Java PipedInputStream Tutorial with Examples
1. PipedInputStream
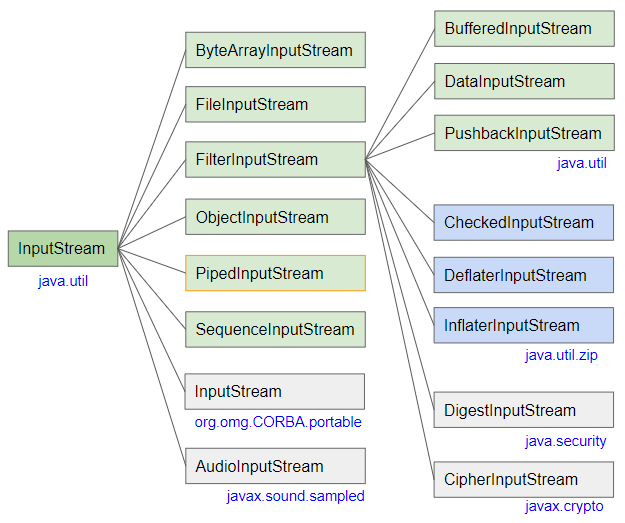
- InputStream
- BufferedInputStream
- SequenceInputStream
- FileInputStream
- ByteArrayInputStream
- ObjectInputStream
- PushbackInputStream
- FilterInputStream
- AudioInputStream
- DataInputStream
- InflaterInputStream
- DigestInputStream
- DeflaterInputStream
- CipherInputStream
- CheckedInputStream
To easily understand PipedInputStream, I illustrate by an example below:
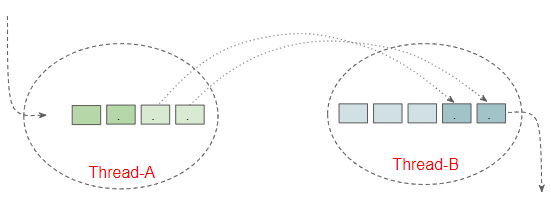
Suppose you are developing a Multithreading app, and you have 2 independent Threads: Thread-A and Thread-B. The question is:
- What needs to be done when every time bytes appear on Thread-A, they will be transfered to Thread-B automatically?
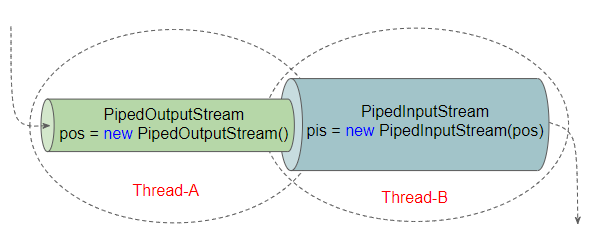
PipedOutputStream and PipedInputStream are created to help you handle situation mentioned above. Each time data is written to PipedOutputStream, they will appear automatically on PipedInputStream.
PipedInputStream constructors
PipedInputStream()
PipedInputStream(int pipeSize)
PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src)
PipedInputStream(PipedOutputStream src, int pipeSize)For data written to PipedOutputStream to appear on PipedInputStream, you must connect these two objects together.
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
pipedOS.connect(pipedIS);The above code is equivalent to the following ways:
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
pipedIS.connect(pipedOS);PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream(pipedOS);PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream(pipedIS);- Java PipedOutputStream
- Java PipedWriter
2. Example 1
PipedInputStreamEx1.java
package org.o7planning.pipedinputstream.ex;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class PipedInputStreamEx1 {
private PipedInputStream pipedIS;
private PipedOutputStream pipedOS;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
new PipedInputStreamEx1().test();
}
private void test() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// Create a PipedInputStream
pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
// Data written to 'pipedOS'
// will appear automatically at 'pipedIS'.
pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream(pipedIS);
new ThreadB().start();
new ThreadA().start();
}
//
class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 'a', 97, 'b', 'c', 101 };
for (byte b : bytes) {
pipedOS.write(b);
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(pipedOS);
}
}
}
//
class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int b = 0;
while ((b = pipedIS.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(b + " " + (char) b);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(pipedIS);
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(InputStream in) {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(OutputStream out) {
if (out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}Output:
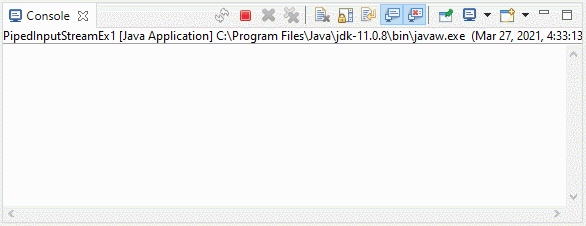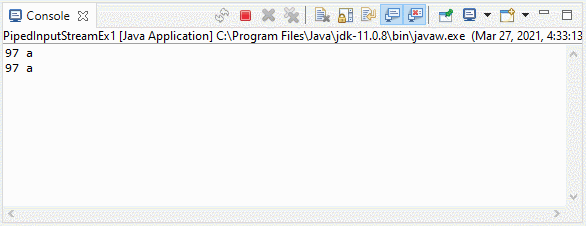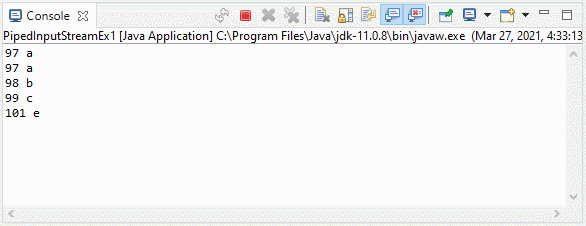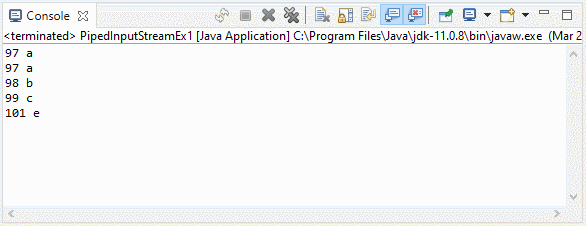
3. Example 2
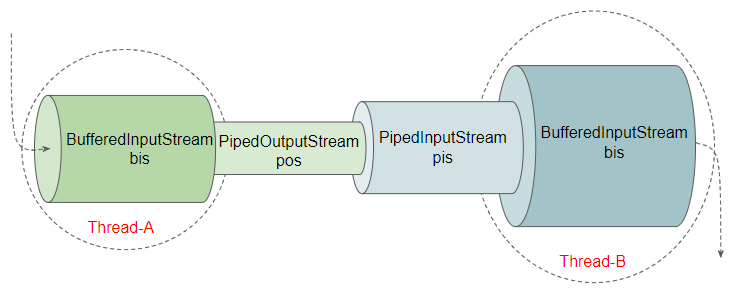
Example: Using PipedInputStream, PipedOutputStream with BufferedInputStream and BufferedOutputStream to improve the program's performance.
PipedInputStreamEx2.java
package org.o7planning.pipedinputstream.ex;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PipedInputStream;
import java.io.PipedOutputStream;
public class PipedInputStreamEx2 {
private BufferedInputStream bufferedIS;
private BufferedOutputStream bufferedOS;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
new PipedInputStreamEx2().test();
}
private void test() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
PipedInputStream pipedIS = new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream pipedOS = new PipedOutputStream();
pipedIS.connect(pipedOS);
this.bufferedIS = new BufferedInputStream(pipedIS);
this.bufferedOS = new BufferedOutputStream(pipedOS);
new ThreadB().start();
new ThreadA().start();
}
//
class ThreadA extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 'a', 97, 'b', 'c', 101 };
for (byte b : bytes) {
bufferedOS.write(b);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(bufferedOS);
}
}
}
//
class ThreadB extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
int code;
while ((code = bufferedIS.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(code + " " + (char)code);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
closeQuietly(bufferedIS);
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(InputStream in) {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
private void closeQuietly(OutputStream out) {
if (out != null) {
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
}Java IO Tutorials
- Java CharArrayWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java FilterReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java FilterWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java PrintStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java StringReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java StringWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java PipedReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java LineNumberReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java PrintWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java IO Binary Streams Tutorial with Examples
- Java IO Character Streams Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ByteArrayOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java DataOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java PipedInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java OutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ObjectOutputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java PushbackInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java SequenceInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java BufferedInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java Reader Tutorial with Examples
- Java Writer Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java CharArrayReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java ByteArrayInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java DataInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java ObjectInputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java InputStreamReader Tutorial with Examples
- Java OutputStreamWriter Tutorial with Examples
- Java InputStream Tutorial with Examples
- Java FileInputStream Tutorial with Examples
Show More