Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
1. Introduction
RMI is a way for you to call remote method. for example, call a method running on a computer B and receive the resulting response. So computer B is a server providing service.
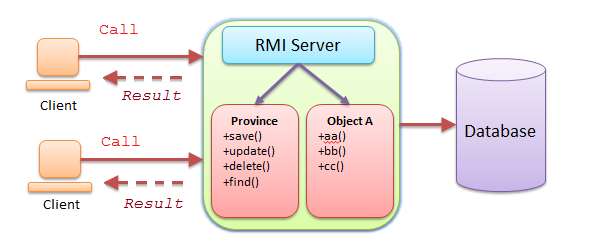
2. Create Project
Create Project RMITutorial
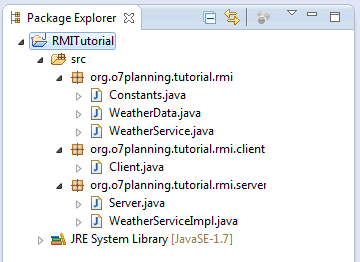
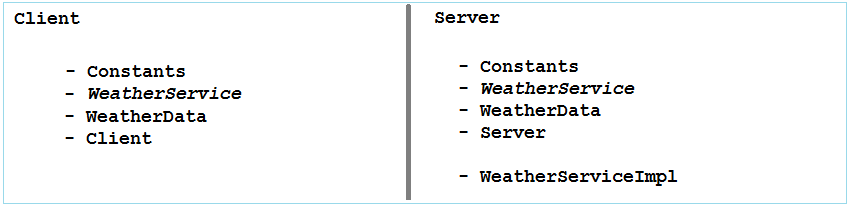
The classes packaged for Client and Server:
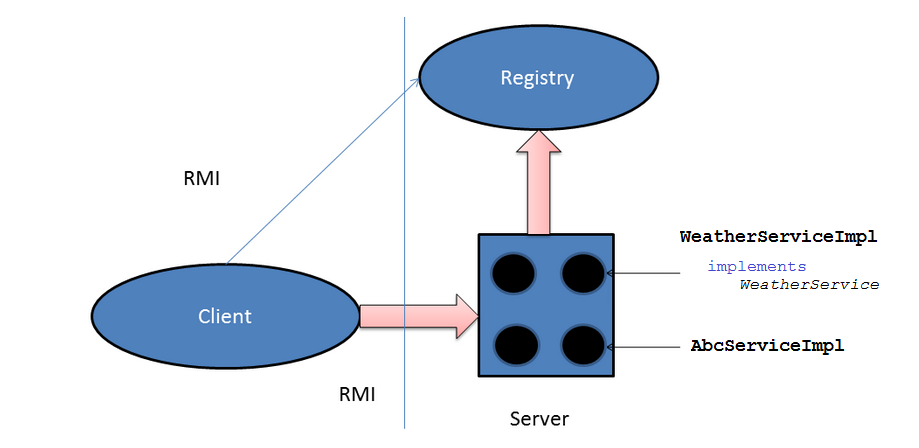
This is the working model of RMI. Server will register the object with Registry. Client will then look the Registry up by IP address and Port, so that it can call methods from objects in Server.
Constants.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
public class Constants {
public static final String LOCATION_HANOI = "HaNoi";
public static final String LOCATION_TOKYO = "Tokyo";
public static final String LOCATION_CHICAGO = "Chicago";
public static final String WEATHER_RAIN ="rain";
public static final String WEATHER_SUNNY ="sunny";
}WeatherData.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Date;
public class WeatherData implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private Date date;
private String location;
private String weather;
public WeatherData(Date date, String location, String weather) {
this.date = date;
this.location = location;
this.weather = weather;
}
public Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public String getWeather() {
return weather;
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
}
}WeatherService.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.util.Date;
public interface WeatherService extends Remote {
// Method to retrieve weather information.
public WeatherData getWeather(Date date, String location)
throws RemoteException;
}WeatherServiceImpl.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.Constants;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherData;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class WeatherServiceImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements
WeatherService {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public WeatherServiceImpl() throws RemoteException {
super();
}
@Override
public synchronized WeatherData getWeather(Date date, String location)
throws RemoteException {
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.setTime(date);
int dayOfWeek = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
// Sunday, Monday
if (dayOfWeek == 1 || dayOfWeek == 2) {
if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_CHICAGO)) {
// Rain
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_RAIN);
} else if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_HANOI)) {
// Sunny
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
} else if (location.equals(Constants.LOCATION_TOKYO)) {
// Sunny
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
}
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
} else {
return new WeatherData(date, location, Constants.WEATHER_SUNNY);
}
}
}Client.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.client;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.Date;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.Constants;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherData;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class Client {
// Host or IP of Server
private static final String HOST = "localhost";
private static final int PORT = 1099;
private static Registry registry;
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Search the registry in the specific Host, Port.
registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(HOST, PORT);
// Lookup WeatherService in the Registry.
WeatherService service = (WeatherService) registry
.lookup(WeatherService.class.getSimpleName());
Date today = new Date();
// Get Chicago weather info:
WeatherData chicagoWeather = service.getWeather(today,
Constants.LOCATION_CHICAGO);
System.out.println("Chicago weather today: "
+ chicagoWeather.getWeather());
// Get Hanoi weather info:
WeatherData hanoiWeather = service.getWeather(today,
Constants.LOCATION_HANOI);
System.out.println("Hanoi weather today: " + hanoiWeather.getWeather());
}
}Server.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server;
import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException;
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.WeatherService;
public class Server {
private static final int PORT = 1099;
private static Registry registry;
public static void startRegistry() throws RemoteException {
// Create server registry
registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(PORT);
}
public static void registerObject(String name, Remote remoteObj)
throws RemoteException, AlreadyBoundException {
// Bind the object in the registry.
// It is bind with certain name.
// Client will lookup on the registration of the name to get object.
registry.bind(name, remoteObj);
System.out.println("Registered: " + name + " -> "
+ remoteObj.getClass().getName() + "[" + remoteObj + "]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("Server starting...");
startRegistry();
registerObject(WeatherService.class.getSimpleName(), new WeatherServiceImpl());
// Server was the start, and was listening to the request from the client.
System.out.println("Server started!");
}
}3. Run Application
To run the RMI application, you need to pack your project into two jar files. The first jar file includes the classes to run in client machine. And second Jar file, including the classes to run in server machine.
This is the illustration:
However, you can run Demo on the Eclipse:
First run the class Server:
Server starting...
Registered: WeatherService -> org.o7planning.tutorial.rmi.server.WeatherServiceImpl[WeatherServiceImpl[UnicastServerRef [liveRef: [endpoint:[192.168.0.102:64865](local),objID:[6aadac58:179707abf4c:-7fff, -728182817779393915]]]]]
Server started!Server is running, and it registers Remote Object with the Registry. Next, you run class in Client.
Chicago weather today: sunny
Hanoi weather today: sunnyJava Basic
- Customize java compiler processing your Annotation (Annotation Processing Tool)
- Java Programming for team using Eclipse and SVN
- Java WeakReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java PhantomReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Compression and Decompression Tutorial with Examples
- Configuring Eclipse to use the JDK instead of JRE
- Java String.format() and printf() methods
- Syntax and new features in Java 8
- Java Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Java Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- JDBC Driver Libraries for different types of database in Java
- Java JDBC Tutorial with Examples
- Get the values of the columns automatically increment when Insert a record using JDBC
- Java Stream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Functional Interface Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to the Raspberry Pi
- Java Predicate Tutorial with Examples
- Abstract class and Interface in Java
- Access modifiers in Java
- Java Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Java Annotations Tutorial with Examples
- Comparing and Sorting in Java
- Java String, StringBuffer and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- Java Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- Java Generics Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in Java
- Java BiPredicate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Consumer Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiConsumer Tutorial with Examples
- What is needed to get started with Java?
- History of Java and the difference between Oracle JDK and OpenJDK
- Install Java on Windows
- Install Java on Ubuntu
- Install OpenJDK on Ubuntu
- Install Eclipse
- Install Eclipse on Ubuntu
- Quick Learning Java for beginners
- History of bits and bytes in computer science
- Data Types in java
- Bitwise Operations
- if else statement in java
- Switch Statement in Java
- Loops in Java
- Arrays in Java
- JDK Javadoc in CHM format
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Java
- Java Function Tutorial with Examples
- Java BiFunction Tutorial with Examples
- Example of Java encoding and decoding using Apache Base64
- Java Reflection Tutorial with Examples
- Java remote method invocation - Java RMI Tutorial with Examples
- Java Socket Programming Tutorial with Examples
- Which Platform Should You Choose for Developing Java Desktop Applications?
- Java Commons IO Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Email Tutorial with Examples
- Java Commons Logging Tutorial with Examples
- Understanding Java System.identityHashCode, Object.hashCode and Object.equals
- Java SoftReference Tutorial with Examples
- Java Supplier Tutorial with Examples
- Java Aspect Oriented Programming with AspectJ (AOP)
Show More
- Java Servlet/Jsp Tutorials
- Java Collections Framework Tutorials
- Java API for HTML & XML
- Java IO Tutorials
- Java Date Time Tutorials
- Spring Boot Tutorials
- Maven Tutorials
- Gradle Tutorials
- Java Web Services Tutorials
- Java SWT Tutorials
- JavaFX Tutorials
- Java Oracle ADF Tutorials
- Struts2 Framework Tutorials
- Spring Cloud Tutorials