Python Dictionary Tutorial with Examples
1. Python Dictionary
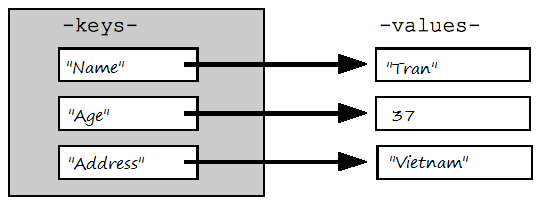
In Python, dictionary is a data type and it is a list of elements, each of which is a pair of key & value and is quite similar to the Map concept in Java.
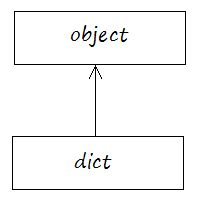
Dictionaries all are objects of the dict class.
In order to write a dictionary, you need to use { }, and write the elements into it, the elements are separated by comma. Each element is a pair of key and value separated by a colon ':'.
Example:
# Dictionary
myinfo = {"Name": "Tran", "Age": 37, "Address" : "Vietnam" }You can also create a dictionary object from the constructor of the dict class.
createDictionaryFromClass.py
# Create a dictionary via constructor of dict class.
mydict = dict()
mydict["E01"] = "John"
mydict["E02"] = "King"
print ("mydict: ", mydict)Output:
mydict: {'E01': 'John', 'E02': 'King'}Features of the value in the dictionary:
- Each element of the dictionary is a pair of key and value, the value can be a certain type (string, number, user-defined types,...), and can be the same.
Features of the key in the dictionary.
- The key in dictionary is a immutable type. So, it can be string, number, Tuple,...
- Some types are not allowed (for example: List) because List is a mutable data type.
- Các khóa trong dictionary không được phép trùng lặp.
Example:
dictionaryExample.py
# Dictionary
myinfo = {"Name": "Tran", "Age": 37, "Address" : "Vietnam" }
print ("myinfo['Name'] = ", myinfo["Name"])
print ("myinfo['Age'] = ", myinfo["Age"])
print ("myinfo['Address'] = ", myinfo["Address"])Output:
myinfo['Name'] = Tran
myinfo['Age'] = 37
myinfo['Address'] = Vietnam2. Update Dictionary
Dictionary allows you to update the value of a certain key, it adds a new element if the key does not exist on the dictionary.
updateDictionaryExample.py
# Dictionary
myinfo = {"Name": "Tran", "Age": 37, "Address" : "Vietnam" }
# update value for key 'Address'
myinfo["Address"] = "HCM Vietnam"
# Add new element with key 'Phone'
myinfo["Phone"] = "12345"
print ("Element count: ", len(myinfo) )
print ("myinfo['Name'] = ", myinfo["Name"])
print ("myinfo['Age'] = ", myinfo["Age"])
print ("myinfo['Address'] = ", myinfo["Address"])
print ("myinfo['Phone'] = ", myinfo["Phone"])Output:
Element count: 4
myinfo['Name'] = Tran
myinfo['Age'] = 37
myinfo['Address'] = HCM Vietnam
myinfo['Phone'] = 123453. Delete dictionary
There are 2 ways to remove an element from a dictionary.
- Use the del operator
- Using the "__delitem __ (key)" method
deleteDictionaryExample.py
# (Key,Value) = (Name, Phone)
contacts = {"John": "01217000111", \
"Tom": "01234000111", \
"Addison":"01217000222", "Jack":"01227000123"}
print ("Contacts: ", contacts)
print ("\n")
print ("Delete key = 'John' ")
# Delete element with key 'John'
del contacts["John"]
print ("Contacts (After delete): ", contacts)
print ("\n")
print ("Delete key = 'Tom' ")
# Delete element with key 'Tom'
contacts.__delitem__( "Tom")
print ("Contacts (After delete): ", contacts)
print ("Clear all element")
# Clear all element
contacts.clear()
print ("Contacts (After clear): ", contacts)
# Delete dictionary 'contact' from memory
del contacts
# An error occured while accessing a variable that does not exist in memory
print ("Contacts (After delete): ", contacts)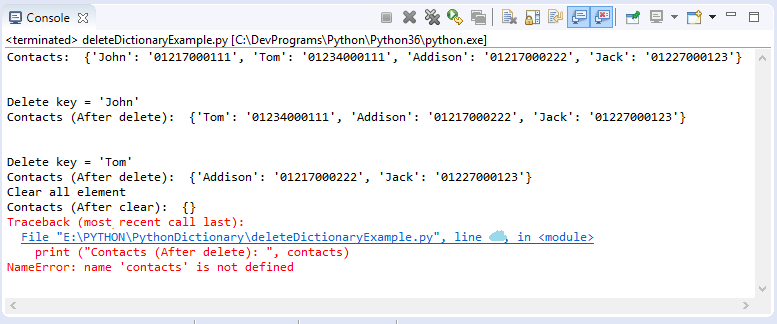
4. Functions for Dictionary
Function | Description |
len(dict) | Return elements count of dict. |
str(dict) | Produces a printable string representation of a dictionary |
type(variable) | Returns the type of the passed variable. If passed variable is dictionary, then it will return the object representing the 'dict' class. |
dir(clazzOrObject) | Returns the members of the passed class (or object). If passed class is dict class, then it will return the members of dict class. |
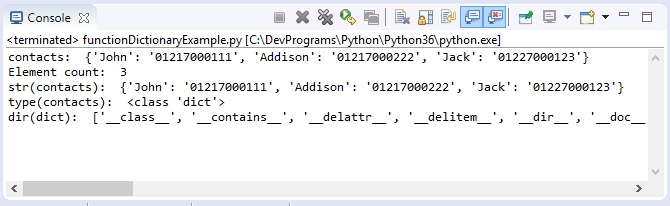
functionDictionaryExample.py
contacts = {"John": "01217000111" ,"Addison": "01217000222","Jack": "01227000123"}
print ("contacts: ", contacts)
print ("Element count: ", len(contacts) )
contactsAsString = str(contacts)
print ("str(contacts): ", contactsAsString )
# An object representing the 'dict' class.
aType = type(contacts)
print ("type(contacts): ", aType )
# dir(dict) function returns members of 'dict' class.
print ("dir(dict): ", dir(dict) )
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ['__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__',
# '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__',
# '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__',
# '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__',
# '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'clear',
# 'copy', 'fromkeys', 'get', 'items', 'keys', 'pop', 'popitem',
# 'setdefault', 'update', 'values']
# -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Python Programming Tutorials
- Lookup Python documentation
- Branching statements in Python
- Python Function Tutorial with Examples
- Class and Object in Python
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Python
- Python Dictionary Tutorial with Examples
- Python Lists Tutorial with Examples
- Python Tuples Tutorial with Examples
- Python Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- Connect to MySQL Database in Python using PyMySQL
- Python exception handling Tutorial with Examples
- Python String Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Python
- Install Python on Windows
- Install Python on Ubuntu
- Install PyDev for Eclipse
- Conventions and Grammar versions in Python
- Python Tutorial for Beginners
- Python Loops Tutorial with Examples
Show More