Data Types in java
1. Overview of data types
Any programming language has a set of data types. Data types are basic, and quite similar for all languages. All data types are composed from bits, therefore, I dedicate a post to introduce the history of bits and bytes. My advice is that you should read it before continuing reading this post.
Java has two types of data types:
- Primitive Types
- Reference Types
There are 8 primitive data types which are boolean, byte, char, short, int, long, float, double.
Data type | Default Value | Size |
boolean | false | 1 bit |
char | '\u0000' | 2 byte |
byte | 0 | 1 byte |
short | 0 | 2 byte |
int | 0 | 4 byte |
long | 0L | 8 byte |
float | 0.0f | 4 byte |
double | 0.0d | 8 byte |
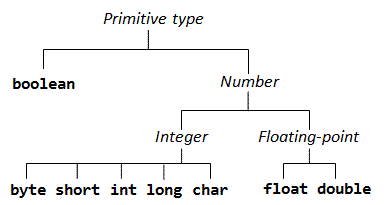
- Logic type: boolean.
- Integer types: byte, short, char, int, long.
- Real number type is also called floating point: float, double.
Reference types, which are objects created by the constructor of classes.
2. byte
1 byte a byte is composed of 8 consecutive bits in the memory of computer. Each bit is a binary number of 0 or 1. Java uses "byte" to name a integer type with small scope (Size: 1 byte).

The first bit in a row of 8 bits has value of 0 or 1.
But wait, it is supposed to be [-128, 127], why?
- If it is 0, Java considers it as + (Represent a positive number)
- If it is 1 Java considers it as - (Represent a negative number)
But wait, it is supposed to be [-128, 127], why?
Why is the smallest number of byte type in Java -128?
If the rules that the first bit has a value of 0 equivalent to +, the value of 1 equivalent to -, then we have two ways to represent 0 (see the illustration).

Therefore, the binary sequence of "1 0 0 0 0 0 0" should be considered as the smallest number of byte data type in Java. It represents -128.

3. boolean
boolean is the simplest data type. It has size of 1 bit. It has 2 values of true and false.
The default value for the boolean type isfalse.
// Declare a variable named 'valid', data type is boolean
// The value will be false by default.
boolean valid;
// Declare a variable named 'active', data type is boolean
// Value is true.
boolean active = true;4. char
Although "char" is the first four characters of the "Character" term, the char type in Java is used to store non-negative integers with the two-byte size. It is also used to represent for a Unicode character because in nature, each character corresponds to a specific number. (This number is understood as the code of character.)
Because char is non-negative integer type, size: 2 bytes, its scope is [0, 2*16-1] ( [0, 65535] ).
When char is understood as a Unicode character, the smallest character is '\u0000' (Mã 0), and the largest character is '\uffff' (code: 65535).
What is Unicode character?
- TODO
5. short
short is data type for the purpose of representing a two-byte integer (16 bits), including negative integer.
- The smallest value is -32,768 (-2^15) and the largest value is 32,767 (2^15 -1).
- Default value is 0.
** Note: See the explanation of the rule to determine the positive or negative number in the section of byte data type.
6. int
int data type is used to represent an integer with the size of 4 bytes (32 bits).
- The smallest value: -2,147,483,648 (-2^31)
- The largest value: 2,147,483,647 (2^31 -1)
- Default value: 0.
In Java, the int data type is considered as default data type for integers. Therefore, if you write 100, Java will create a four- byte memory area for storage. And if you want Java to create an eight- byte memory area to store 100, you have to write 100L. (long is an eight-byte integer type, introduced in the following section).
int a = 100;7. long
The long data type is used to represent integers with the size of 8 bytes (64 bits).
- The smallest value is -9,223,372,036,854,775,808.(-2^63)
- The largest value is 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. (2^63 -1)
- This type is used when a value pattern wider than int is necessary.
- Default value is 0L.
// You need to add 'L' immediately after 100
// so that Java creates an 8 byte memory area to store 100
long a = 100L;8. float
float data type is used to represent a real number with the size of 4 bytes (32 bits).
- The smallest value: -3.4028235 x 10^38
- The largest value:: 3.4028235 x 10^38
- Default value: 0.0f
Example:
float value = 2.5f;9. double
double data type is used to represent a real number with the size of 8 bytes (64 bits). It is the default type for real numbers.
- The smallest value: -1.7976931348623157 x 10^308
- The largest value: 1.7976931348623157 x 10^308
- Default value: 0.0d
Example:
double a = 2.5d;
// Since doubling is the default type for real numbers,
// You can write more concisely:
double b = 2.5;10. Reference Types
In Java, a data type created by a combination of primitive types is called a reference type. The most commonly used reference type is the String, which is a combination of characters.
Reference types are created based on a class. The class is like a blueprint to define a reference type.
class Address {
String address;
String cityName;
}
class Student {
String fullName;
int age;
Address address;
}Java Basic
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Install Java on Windows
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Install Eclipse
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Data Types in java
- Bitwise Operations
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Loops in Java
- Arrays in Java
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials