if else statement in java
1. if statment
The if statement is the most basic of all the control flow statements. It tells your program to execute a certain section of code only if a particular test evaluates to true.
Below is the structure of if statement:
if (condition) {
// Do something here if 'condition' is true.
}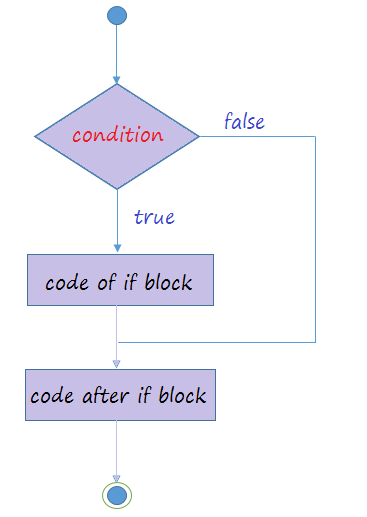
The above image illustrates the flow of application when it meets a if statement.
- The program checks the condition.
- If the condition is true, code in the if block will be executed. It then continues executing the codes below theif block.
- If the condition is false, the program will ignores the code in the if block and execute code snippets below theif block.
Example:
IfExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class IfExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable, representing your age
int age = 30;
System.out.println("Your age: " + age);
// The condition to test is 'age> 20'
if (age > 20) {
System.out.println("Okey!");
System.out.println("Age is greater than 20");
}
// The code after the 'if' block.
System.out.println("Done!");
}
}Run the example:
Your age: 30
Okey!
Age is greater than 20
Done!2. if - else statement
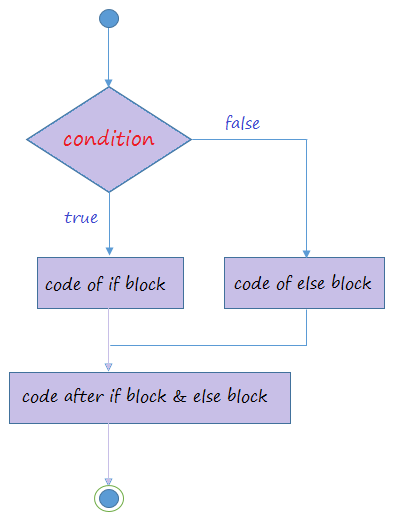
The if-else statement also tests the condition. It executes the if block if condition is true otherwise else block is executed.
** if - else **
if( condition ) {
// Do something here
}
// Else
else {
// Do something here
}
Example:
IfElseExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class IfElseExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable, representing your age
int age = 15;
System.out.println("Your age: " + age);
// The condition to test is 'age> 18'
if (age >= 18) {
System.out.println("Okey!");
System.out.println("You are accepted!");
} else {
System.out.println("Sorry!");
System.out.println("Age is less than 18");
}
// The code after the 'if' block and 'else' block.
System.out.println("Done!");
}
}Running the example:
Your age: 15
Sorry!
Age is less than 18
Done!3. if - else if - else statement
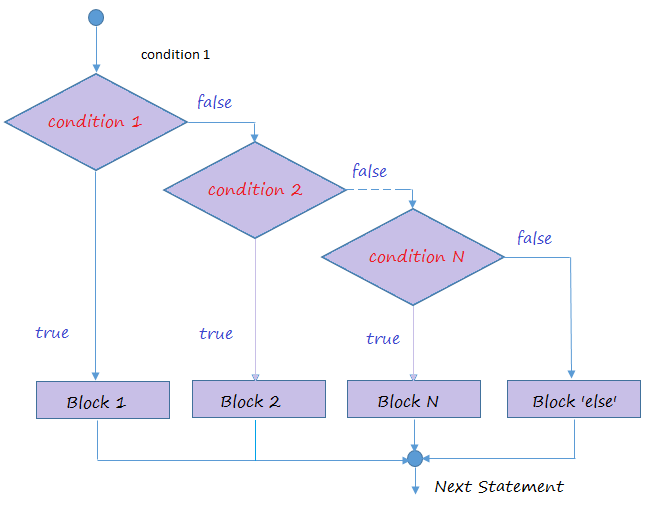
The structure of an if - else if - else statement is:
if(condition 1) {
// Do something here
} else if(condition 2) {
// Do something here
} else if(condition 3) {
// Do something here
}
// Else
else {
// Do something here
}
Create ElseIfExample1 class:
ElseIfExample1.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class ElseIfExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declaring a varible of type int (32 bit integer)
// Represent your test scores.
int score = 70;
System.out.println("Your score =" + score);
// If the score is less than 50
if (score < 50) {
System.out.println("You are not pass");
}
// Else if the score more than or equal to 50 and less than 80.
else if (score >= 50 && score < 80) {
System.out.println("You are pass");
}
// Remaining cases (that is greater than or equal to 80)
else {
System.out.println("You are pass, good student!");
}
}
}Results of running the class ElseIfExample1:
Your score =70
You are passChange the value of the variable "score" in the above example and rerun the ElseIfExample1 class:
int score = 20;Your score =20
You are not pass4. Boolean value
boolean is a data type, it only has two values true or false.
Create class BooleanExample:
BooleanExample.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class BooleanExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable of type boolean
boolean value = true;
// If value is true
if (value == true) {
System.out.println("It's true");
}
// Else
else {
System.out.println("It's false");
}
if (value) {
System.out.println("It's true");
}
// Else
else {
System.out.println("It's false");
}
}
}It's true
It's true5. Operators involved in conditional expression
This is a list of operators, commonly used in conditional expressions.
- > Greater Than
- < Less Than
- >= Greater Than or Equal To
- <= Less Than or Equal To
- && AND
- || OR
- == HAS A VALUE OF
- != Not Equal To
- ! NOT
Example:
ElseIfExample2.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.javabasic.controlflow;
public class ElseIfExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Declare a variable of type int, represents your age.
int age = 20;
// Test if age less than or equal 17
if (age <= 17) {
System.out.println("You are 17 or younger");
}
// Test age equals 18
else if (age == 18) {
System.out.println("You are 18 year old");
}
// Test if age greater than 18 and less than 40
else if (age > 18 && age < 40) {
System.out.println("You are between 19 and 39");
}
// Remaining cases (Greater than or equal to 40)
else {
// Nested if statements
// Test age not equals 50.
if (age != 50) {
System.out.println("You are not 50 year old");
}
// Negative statements
if (!(age == 50)) {
System.out.println("You are not 50 year old");
}
// If age is 60 or 70
if (age == 60 || age == 70) {
System.out.println("You are 60 or 70 year old");
}
}
}
}Chạy ví dụ:
You are between 19 and 39You can change the value of "age" and rerun ElseIfExample2 class and see the results
Java Basic
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Install Java on Windows
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Install Eclipse
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Data Types in java
- Bitwise Operations
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Loops in Java
- Arrays in Java
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials