C# Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
1. What is Exception?
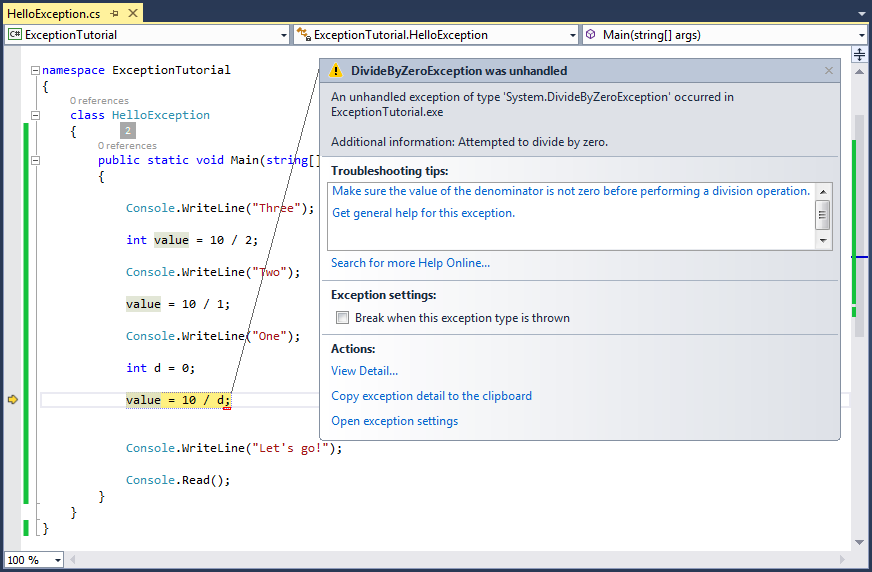
In this example, there is an part of error code which results from the division by 0. The division by 0 causes the exception: DivideByZeroException
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class HelloException
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Three");
// This division no problem.
int value = 10 / 2;
Console.WriteLine("Two");
// This division no problem.
value = 10 / 1;
Console.WriteLine("One");
int d = 0;
// This division has problem, divided by 0.
// An error has occurred here.
value = 10 / d;
// And the following code will not be executed.
Console.WriteLine("Let's go!");
Console.Read();
}
}
}You can see the notification on the Console screen. The error notification is very clear, including the information of code line.
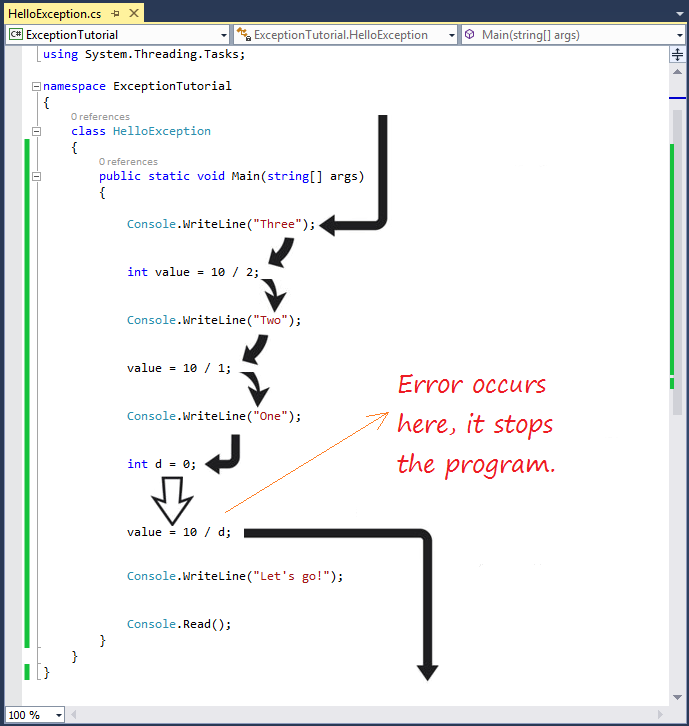
Three
Two
One- The program runs normally from step (1), (2) to (5).
- In step (6), the program divided by 0.
- The program jumps out of main method, and the (7) code line has not been executed.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class HelloCatchException
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Three");
// This division has no problem.
int value = 10 / 2;
Console.WriteLine("Two");
// This division has no problem.
value = 10 / 1;
Console.WriteLine("One");
int d = 0;
try
{
// This division has problem, divided by 0.
// An error has occurred here.
value = 10 / d;
// And the following code will not be executed.
Console.WriteLine("Value =" + value);
}
catch (DivideByZeroException e)
{
// The code in the catch block will be executed
Console.WriteLine("Error: " + e.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Ignore...");
}
// This code is executed.
Console.WriteLine("Let's go!");
Console.Read();
}
}
}Three
Two
One
Error: Attempted to divide by zero.
Ignore...
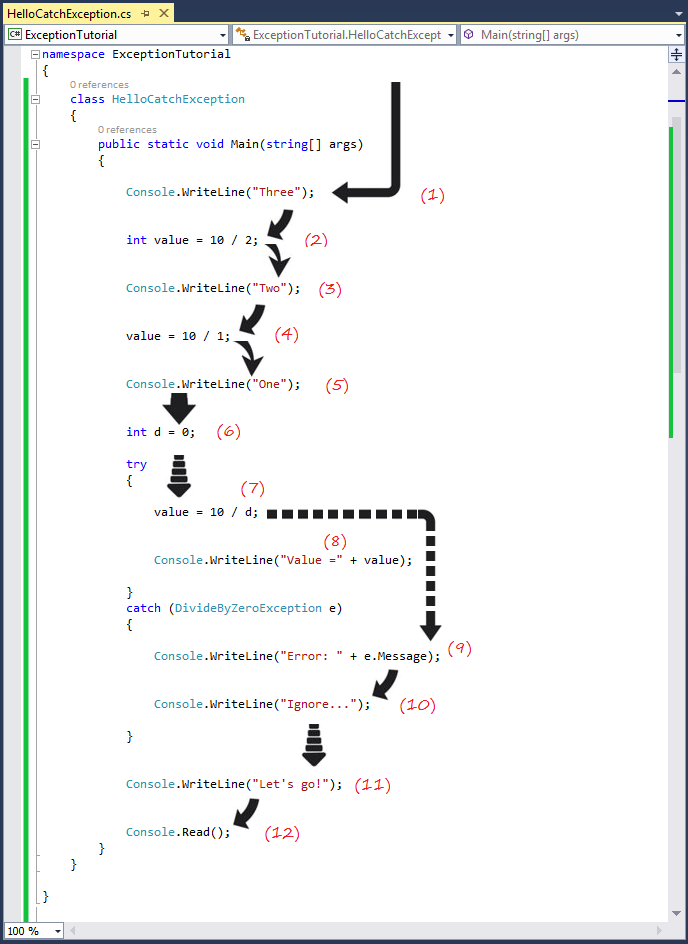
Let't go!- Steps (1) to (6) are completely normal.
- Exception occurs in step (7), the problem divided by zero.
- Immediately it jumps in executing the command in catch block, step (8) is skipped.
- Step (9), (10) is executed.
- Step (11), (12) is executed.
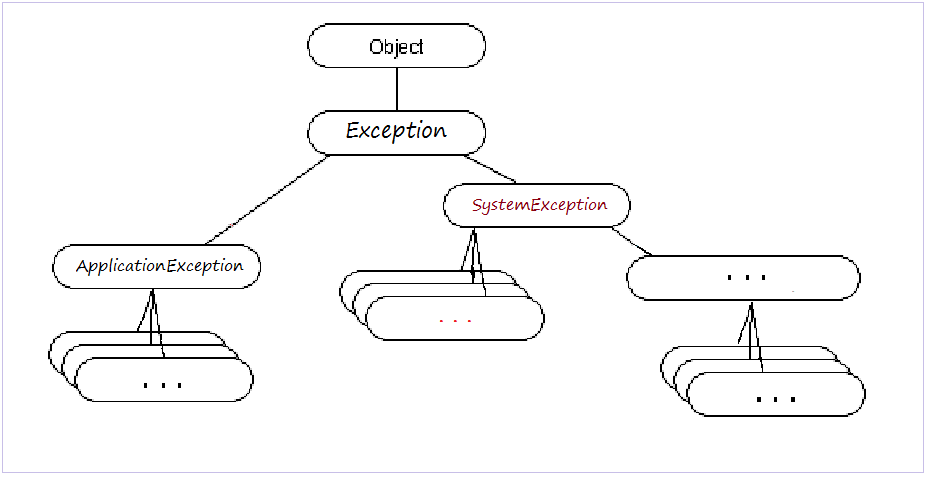
2. Exception Hierarchy
- The highest class is Exception
- Two direct subclasses is SystemError and ApplicationException.
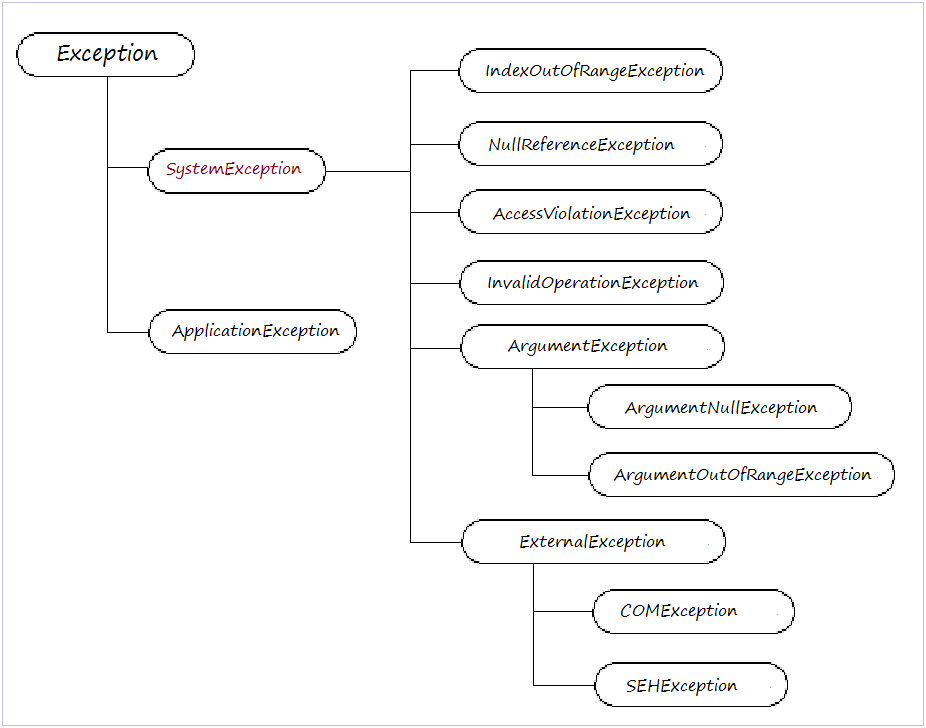
Exception type | Description |
Exception | Base class for all exceptions. |
SystemException | Base class for all runtime-generated errors. |
IndexOutOfRangeException | Thrown by the runtime only when an array is indexed improperly. |
NullReferenceException | Thrown by the runtime only when a null object is referenced. |
AccessViolationException | Thrown by the runtime only when invalid memory is accessed. |
InvalidOperationException | Thrown by methods when in an invalid state. |
ArgumentException | Base class for all argument exceptions. |
ArgumentNullException | Thrown by methods that do not allow an argument to be null. |
ArgumentOutOfRangeException | Thrown by methods that verify that arguments are in a given range. |
ExternalException | Base class for exceptions that occur or are targeted at environments outside the runtime. |
COMException | Exception encapsulating COM HRESULT information. |
SEHException | Exception encapsulating Win32 structured exception handling information. |
3. Handling exception with try-catch
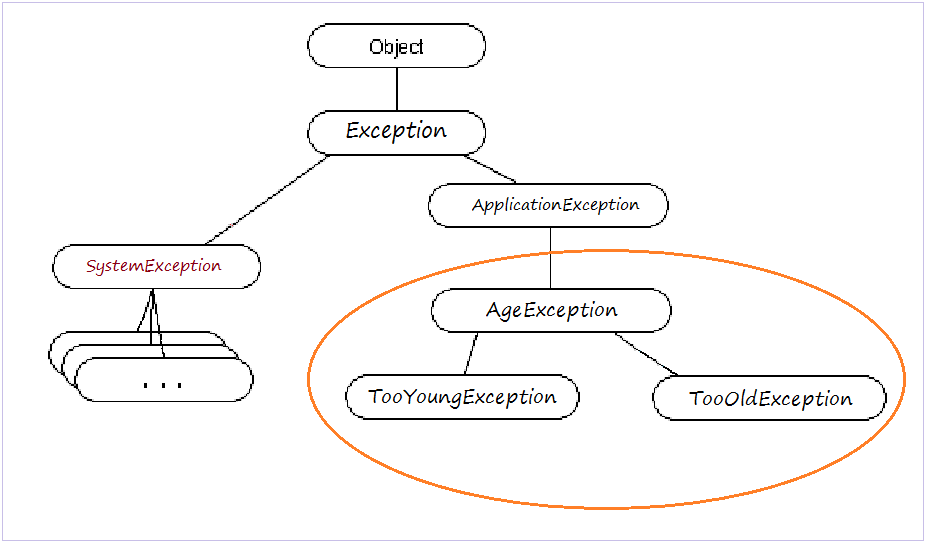
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class AgeException : ApplicationException
{
public AgeException(String message)
: base(message)
{
}
}
class TooYoungException : AgeException
{
public TooYoungException(String message)
: base(message)
{
}
}
class TooOldException : AgeException
{
public TooOldException(String message)
: base(message)
{
}
}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class AgeUtils
{
// This method checks the age.
// If age is less than 18, the method will throw an exception TooYoungException
// If age greater than 40, the method will throw an exception TooOldException
public static void checkAge(int age)
{
if (age < 18)
{
// If age is less than 18, an exception will be thrown
// This method ends here.
throw new TooYoungException("Age " + age + " too young");
}
else if (age > 40)
{
// If age greater than 40, an exception will be thrown.
// This method ends here.
throw new TooOldException("Age " + age + " too old");
}
// If age is between 18-40.
// This code will be execute.
Console.WriteLine("Age " + age + " OK!");
}
}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class TryCatchDemo1
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Start Recruiting ...
Console.WriteLine("Start Recruiting ...");
// Check your age.
Console.WriteLine("Check your Age");
int age = 50;
try
{
AgeUtils.checkAge(age);
Console.WriteLine("You pass!");
}
catch (TooYoungException e)
{
// Notice of "too young" exception.
Console.WriteLine("You are too young, not pass!");
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
catch (TooOldException e)
{
// Notice of "too old" exception.
Console.WriteLine("You are too old, not pass!");
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}Start Recruiting ...
Check your Age
You are too old, not pass!
Age 50 too oldusing System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class TryCatchDemo2
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Start Recruiting ...
Console.WriteLine("Start Recruiting ...");
// Check your age.
Console.WriteLine("Check your Age");
int age = 15;
try
{
// Here can throw TooOldException or TooYoungException
AgeUtils.checkAge(age);
Console.WriteLine("You pass!");
}
// If an exception occurs, type of AgeException
// This catch block will be executed.
catch (AgeException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Your age invalid, you not pass");
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}Start Recruiting ...
Check your Age
Your age invalid, you not pass
Age 15 too young4. try-catch-finally
try {
// Do something here
} catch (Exception1 e) {
// Do something here
} catch (Exception2 e) {
// Do something here
} finally {
// The finally block is always executed
// Do something here.
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class TryCatchFinallyDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
String text = "001234A2";
int value = toInteger(text);
Console.WriteLine("Value= " + value);
Console.Read();
}
public static int toInteger(String text)
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin parse text: " + text);
// An Exception can throw here (FormatException).
int value = int.Parse(text);
return value;
}
catch (FormatException e)
{
// In the case of 'text' is not a number.
// This catch block will be executed.
Console.WriteLine("Number format exception: " + e.Message);
return 0;
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("End parse text: " + text);
}
}
}
}Begin parse text: 001234A2
Number format exception: Input string was not in a correct format.
End parse text: 001234A2
Value= 0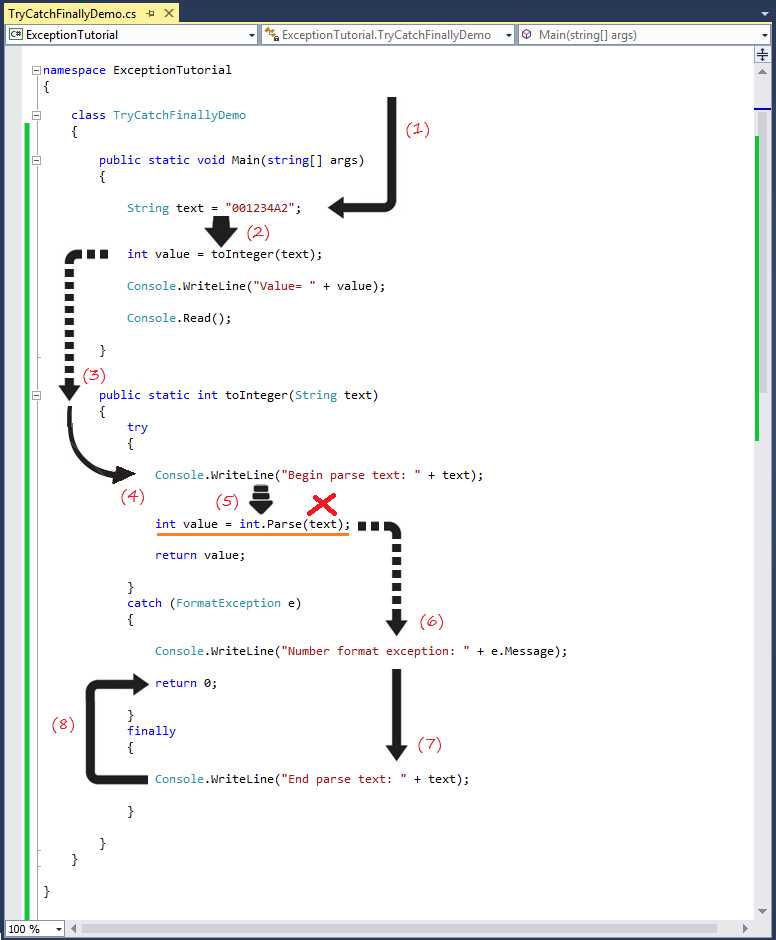
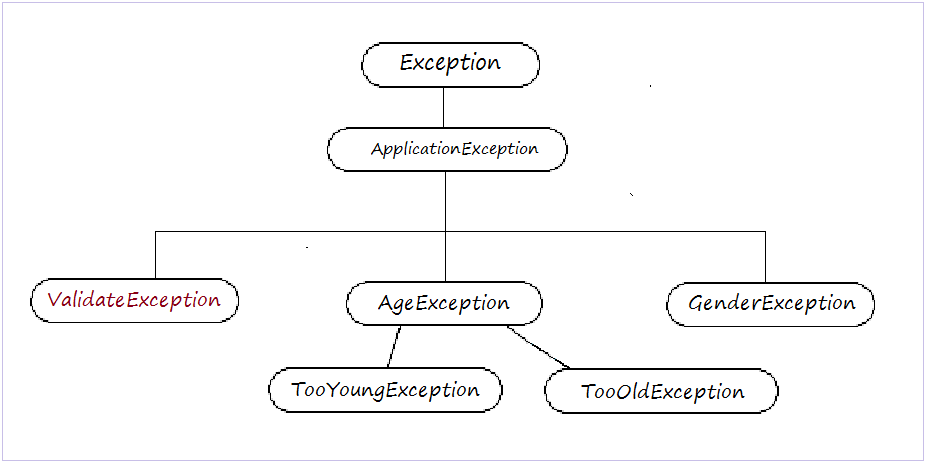
5. Exception Wrapping
- Person: Simulate a participant recruitment into the company with the information: Name, age, gender.
- GenderException: Gender Exception.
- ValidateException: Exception evaluate a candidate.
- ValidateUtils: Class with static method evaluate candidates.
- Valid if age between 18-40 and male
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class Person
{
public static readonly string MALE = "male";
public static readonly string FEMALE = "female";
private string name;
private string gender;
private int age;
public Person(string name, string gender, int age)
{
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public string GetName()
{
return name;
}
public string GetGender()
{
return gender;
}
public int GetAge()
{
return age;
}
}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class GenderException : ApplicationException
{
public GenderException(String message)
: base(message)
{
}
}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class ValidateException : ApplicationException
{
// Wrap an Exception
public ValidateException(Exception e) : base("Something invalid", e)
{
}
}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class ValidateUtils
{
// Method to check a Person.
public static void CheckPerson(Person person)
{
try
{
// Check age.
// Valid if between 18-40
// This method can throw TooOldException, TooYoungException.
AgeUtils.checkAge(person.GetAge());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
// If not valid
// Wrap this exception by ValidateException, and throw.
throw new ValidateException(e);
}
// If that person is Female, then invalid.
if (person.GetGender() == Person.FEMALE)
{
GenderException e = new GenderException("Do not accept women");
throw new ValidateException(e);
}
}
}
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class WrapperExceptionDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// An applicant.
Person person = new Person("Marry", Person.FEMALE, 20);
try
{
// Exceptions may occur here.
ValidateUtils.CheckPerson(person);
}
catch (ValidateException wrap)
{
// Get the real cause.
// May be TooYoungException, TooOldException, GenderException.
Exception cause = wrap.GetBaseException();
if (cause != null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Message: " + wrap.Message);
Console.WriteLine("Base Exception Message: " + cause.Message);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Message: " + wrap.Message);
}
}
Console.Read();
}
}
}Age 20 OK!
Message: Something invalid
Base Exception Message: Do not accept women6. Some common exceptions
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class NullReferenceExceptionDemo
{
// Example, here is a method that can return null string.
public static string GetString()
{
if (1 == 2)
{
return "1==2 !!";
}
return null;
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// This is an object that references not null.
string text1 = "Hello exception";
// Get length of string.
int length = text1.Length;
Console.WriteLine("Length text1 = " + length);
// This is an object that references null.
String text2 = GetString(); // text2 = null.
// Get length of string.
// NullReferenceException will occur here.
length = text2.Length; // ==> Runtime Error!
Console.WriteLine("Finish!");
Console.Read();
}
}
}You can correct the above code to make it similar to the following one with the avoidance of NullReferenceException:
// This is a null object.
String text2 = GetString(); // ==> return null
// Check to make sure 'text2' is not null,
// Instead of using try-catch.
if (text2 != null)
{
length = text2.Length;
}using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace ExceptionTutorial
{
class IndexOutOfRangeExceptionDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
String[] strs = new String[] { "One", "Two", "Three" };
// Access to the element at index 0.
String str1 = strs[0];
Console.WriteLine("String at 0 = " + str1);
// Access to the element has index 5.
// IndexOutOfRangeException occur here.
String str2 = strs[5];
Console.WriteLine("String at 5 = " + str2);
Console.Read();
}
}
}if (strs.length > 5)
{
String str2 = strs[5];
Console.WriteLine("String at 5 = " + str2);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("No elements with index 5");
}C# Programming Tutorials
- Inheritance and polymorphism in C#
- What is needed to get started with C#?
- Quick learning C# for Beginners
- Install Visual Studio 2013 on Windows
- Abstract class and Interface in C#
- Install Visual Studio 2015 on Windows
- Compression and decompression in C#
- C# Multithreading Programming Tutorial with Examples
- C# Delegates and Events Tutorial with Examples
- Install AnkhSVN on Windows
- C# Programming for Team using Visual Studio and SVN
- Install .Net Framework
- Access Modifier in C#
- C# String and StringBuilder Tutorial with Examples
- C# Properties Tutorial with Examples
- C# Enums Tutorial with Examples
- C# Structures Tutorial with Examples
- C# Generics Tutorial with Examples
- C# Exception Handling Tutorial with Examples
- C# Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- Manipulating files and directories in C#
- C# Streams tutorial - binary streams in C#
- C# Regular Expressions Tutorial with Examples
- Connect to SQL Server Database in C#
- Work with SQL Server database in C#
- Connect to MySQL database in C#
- Work with MySQL database in C#
- Connect to Oracle Database in C# without Oracle Client
- Work with Oracle database in C#