CSS combinator Selectors Tutorial with Examples
1. Descendant combinator
Descendant combinator: A white space is placed between 2 Selector, for example ( A B ). Firstly, it searches for all the elements that match Selector 1 and gets result 1. Then it looks for the elements which are the descendants of the elements of result 1 which match Selector 2 and gets result 2. Finally, result 2 is exactly what is expected.

Syntax is:
selector1 selector2 {
}
selector1 selector2 selector3 {
}For example, searching for <span> elements that are descended from the <div> elements:
div span {
background: yellow;
}For example, searching for all the <li> elements which are descended from the "ul.sidebar" elements.
/* List items that are descendants of the "sidebar" list */
ul.sidebar li {
margin: 2em;
}Example:
combinator-example1.css
li {
list-style-type: disc;
}
li li {
list-style-type: circle;
}combinator-example1.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>CSS Descendant combinator</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="combinator-example1.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Descendant combinator</h3>
<ul>
<li>
<div>CSS</div>
<ul>
<li>
<div>CSS Selectors</div>
<ul>
<li>Basic Selectors</li>
<li>Combinator</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>CSS Tables</li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<div>Java</div>
<ul>
<li>Spring</li>
<li>Struts</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>2. Child combinator
Child combinator: The sign (>) is placed between 2 Selectors, for example ( A > B ). Firstly, it searches for all the elements that match Selector 1 and gets result 1. Then it looks for the elements which are the direct children of the elements of result 1 which match Selector 2 and gets result 2. Finally, result 2 is exactly what is expected.

Syntax is:
selector1 > selector2 {
}
selector1 > selector2 > selector3 {
}Example:
combinator-example3.css
div.box {
margin: 5px;
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid green;
}
div.box > p.title {
font-size: 20px;
color: blue;
}combinator-example3.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>CSS Descendant combinator</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="combinator-example3.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Child combinator</h3>
<div class="box">
<p class="title">CSS</p>
<p class="content">
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets,...
</p>
</div>
<div class="box">
<p class="title">Javascript</p>
<p class="content">
JavaScript is a scripting or programming language that
allows you to implement complex features on web pages,...
</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>3. General sibling combinator
General sibling combinator: A hyphen (~) is placed between 2 Selectors, for example (A ~ B). Firstly, it searches for all the elements that match Selector 1 and gets result 1. Then it searches for the elements which are "younger siblings" of the elements of result 1 which match Selector 2 and gets result 2. Finally, result 2 is exactly what is expected.
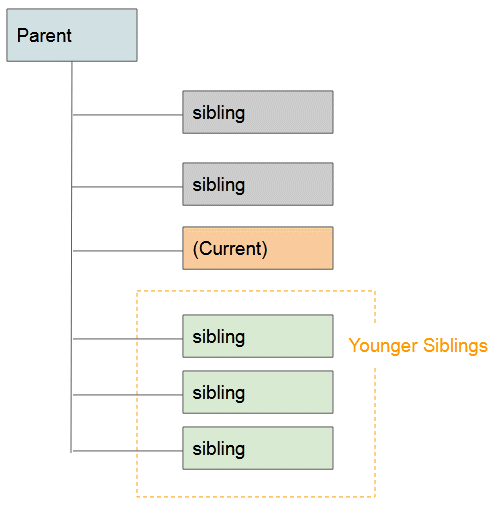
Example:
combinator-example5.css
a {
margin:5px;
font-size: 20px;
}
.menubar {
margin: 10px 0px;
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
a:hover {
color: blue;
font-weight: bold;
}
a:hover ~ a {
font-size: 80%;
font-style: italic;
color: black;
}combinator-example5.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>CSS General Sibling combinator</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="combinator-example5.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS General Sibling combinator</h3>
<a href="#">Top Link</a>
<div class="menubar">
<a href="#">CSS</a>
<a href="#">Javascript</a>
<a href="#">HTML</a>
<a href="#">Bootstrap</a>
<a href="#">jQuery</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>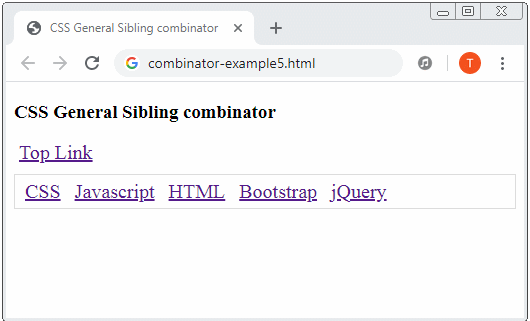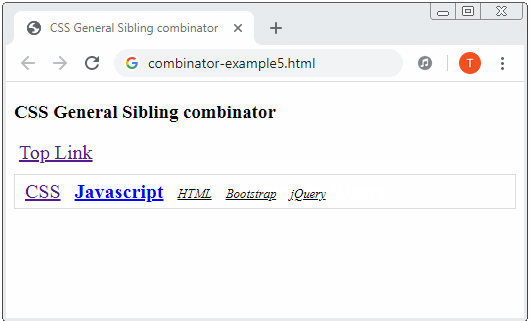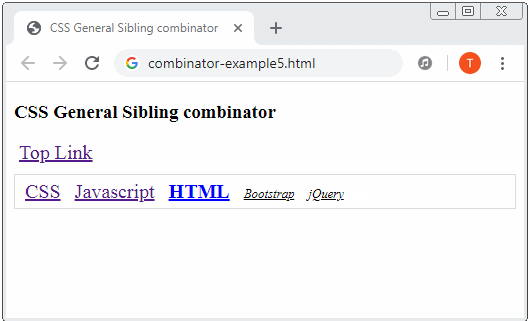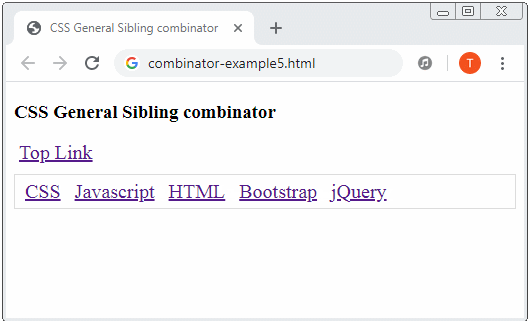
4. Adjacent sibling combinator
Adjacent sibling combinator The plus sign (+) is placed between 2 Selectors, for example (A + B). First, it searches for all the elements that match Selector 1 and gets result 1. Then it searches for the elements that are "younger adjacent siblings" of the elements of result 1 which match Selector 2 and gets result 2. Finally, result 2 is exactly what is expected.

Example:
combinator-example7.css
a {
margin:5px;
font-size: 20px;
}
.menubar {
margin: 10px 0px;
padding: 5px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
}
a:hover {
color: red;
font-weight: bold;
}
a:hover + a {
font-size: 80%;
font-style: italic;
color: black;
}combinator-example7.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8"/>
<title>CSS Adjacent Sibling combinator</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="combinator-example7.css" />
</head>
<body>
<h3>CSS Adjacent Sibling combinator</h3>
<a href="#">Top Link</a>
<div class="menubar">
<a href="#">CSS</a>
<a href="#">Javascript</a>
<a href="#">HTML</a>
<a href="#">Bootstrap</a>
<a href="#">jQuery</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>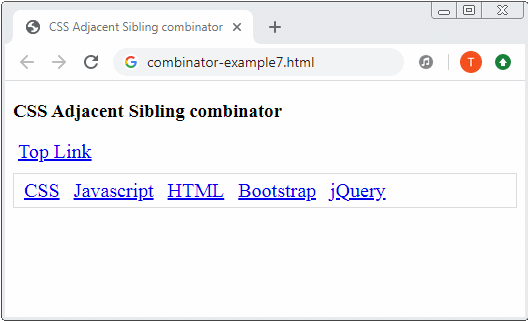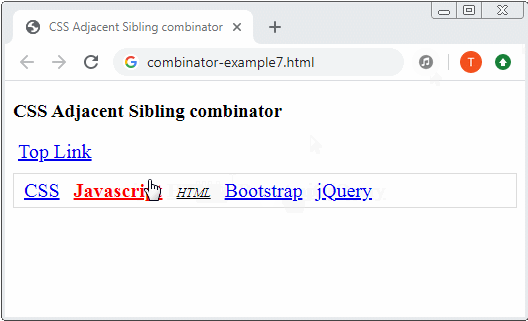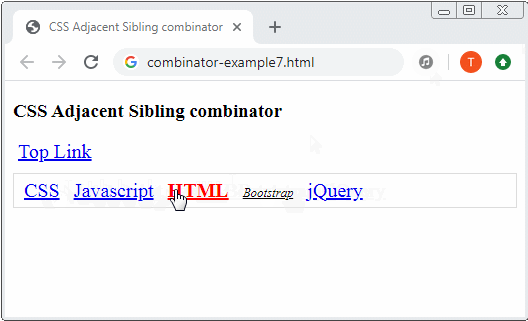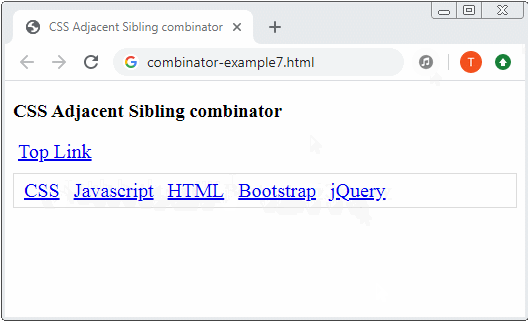
CSS Tutorials
- Units in CSS
- Basic CSS Selectors Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Attribute Selector Tutorial with Examples
- CSS combinator Selectors Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Backgrounds Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Opacity Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Padding Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Margins Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Borders Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Outline Tutorial with Examples
- CSS box-sizing Tutorial with Examples
- CSS max-width and min-width Tutorial with Examples
- The keywords min-content, max-content, fit-content, stretch in CSS
- CSS Links Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Fonts Tutorial with Examples
- Understanding Generic Font Family Names in CSS
- CSS @font-face Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Align Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Cursors Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Overflow Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Lists Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Tables Tutorial with Examples
- CSS visibility Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Display Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Grid Layout Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Float and Clear Tutorial with Examples
- CSS Position Tutorial with Examples
- CSS line-height Tutorial with Examples
- CSS text-align Tutorial with Examples
- CSS text-decoration Tutorial with Examples
Show More