Java String.format() and printf() methods
1. printf()
In Java programming, you often come across System.out.printf(..) code. Actually, method printf(..) is defined in both PrintStream and PrintWriter classes, their usage is similar, printf stands for "Print + Format".
printf methods
// Definition of the printf methods in the PrintWriter class:
public PrintStream printf(Locale l, String format, Object... args)
public PrintStream printf(String format, Object... args)
// Definition of the printf methods in PrintWriter class:
public PrintWriter printf(Locale l, String format, Object... args)
public PrintWriter format(String format, Object... args)System.out.printf(..) is a special case, used to write a formatted text to the Console screen, where System.out is essentially an object of type PrintStream.
System class
package java.lang;
public final class System {
public static final PrintStream out = ...;
}Before we start, let's see a simple example:
Printf_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.printf.ex;
public class Printf_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String firstName = "James";
String lastName = "Smith";
int age = 20;
System.out.printf("My name is %s %s, I'm %d years old.", firstName, lastName, age);
}
}Output:
My name is James Smith, I'm 20 years old.2. Format rules
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterThese parameters: flags, width, precision are optional.
3. conversion-character
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterconversion-character | Description | Type |
d | decimal integer | byte, short, int, long |
f | floating-point number | float, double |
b | Boolean | Object |
B | will uppercase the boolean | Object |
c | Character Capital | String |
C | will uppercase the letter | String |
s | String Capital | String |
S | will uppercase all the letters in the string | String |
h | hashcode - A hashcode is like an address. This is useful for printing a reference | Object |
n | newline - Platform specific newline character - use %n instead of \n for greater compatibility |
conversion-character: n
System.out.printf("One%nTwo%nThree");Output:
One
Two
Threeconversion-character: s
System.out.printf("My name is %s %s", "James", "Smith");Output:
My name is James Smithconversion-character: S
System.out.printf("My name is %S %S", "James", "Smith");Output:
My name is JAMES SMITHconversion-character: b
System.out.printf("%b%n", null);
System.out.printf("%b%n", false);
System.out.printf("%b%n", 5.3);
System.out.printf("%b%n", "Any text");
System.out.printf("%b%n", new Object());Output:
false
false
true
true
trueconversion-character: B
System.out.printf("%B%n", null);
System.out.printf("%B%n", false);
System.out.printf("%B%n", 5.3);
System.out.printf("%B%n", "Any text");
System.out.printf("%B%n", new Object());Output:
FALSE
FALSE
TRUE
TRUE
TRUEconversion-character: d
System.out.printf("There are %d teachers and %d students in the class", 2, 25);Output:
There are 2 teachers and 25 students in the classconversion-character: f
System.out.printf("Exchange rate today: EUR %f = USD %f", 1.0, 1.2059);Output:
Exchange rate today: EUR 1.000000 = USD 1.205900conversion-character: c
char ch = 'a';
System.out.printf("Code of '%c' character is %d", ch, (int)ch);Output:
Code of 'a' character is 97conversion-character: C
char ch = 'a';
System.out.printf("'%C' is the upper case of '%c'", ch, ch);Output:
'A' is the upper case of 'a'conversion-character: h
Printf_cc_h_ex.java
package org.o7planning.printf.ex;
public class Printf_cc_h_ex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// h (Hashcode HEX)
Object myObject = new AnyObject("Something");
System.out.println("Hashcode: " + myObject.hashCode());
System.out.println("Identity Hashcode: " + System.identityHashCode(myObject));
System.out.println("Hashcode (HEX): " + Integer.toHexString(myObject.hashCode()));
System.out.println("toString : " + String.valueOf(myObject));
System.out.printf("Printf: %h", myObject);
}
}
class AnyObject {
private String val;
public AnyObject(String val) {
this.val = val;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
if (this.val == null || this.val.isEmpty()) {
return 0;
}
return 1000 + (int) this.val.charAt(0);
}
}Output:
Hashcode: 1083
Identity Hashcode: 1579572132
Hashcode (HEX): 43b
toString : org.o7planning.printf.ex.AnyObject@43b
Printf: 43b4. width
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterwidth - specifies the minimum amount of space (number of characters) to hold for printing the contents of a corresponding argument.
printf(format, arg1, arg2,.., argN)5. flags
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterflag | Description |
- | left-justify (default is to right-justify ) |
+ | output a plus ( + ) or minus ( - ) sign for a numerical value |
0 | forces numerical values to be zero-padded (default is blank padding ) |
, | comma grouping separator (for numbers > 1000) |
space will display a minus sign if the number is negative or a space if it is positive |
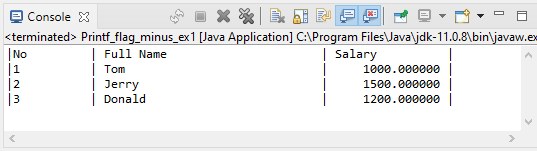
flag: -
String[] fullNames = new String[] {"Tom", "Jerry", "Donald"};
float[] salaries = new float[] {1000, 1500, 1200};
// s
System.out.printf("|%-10s | %-30s | %-15s |%n", "No", "Full Name", "Salary");
for(int i=0; i< fullNames.length; i++) {
System.out.printf("|%-10d | %-30s | %15f |%n", (i+1), fullNames[i], salaries[i]);
}Output:
flag: +
// flag: +
System.out.printf("The world's economy increased by %+f percent in 2020. %n", -3.3);
System.out.printf("China's economy increased by %+f percent in 2020. %n", 2.3);
System.out.println();
// without flag: +
System.out.printf("The world's economy increased by %f percent in 2020. %n", -3.3);
System.out.printf("China's economy increased by %f percent in 2020. %n", 2.3);Output:
The world's economy increased by -3.300000 percent in 2020.
China's economy increased by +2.300000 percent in 2020.
The world's economy increased by -3.300000 percent in 2020.
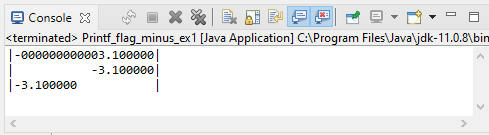
China's economy increased by 2.300000 percent in 2020.flag: 0 (zero)
// flag: 0 & with: 20
System.out.printf("|%020f|%n", -3.1);
// without flag & with: 20
System.out.printf("|%20f|%n", -3.1);
// flag: - (left align) & with: 20
System.out.printf("|%-20fOutput:
flag: , (comma)
// flag: ,
System.out.printf("%,f %n", 12345678.9);
// flag: ,
System.out.printf("%,f %n", -12345678.9);Output:
12,345,678.900000
-12,345,678.900000flag: (space)
// flag: (space)
System.out.printf("% f %n", 12345678.9);
System.out.printf("% f %n", -12345678.9);
System.out.println();
// flags: , (space + comma)
System.out.printf("% ,f %n", 12345678.9);
System.out.printf("% ,Output:
12345678.900000
-12345678.900000
12,345,678.900000
-12,345,678.9000006. precision
%[flags][width][.precision]conversion-characterSystem.out.printf("%f %n", 12345678.911);
System.out.printf("%f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flag: , (comma)
System.out.printf("%,f %n", 12345678.911);
// flag: , (comma)
System.out.printf("%,f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flags: , (space + comma)
System.out.printf("% ,f %n", 12345678.911);
// flags: , (space + comma)
System.out.printf("% ,f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flag: , (comma) & precision: .2
System.out.printf("%,.2f %n", 12345678.911);
// flag: , (comma) & precision: .3
System.out.printf("%,.3f %n", -12345678.911);
System.out.println();
// flags: , (space + comma) & precision: .2
System.out.printf("% ,.2f %n", 12345678.911);
// flags: , (space + comma) & precision: .3
System.out.printf("% ,.3f %n", -12345678.911);Output:
12345678.911000
-12345678.911000
12,345,678.911000
-12,345,678.911000
12,345,678.911000
-12,345,678.911000
12,345,678.91
-12,345,678.911
12,345,678.91
-12,345,678.911Java Basic
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Install Java on Windows
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Install Eclipse
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Data Types in java
- Bitwise Operations
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Loops in Java
- Arrays in Java
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials