Spring Boot, Spring JDBC and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
1. Objective of the Post
This document is based on:
- Spring Boot 2.x
- Spring JDBC
- Eclipse 4.7 (Oxygen)
In this post, I will guide you for creating a Spring Boot project and work with a database (Oracle, MySQL, SQL Server, Postgres,..) using Spring JDBC & Spring Transaction. The matters that will be discussed in this post include:
- Declare the libraries necessary to be able to work with a database.
- Configure Spring Boot to be able to connect to a database.
- Manipulate with a database using the Spring JDBC.
- Use Spring Transaction and explain the operating principle of Spring Transaction.
2. Prepare a database
MySQL
-- Create table
create table BANK_ACCOUNT
(
ID BIGINT not null,
FULL_NAME VARCHAR(128) not null,
BALANCE DOUBLE not null
) ;
--
alter table BANK_ACCOUNT
add constraint BANK_ACCOUNT_PK primary key (ID);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (1, 'Tom', 1000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (2, 'Jerry', 2000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (3, 'Donald', 3000);
commit;SQL Server
-- Create table
create table BANK_ACCOUNT
(
ID BIGINT not null,
FULL_NAME VARCHAR(128) not null,
BALANCE DOUBLE PRECISION not null
) ;
--
alter table BANK_ACCOUNT
add constraint BANK_ACCOUNT_PK primary key (ID);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (1, 'Tom', 1000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (2, 'Jerry', 2000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (3, 'Donald', 3000);Oracle
-- Create table
create table BANK_ACCOUNT
(
ID NUMBER(19) not null,
FULL_NAME VARCHAR2(128) not null,
BALANCE NUMBER not null
) ;
--
alter table BANK_ACCOUNT
add constraint BANK_ACCOUNT_PK primary key (ID);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (1, 'Tom', 1000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (2, 'Jerry', 2000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (3, 'Donald', 3000);
commit;PostGres
Create table Bank_Account (
ID Bigint not null,
Full_Name Varchar(128) not null,
Balance real not null,
CONSTRAINT Bank_Account_pk PRIMARY KEY (ID)
);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (1, 'Tom', 1000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (2, 'Jerry', 2000);
Insert into Bank_Account(ID, Full_Name, Balance) values (3, 'Donald', 3000);3. Create a Spring Boot project
On the Eclipse, create a Spring Boot project
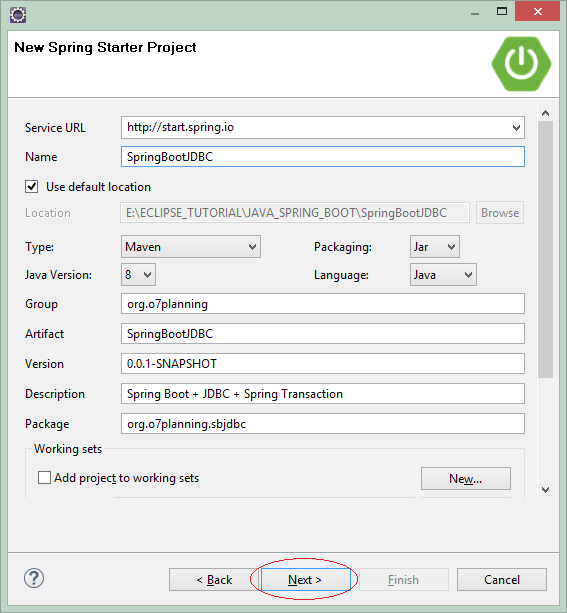
Enter:
- Name: SpringBootJDBC
- Group: org.o7planning
- Artifact: SpringBootJDBC
- Description: Spring Boot + Spring JDBC + Spring Transaction
- Package: org.o7planning.sbjdbc
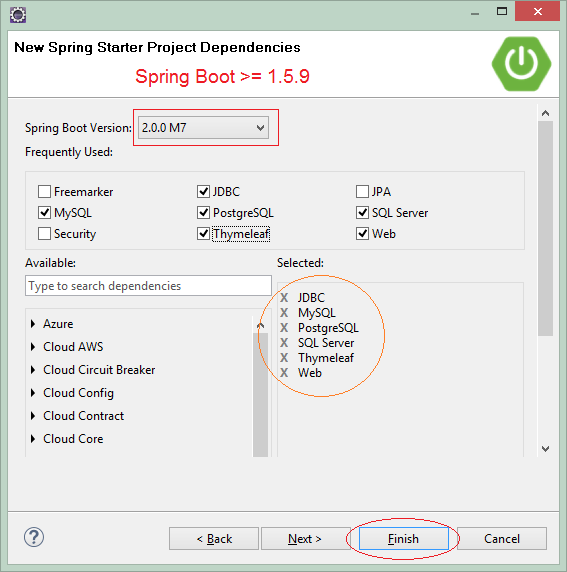
Select the technologies and libraries to be used:
- JDBC
- MySQL
- PostgrsSQL
- SQL Server
- Web
- Thymeleaf
4. Configure pom.xml
If you work with the Oracle database, you need to declare the following libraries on the pom.xml:
* Oracle *
<dependencies>
.....
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
.....
</dependencies>
<repositories>
....
<!-- Repository for ORACLE JDBC Driver -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
.....
</repositories>If you connect to the SQL Service database, you can use either JTDS library orMssql-Jdbc library:
* SQL Server *
<dependencies>
.....
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.jtds</groupId>
<artifactId>jtds</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
.....
</dependencies>The full content of the pom.xml file:
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringBootJDBC</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SpringBootJDBC</name>
<description>Spring Boot + JDBC + Spring Transaction</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- SQL Server - Mssql-Jdbc driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.sqlserver</groupId>
<artifactId>mssql-jdbc</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- SQL Server - JTDS driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.sourceforge.jtds</groupId>
<artifactId>jtds</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Oracle Driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.oracle</groupId>
<artifactId>ojdbc6</artifactId>
<version>11.2.0.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.threeten/threetenbp -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.threeten</groupId>
<artifactId>threetenbp</artifactId>
<version>1.3.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<repositories>
<!-- Repository for ORACLE JDBC Driver -->
<repository>
<id>codelds</id>
<url>https://code.lds.org/nexus/content/groups/main-repo</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
</project>5. Configure DataSource
For Spring can connect to a Database, you need to configure necessary parameters in the application.properties file.
application.properties (MySQL)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydatabase
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=12345application.properites (Sql Server + Mssql-Jdbc)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:sqlserver://tran-vmware-pc\\SQLEXPRESS:1433;databaseName=testdb
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=12345application.properites (Sql Server + JTDS)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://tran-vmware-pc:1433/testdb;instance=SQLEXPRESS
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=12345application.properties (Oracle)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:db12c
spring.datasource.username=Test
spring.datasource.password=12345application.properties (PostGres)
# ===============================
# DATABASE
# ===============================
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://tran-vmware-pc:5432/bank
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=12345
# Fix Postgres JPA Error:
# Method org.postgresql.jdbc.PgConnection.createClob() is not yet implemented.
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.temp.use_jdbc_metadata_defaults= falseSee more:
Note: By default Spring Boot will automatically configures Spring JDBC, and creates Spring BEANs related to the Spring JDBC. These automatic configurations of the Spring Boot include:
- DataSourceAutoConfiguration
- DataSourceTransactionManagerAutoConfiguration
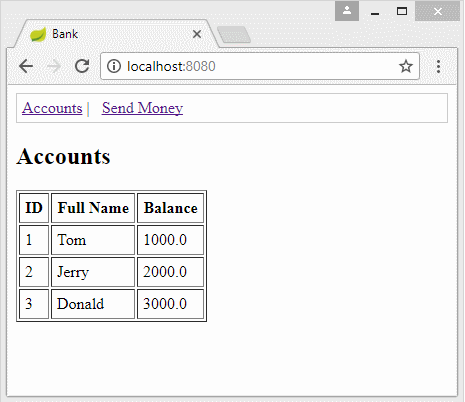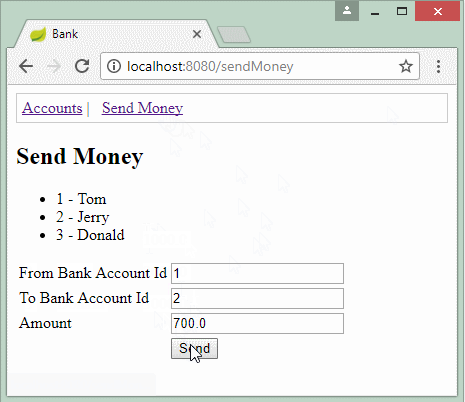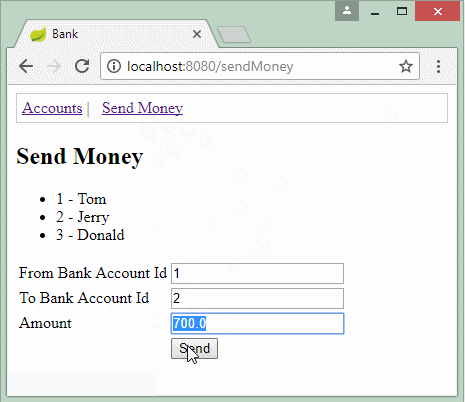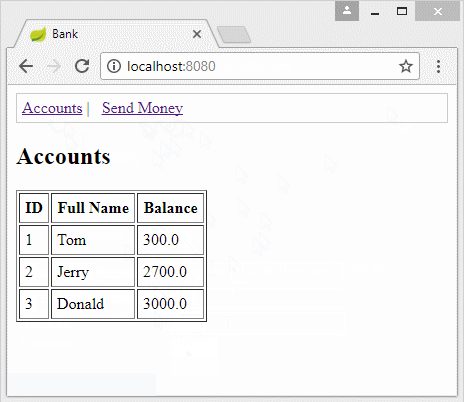
6. Model, Mapper, Form, DAO
In the Spring, a class representing for the data of a record, obtained from query statement is called model class. The BankAccountInfo class is a model one.
BankAccountInfo.java
package org.o7planning.sbjdbc.model;
public class BankAccountInfo {
private Long id;
private String fullName;
private double balance;
public BankAccountInfo(Long id, String fullName, double balance) {
super();
this.id = id;
this.fullName = fullName;
this.balance = balance;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFullName() {
return fullName;
}
public void setFullName(String fullName) {
this.fullName = fullName;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}A class used for mapping corresponding to 1-1 between 1 column in query statement and 1 field in the model class is called a mapper class. BankAccountMapper is a such class.
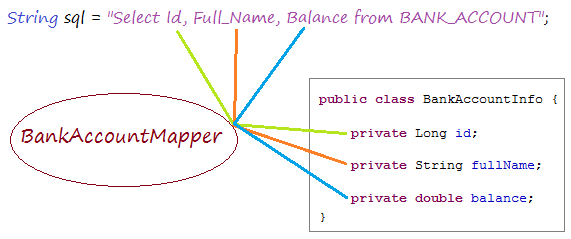
See more:
BankAccountMapper.java
package org.o7planning.sbjdbc.mapper;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.model.BankAccountInfo;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
public class BankAccountMapper implements RowMapper<BankAccountInfo> {
public static final String BASE_SQL //
= "Select ba.Id, ba.Full_Name, ba.Balance From Bank_Account ba ";
@Override
public BankAccountInfo mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
Long id = rs.getLong("Id");
String fullName = rs.getString("Full_Name");
double balance = rs.getDouble("Balance");
return new BankAccountInfo(id, fullName, balance);
}
}BankAccountDAO.java
package org.o7planning.sbjdbc.dao;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.exception.BankTransactionException;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.mapper.BankAccountMapper;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.model.BankAccountInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.dao.EmptyResultDataAccessException;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.support.JdbcDaoSupport;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@Repository
@Transactional
public class BankAccountDAO extends JdbcDaoSupport {
@Autowired
public BankAccountDAO(DataSource dataSource) {
this.setDataSource(dataSource);
}
public List<BankAccountInfo> getBankAccounts() {
// Select ba.Id, ba.Full_Name, ba.Balance From Bank_Account ba
String sql = BankAccountMapper.BASE_SQL;
Object[] params = new Object[] {};
BankAccountMapper mapper = new BankAccountMapper();
List<BankAccountInfo> list = this.getJdbcTemplate().query(sql, params, mapper);
return list;
}
public BankAccountInfo findBankAccount(Long id) {
// Select ba.Id, ba.Full_Name, ba.Balance From Bank_Account ba
// Where ba.Id = ?
String sql = BankAccountMapper.BASE_SQL + " where ba.Id = ? ";
Object[] params = new Object[] { id };
BankAccountMapper mapper = new BankAccountMapper();
try {
BankAccountInfo bankAccount = this.getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(sql, params, mapper);
return bankAccount;
} catch (EmptyResultDataAccessException e) {
return null;
}
}
// MANDATORY: Transaction must be created before.
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.MANDATORY)
public void addAmount(Long id, double amount) throws BankTransactionException {
BankAccountInfo accountInfo = this.findBankAccount(id);
if (accountInfo == null) {
throw new BankTransactionException("Account not found " + id);
}
double newBalance = accountInfo.getBalance() + amount;
if (accountInfo.getBalance() + amount < 0) {
throw new BankTransactionException(
"The money in the account '" + id + "' is not enough (" + accountInfo.getBalance() + ")");
}
accountInfo.setBalance(newBalance);
// Update to DB
String sqlUpdate = "Update Bank_Account set Balance = ? where Id = ?";
this.getJdbcTemplate().update(sqlUpdate, accountInfo.getBalance(), accountInfo.getId());
}
// Do not catch BankTransactionException in this method.
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW, rollbackFor = BankTransactionException.class)
public void sendMoney(Long fromAccountId, Long toAccountId, double amount) throws BankTransactionException {
addAmount(toAccountId, amount);
addAmount(fromAccountId, -amount);
}
}BankTransactionException.java
package org.o7planning.sbjdbc.exception;
public class BankTransactionException extends Exception {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3128681006635769411L;
public BankTransactionException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}SendMoneyForm.java
package org.o7planning.sbjdbc.form;
public class SendMoneyForm {
private Long fromAccountId;
private Long toAccountId;
private Double amount;
public SendMoneyForm() {
}
public SendMoneyForm(Long fromAccountId, Long toAccountId, Double amount) {
this.fromAccountId = fromAccountId;
this.toAccountId = toAccountId;
this.amount = amount;
}
public Long getFromAccountId() {
return fromAccountId;
}
public void setFromAccountId(Long fromAccountId) {
this.fromAccountId = fromAccountId;
}
public Long getToAccountId() {
return toAccountId;
}
public void setToAccountId(Long toAccountId) {
this.toAccountId = toAccountId;
}
public Double getAmount() {
return amount;
}
public void setAmount(Double amount) {
this.amount = amount;
}
}Explain the operation mechanism of Spring Transaction:

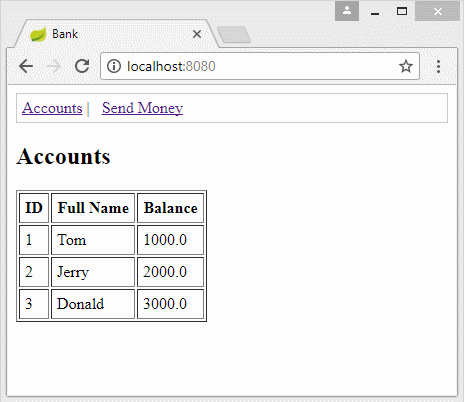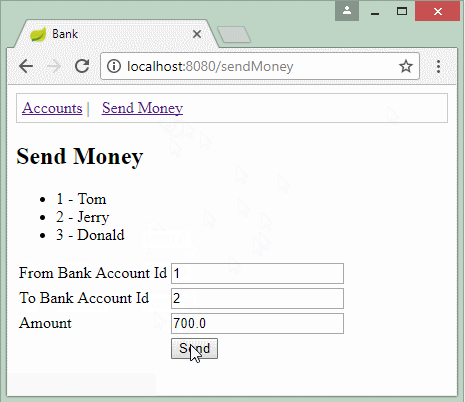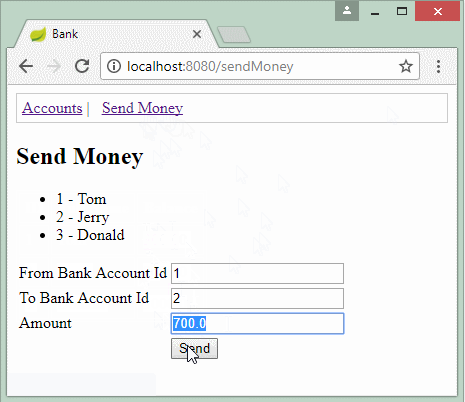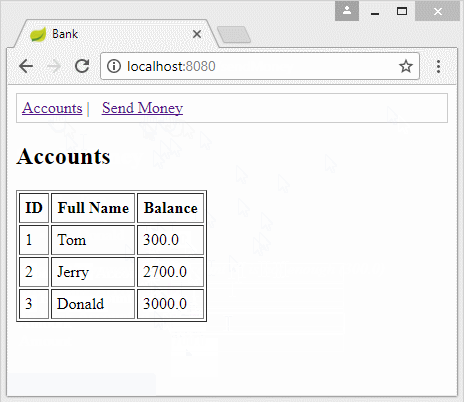
In this example, I simulate a bank transaction. A account sends to B account an amount of 700$. Thus, two actions will be created in the database:
- Add 700$ to B account.
- Subtract 700$ from A account.
If the first action succeeds (add $ 700 to B account), but the second action fails for a reason, the bank will suffer a damage.
Therefore, it needs to manage the transaction to ensure that if an action fails, the data will rollback the original state (before transaction). The transaction is considered successful when all actions are successful.
Therefore, it needs to manage the transaction to ensure that if an action fails, the data will rollback the original state (before transaction). The transaction is considered successful when all actions are successful.
Usethe @Transactional(rollbackFor = BankTransactionException.class) to annotate on a method to tell the "Spring Transaction" "let's apply the AOP to this method".
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW,
rollbackFor = BankTransactionException.class)
public void sendMoney(Long fromAccountId, Long toAccountId,
double amount) throws BankTransactionException {
addAmount(toAccountId, amount);
addAmount(fromAccountId, -amount);
}The Spring Transaction applies the Spring AOP to your method, which is like changing thecode of the method, add an exception to the code snippet and call Rollback to transact when the exception occurs, then it rethrows the exception out of the method. All are the same as the following illustration:

7. Controller
MainController.java
package org.o7planning.sbjdbc.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.dao.BankAccountDAO;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.exception.BankTransactionException;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.form.SendMoneyForm;
import org.o7planning.sbjdbc.model.BankAccountInfo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@Autowired
private BankAccountDAO bankAccountDAO;
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String showBankAccounts(Model model) {
List<BankAccountInfo> list = bankAccountDAO.getBankAccounts();
model.addAttribute("accountInfos", list);
return "accountsPage";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/sendMoney", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String viewSendMoneyPage(Model model) {
SendMoneyForm form = new SendMoneyForm(1L, 2L, 700d);
model.addAttribute("sendMoneyForm", form);
return "sendMoneyPage";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/sendMoney", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String processSendMoney(Model model, SendMoneyForm sendMoneyForm) {
System.out.println("Send Money::" + sendMoneyForm.getAmount());
try {
bankAccountDAO.sendMoney(sendMoneyForm.getFromAccountId(), //
sendMoneyForm.getToAccountId(), //
sendMoneyForm.getAmount());
} catch (BankTransactionException e) {
model.addAttribute("errorMessage", "Error: " + e.getMessage());
return "/sendMoneyPage";
}
return "redirect:/";
}
}8. Thymeleaf Template
_menu.html
<div xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
style="border: 1px solid #ccc;padding:5px;margin-bottom:20px;">
<a th:href="@{/}">Accounts</a>
|
<a th:href="@{/sendMoney}">Send Money</a>
</div>accountsPage.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Bank</title>
<style>
th, td {
padding: 5px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Include _menu.html -->
<th:block th:include="/_menu"></th:block>
<h2>Accounts</h2>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>ID</th>
<th>Full Name</th>
<th>Balance</th>
</tr>
<tr th:each="accountInfo : ${accountInfos}">
<td th:utext="${accountInfo.id}">..</td>
<td th:utext="${accountInfo.fullName}">..</td>
<td th:utext="${accountInfo.balance}">..</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>sendMoneyPage.html
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Bank</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Include _menu.html -->
<th:block th:include="/_menu"></th:block>
<h2>Send Money</h2>
<ul>
<li>1 - Tom</li>
<li>2 - Jerry</li>
<li>3 - Donald</li>
</ul>
<div th:if="${errorMessage!=null}"
style="color:red;font-style:italic" th:utext="${errorMessage}">..</div>
<form th:action="@{/sendMoney}" th:object="${sendMoneyForm}" method="POST">
<table>
<tr>
<td>From Bank Account Id</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{fromAccountId}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>To Bank Account Id</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{toAccountId}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Amount</td>
<td><input type="text" th:field="*{amount}" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td> </td>
<td><input type="submit" value="Send"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>Spring Boot Tutorials
- Install Spring Tool Suite for Eclipse
- Spring Tutorial for Beginners
- Spring Boot Tutorial for Beginners
- Spring Boot Common Properties
- Spring Boot and Thymeleaf Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and FreeMarker Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Groovy Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Mustache Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and JSP Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Apache Tiles, JSP Tutorial with Examples
- Use Logging in Spring Boot
- Application Monitoring with Spring Boot Actuator
- Create a Multi Language web application with Spring Boot
- Use multiple ViewResolvers in Spring Boot
- Use Twitter Bootstrap in Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Interceptors Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Spring JDBC and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Spring JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, JPA and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot and Spring Data JPA Tutorial with Examples
- Spring Boot, Hibernate and Spring Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Integrating Spring Boot, JPA and H2 Database
- Spring Boot and MongoDB Tutorial with Examples
- Use Multiple DataSources with Spring Boot and JPA
- Use Multiple DataSources with Spring Boot and RoutingDataSource
- Create a Login Application with Spring Boot, Spring Security, Spring JDBC
- Create a Login Application with Spring Boot, Spring Security, JPA
- Create a User Registration Application with Spring Boot, Spring Form Validation
- Example of OAuth2 Social Login in Spring Boot
- Run background scheduled tasks in Spring
- CRUD Restful Web Service Example with Spring Boot
- Spring Boot Restful Client with RestTemplate Example
- CRUD Example with Spring Boot, REST and AngularJS
- Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Basic Authentication
- Secure Spring Boot RESTful Service using Auth0 JWT
- Spring Boot File Upload Example
- Spring Boot File Download Example
- Spring Boot File Upload with jQuery Ajax Example
- Spring Boot File Upload with AngularJS Example
- Create a Shopping Cart Web Application with Spring Boot, Hibernate
- Spring Email Tutorial with Examples
- Create a simple Chat application with Spring Boot and Websocket
- Deploy Spring Boot Application on Tomcat Server
- Deploy Spring Boot Application on Oracle WebLogic Server
- Install a free Let's Encrypt SSL certificate for Spring Boot
- Configure Spring Boot to redirect HTTP to HTTPS
- Fetch data with Spring Data JPA DTO Projections
Show More