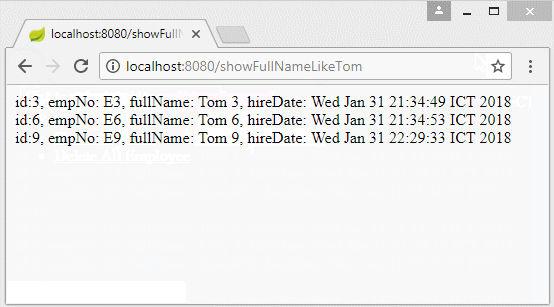
public String showFullNameLikeTom() {
List<Employee> employees = this.employeeRepository.findByFullNameLike("Tom");
String html = "";
for (Employee emp : employees) {
html += emp + "<br>";
}
return html;
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/deleteAllEmployee")
public String deleteAllEmployee() {
this.employeeRepository.deleteAll();
return "Deleted!";
}
}Spring Boot Tutorials
- Install Spring Tool Suite for Eclipse
- Spring Tutorial for Beginners
- Spring Boot Tutorial for Beginners
- Spring Boot Common Properties
- Spring Boot and Thymeleaf Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and FreeMarker Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Groovy Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Mustache Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and JSP Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP Tutorial with Examples
- Use Logging in Spring Boot
- Application Monitoring with Spring Boot Actuator
- Create a Multi Language web application with Spring Boot
- Use multiple ViewResolvers in Spring Boot
- Use Twitter Bootstrap in Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Interceptors Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Spring JDBC and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Spring JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, JPA and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Spring Data JPA Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Hibernate and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Integrating Spring Boot, JPA and H2 Database
- Spring Boot and MongoDB Tutorial with Examples
- Use Multiple DataSources with Spring Boot and JPA
- Use Multiple DataSources with Spring Boot and RoutingDataSource
- Create a Login Application with Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Create a Login Application with Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Create a User Registration Application with Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Example of OAuth2 Social Login in Spring Boot
- Run background scheduled tasks in Spring
- CRUD Restful Web Service Example with Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Restful Client with RestTemplate Example
- CRUD Example with Spring Boot, REST and AngularJS
- Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Basic Authentication
- Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Auth0 JWT
- Spring Boot File Upload Example
- Spring Boot File Download Example
- Spring Boot File Upload with jQuery Ajax Example
- Spring Boot File Upload with AngularJS Example
- Create a Shopping Cart Web Application with Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Spring Email Tutorial with Examples
- Create a simple Chat application with Spring Boot and Websocket
- Deploy Spring Boot Application on Tomcat Server
- Deploy Spring Boot Application on Oracle WebLogic Server
- Install a free Let's Encrypt SSL certificate for Spring Boot
- Configure Spring Boot to redirect HTTP to HTTPS
- Fetch data with Spring Data JPA DTO Projections
Show More