Use Top Command - Task Manager for Ubuntu
1. Top Command
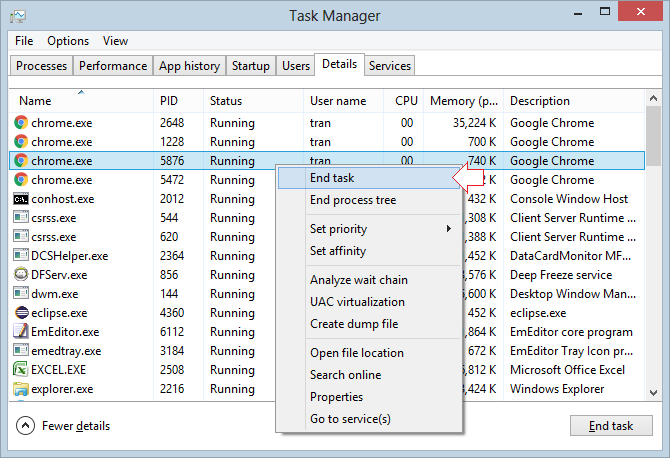
When you are familiar with Task Manager in the Windows OS, you will wonder if there is something similar to Task Manager in Ubuntu Server or not.
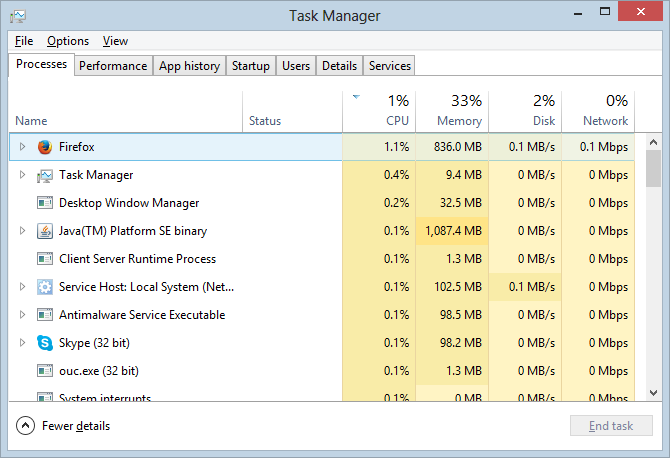
In Windows, Task Manager is a utility program allowing you to know which application is running on the system and resources it uses
Ubuntu supplies you with a similar program, however its interface is very rudimentary. The application is called as "Top Command".
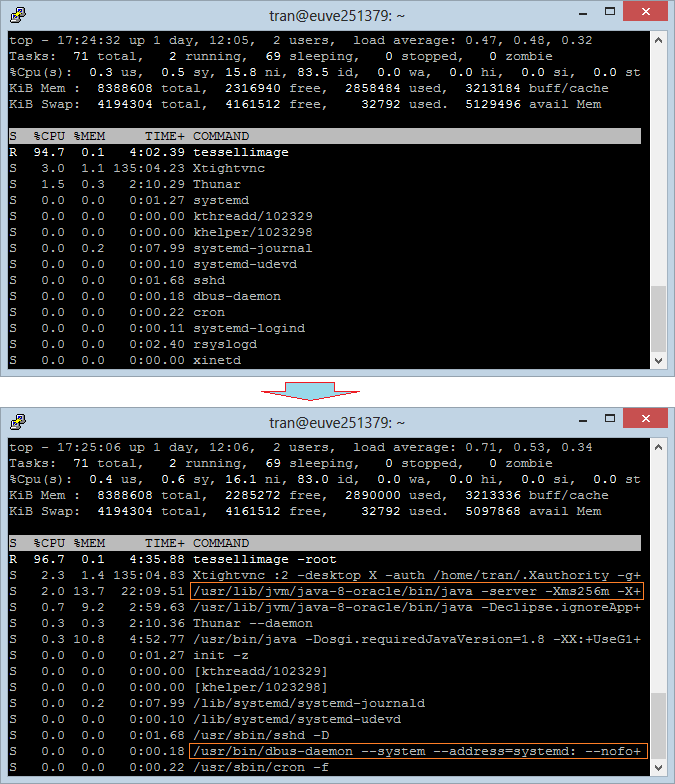
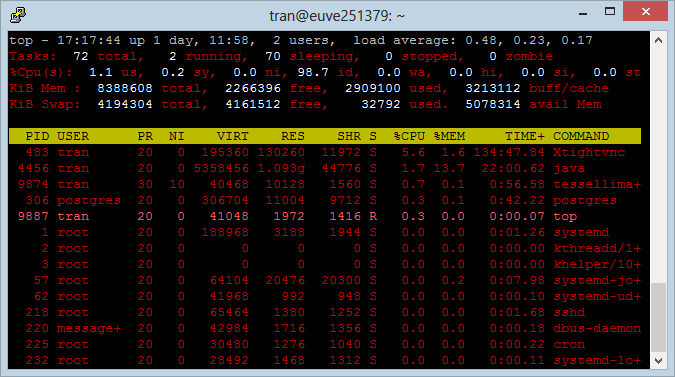
To run "Top Command", you run the top command:
Top Command:
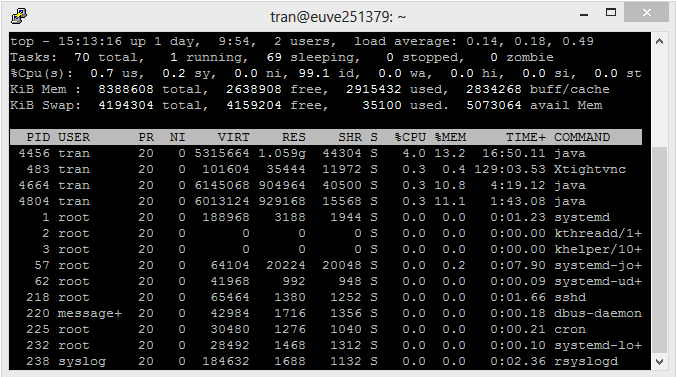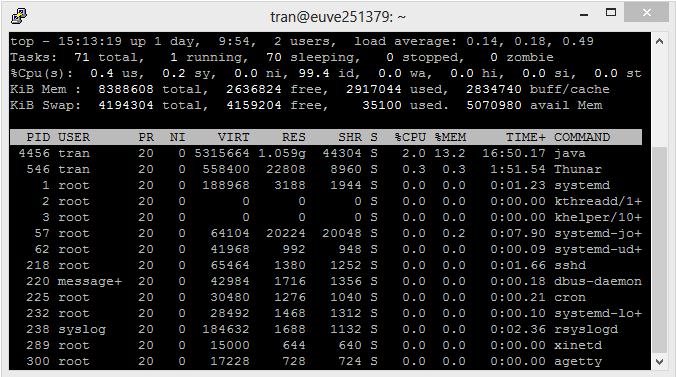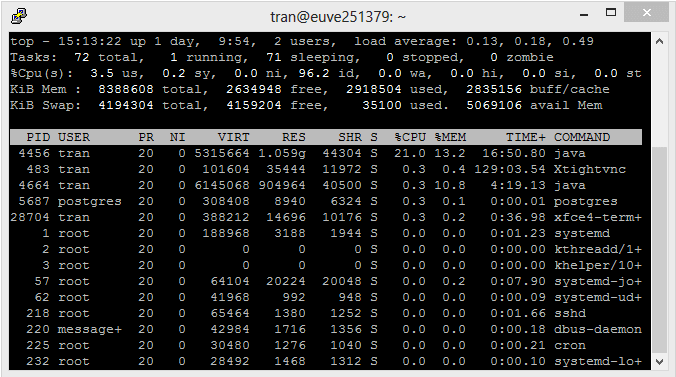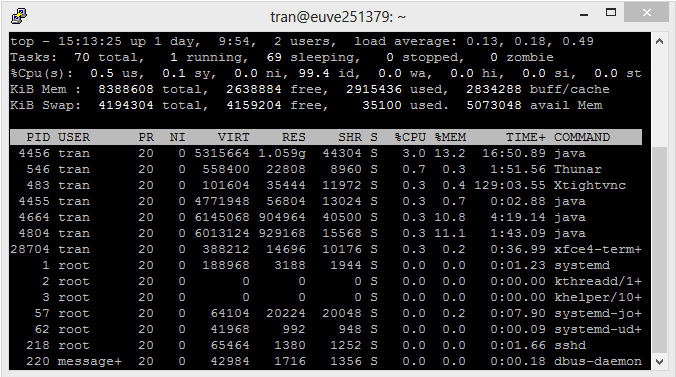
Note: To exit "Top Command", press 'q'.
3. Add/remove Fields
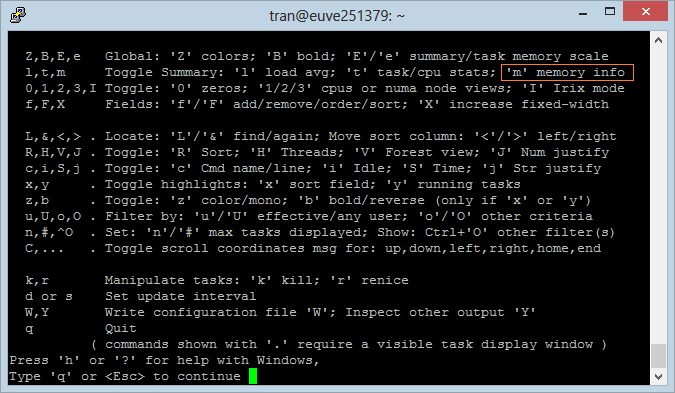
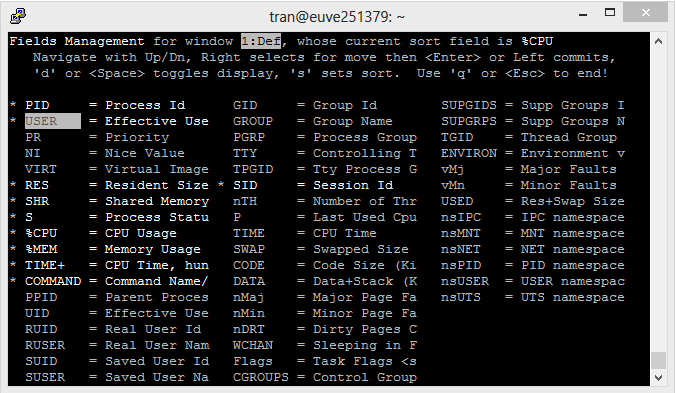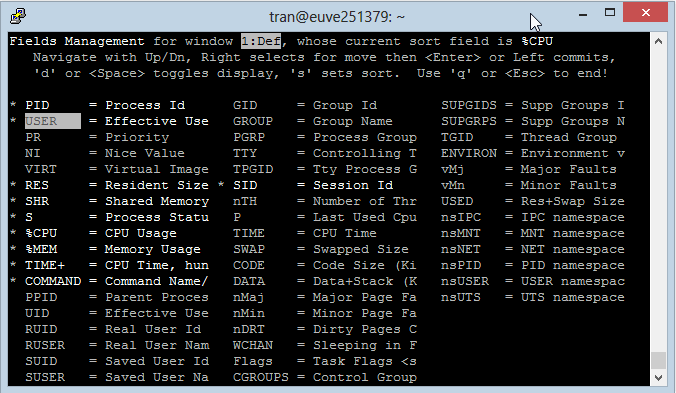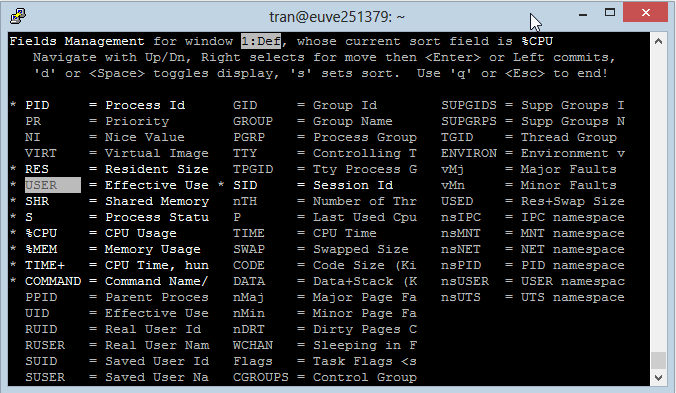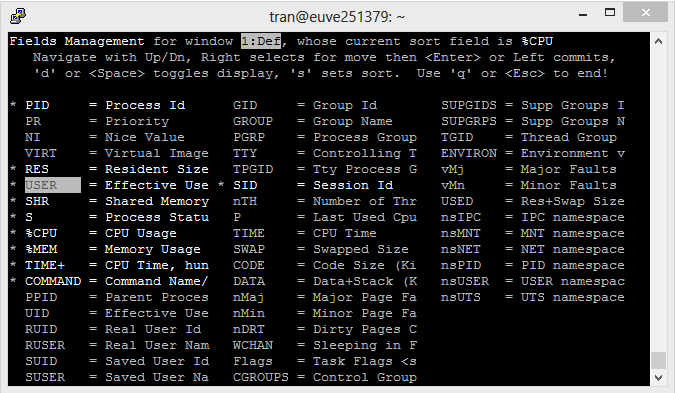
There are lots of Fields you can care for. By default, "Top Command" only displays some Fields. Press 'f' to add or remove Fields:
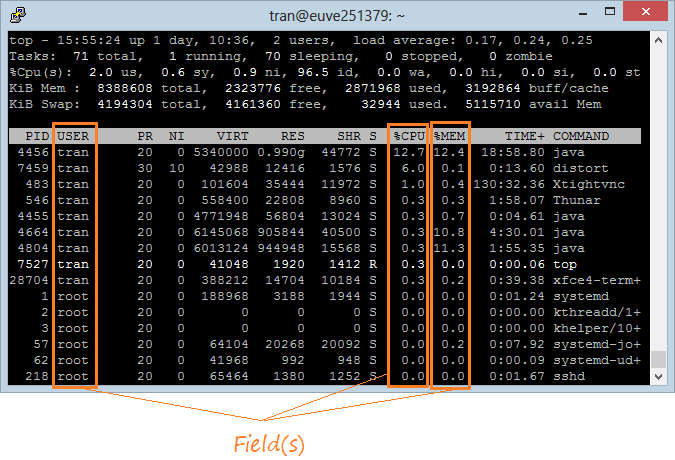
The Fields with (*) are the displayed fields, other ones don't display on "Top Command".
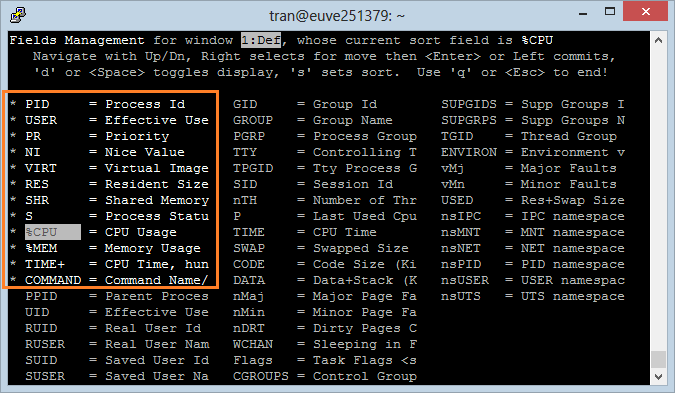
Use up or down arrow keys to move to the the desired Field.
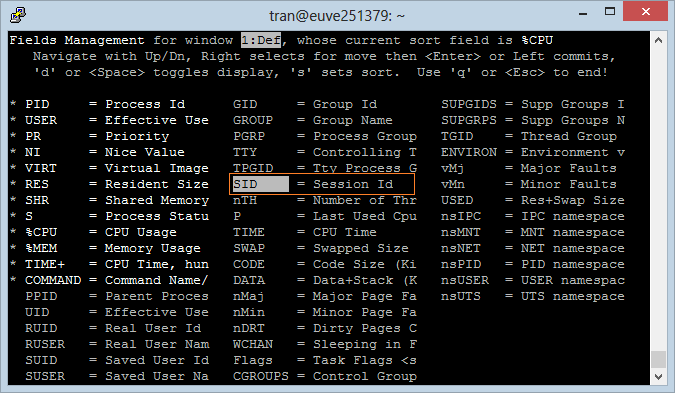
- Press ENTER.
- Press Whitespace to select or deselect Field.
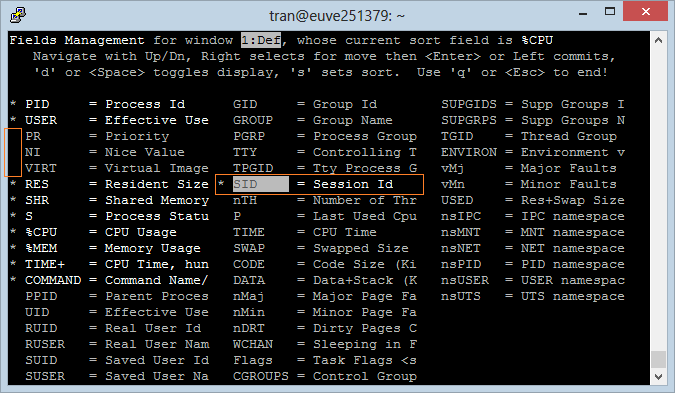
Press "ESC" to return to the main screen.
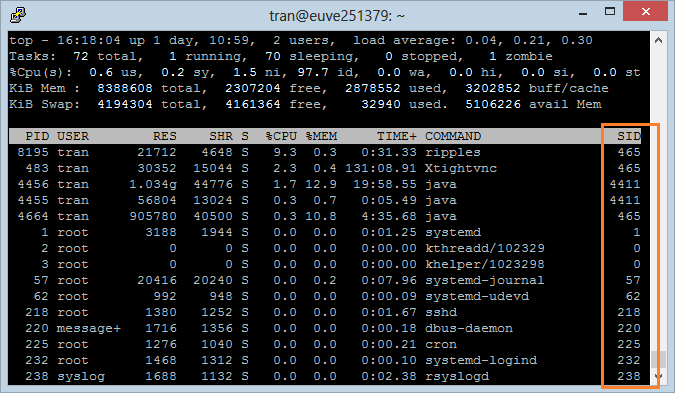
4. Change the order of the Fields
It will be more visible when you change the order of the Field on the screen of the "Top Command".
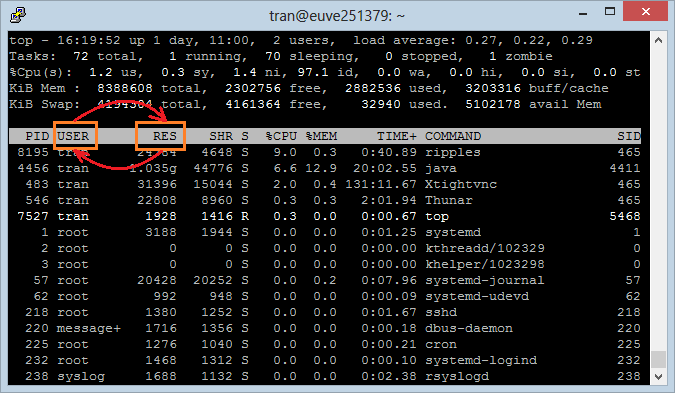
Press 'f' to see a list of Fields.
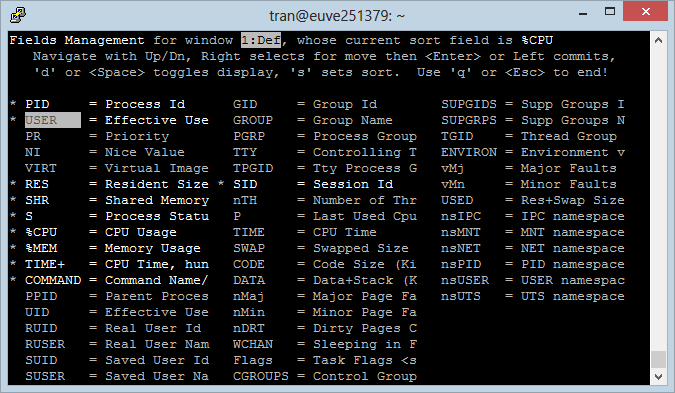
- Press the right arrow key to mark the Field that need to move.
- Press the up/ down arrow to move the Field marked above to another location.
- Press ENTER to complete it.
Press "ESC" to return to the main screen.
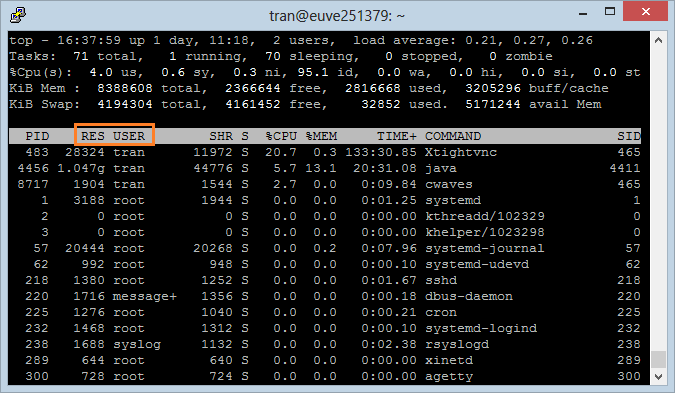
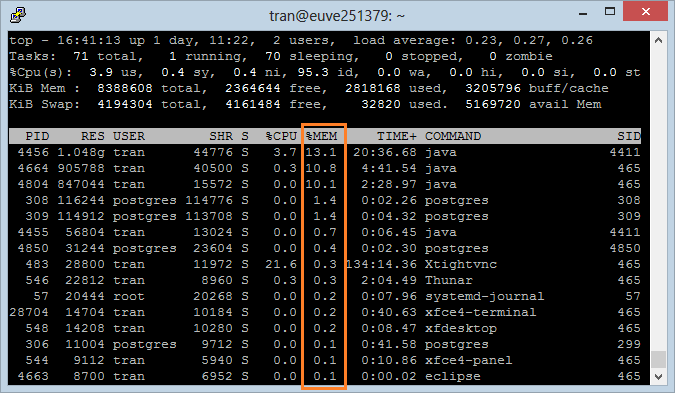
5. Sort on Field
Assume that you want to know which program is using the most memory, you need to sort it by %MEM (% Memory).
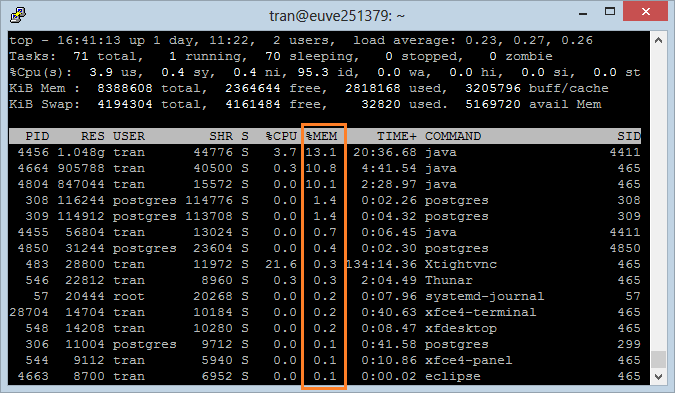
Press 'f' to see the list of Fields.
- Select the Field to sort.
- Press 's'.
- Press "ESC" to return to the main screen.
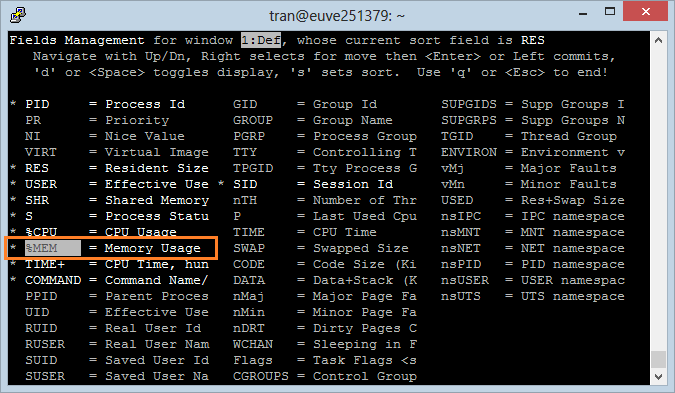
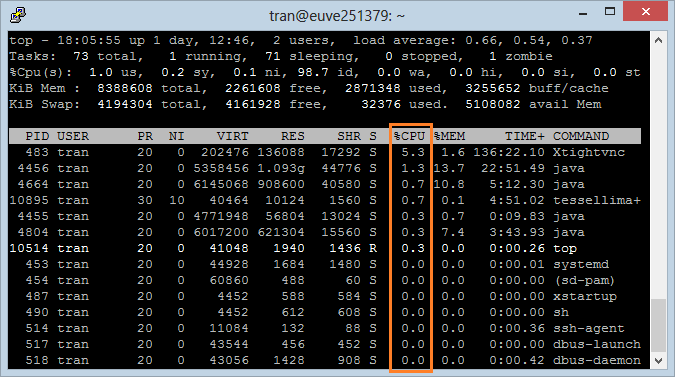
6. Sort by CPU
CPU is an important field, it tells you which Process enables computer to process the most at the moment. Press "Shift + P" to sort by CPU.
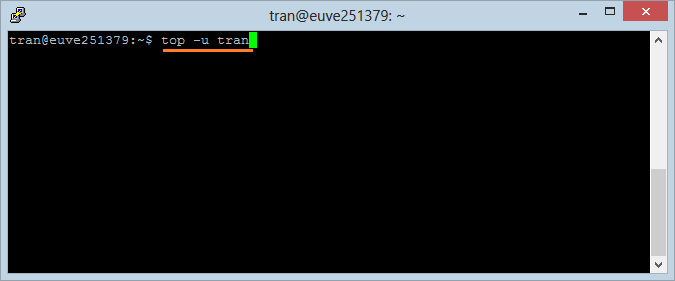
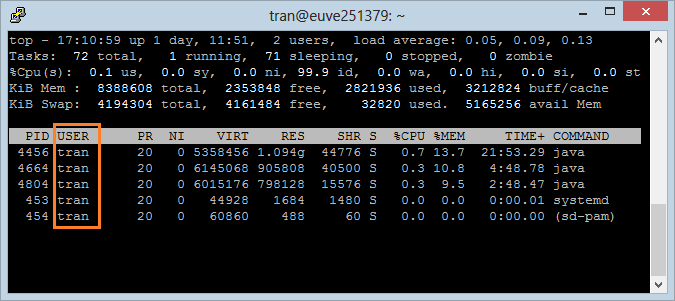
7. Display Specific User Processes
Use the option '-u' allowing you to specify user and to view which process is executed by this user.
top -u user_nameFor example, see the processes that are executed by user 'tran':
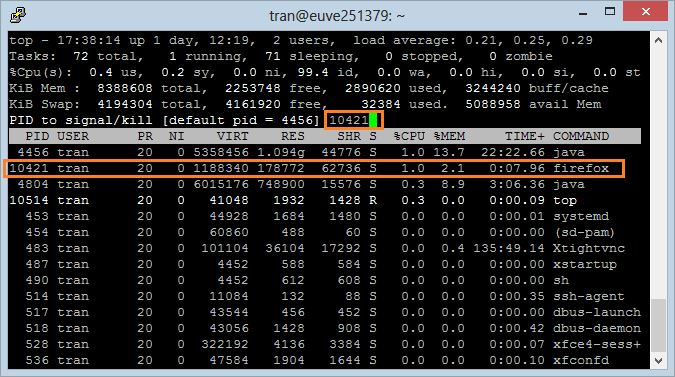
8. Highlight Running Processes
Press 'z', the program "Top Command" will display processes running with the colors. This helps you to identify the running processes easily.
Ubuntu Tutorials
- Install GParted hard drive partition software on Ubuntu
- Install Ubuntu Desktop in VmWare
- Install Ubuntu Desktop on VirtualBox
- Create a Launcher (Shortcut) for a program in Ubuntu
- Install Ubuntu Server in VmWare
- Install GUI and VNC for Ubuntu Server
- Install OpenSSH Server on Ubuntu
- The softwares create note windows on Desktop for Ubuntu
- Install TeamViewer on Ubuntu
- Peek: Animated GIF Screen Recorder Software for Ubuntu
- Install GUI and Remote Desktop for Ubuntu Server
- Transfer files between computers using Cyberduck on Mac OS
- How to use the "hosts" file?
- Install Firefox Browser on Ubuntu
- Redirect port 80, 443 on Ubuntu using iptables
- Use WinSCP to transfer files between Computers
- Use Top Command - Task Manager for Ubuntu
- Check Internet Speed with speedtest-cli on Ubuntu
- Install Winrar on Ubuntu
- Install xChm Viewer to read the CHM file on Ubuntu
- Install FFmpeg on Ubuntu
- Setup environment variables on Ubuntu
Show More