Python Tutorial for Beginners
1. Requirements
Make sure that your computer has already installed Python and a tool (IDE) for Python programming (E.g: PyDev). If not, you can see the guides below:

Windows:
Ubuntu

2. Create Project
From Eclipse, let's select:
- File/New/Other..
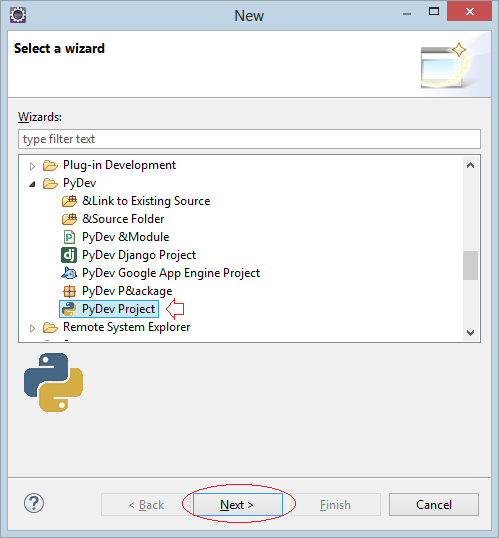
Use "Grammar Version" 3.x
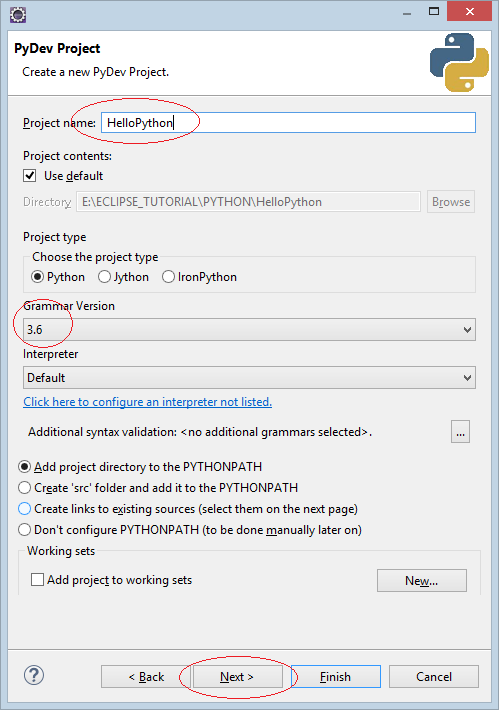
Note: Here I use "Grammar Version 3.6", the Grammar Versions of Python are a bit different, you can see more at:
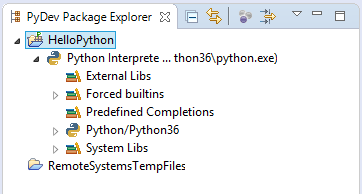
Project was created.
3. Create your first module
On Eclipse select:
- File/New/File
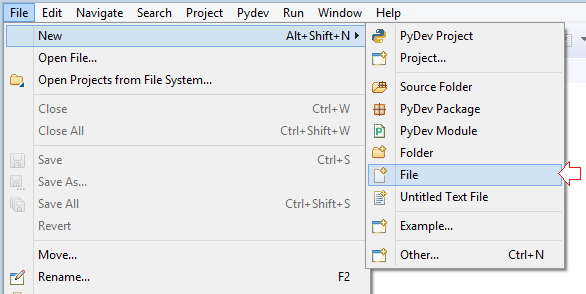
Enter name of file:
- main.py
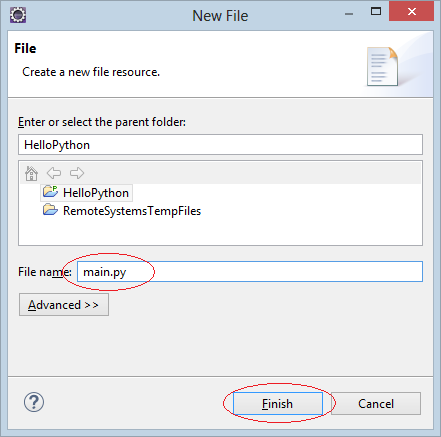
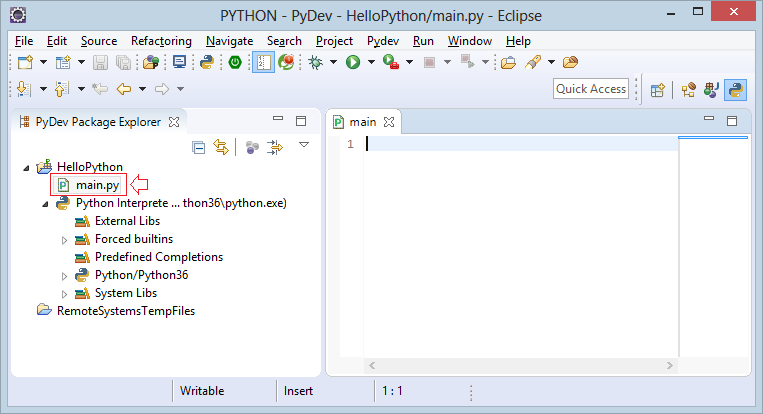
Add content to main.py:
main.py
print ("Hello Python!");
x = 5;
y = 10;
z = 20;
print (x + y + z);Run the main.py file by right-clicking it and select:
- Run As/Python Run
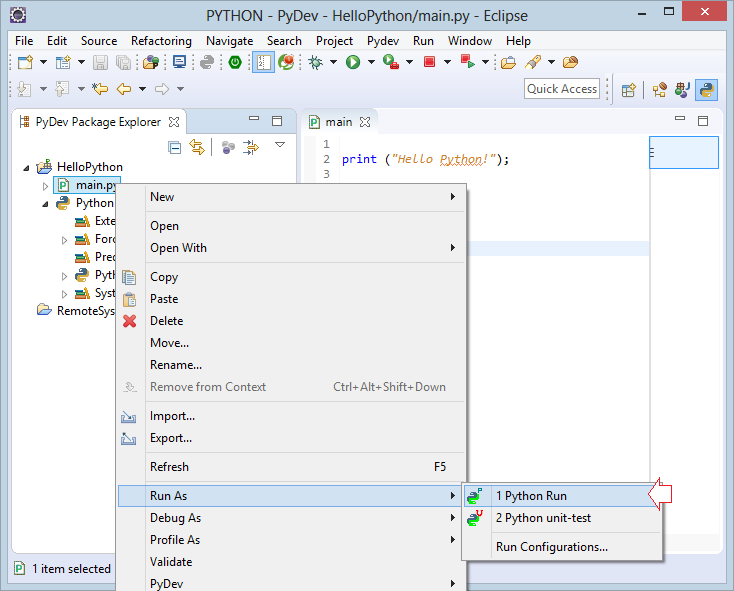
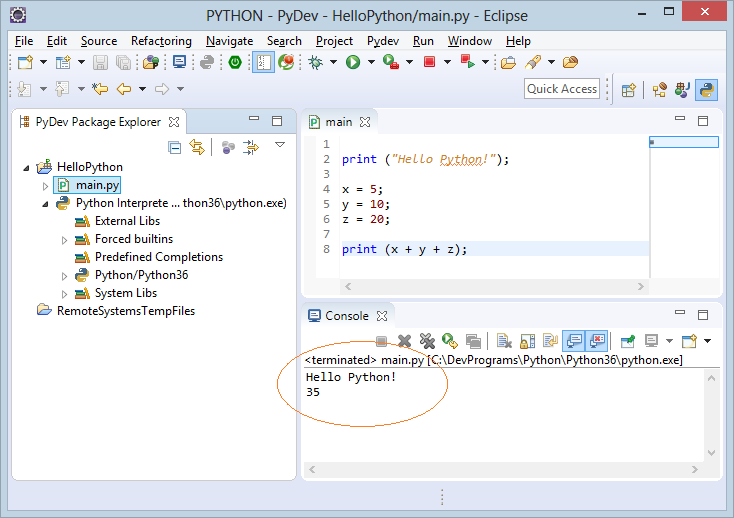
The result received when running main.py:
4. Python Module and Python Package
A Python module is simply a Python source file, which can expose classes, functions and global variables.
When imported from another Python source file, the file name is treated as a namespace.
When imported from another Python source file, the file name is treated as a namespace.
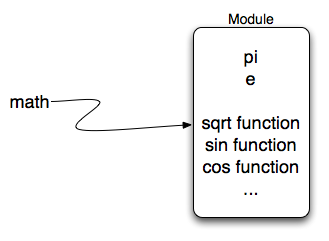
A Python package is simply a directory of Python module(s).
Create a "package":
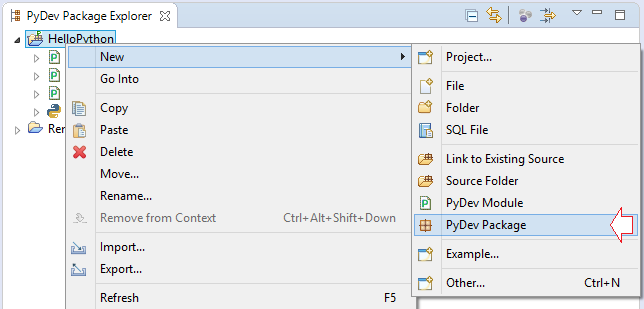
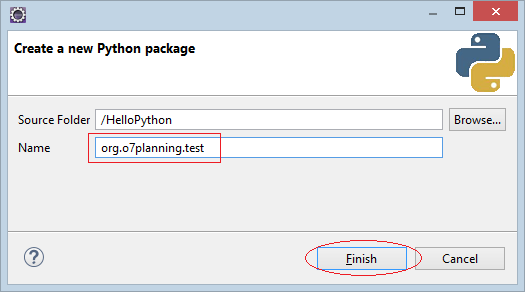
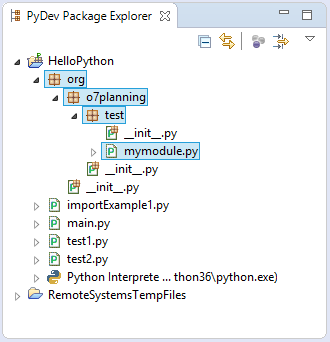
When you create a package named "org.o7planning.test", there are 3 folders created including "org", "o7planning", "test". Each of folders has a file already been created named "__init__.py". "__init__.py" folders have no content inside but they ask Python to treat the folders containing it as a "package".
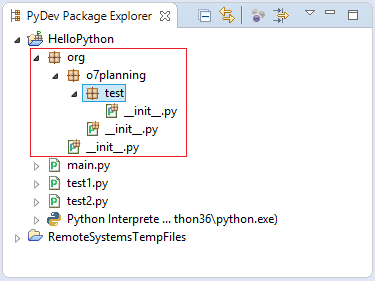
You can create a module inside package, for example, I create a module named as "mymodule.py" inside the "org.o7planning.test" package:
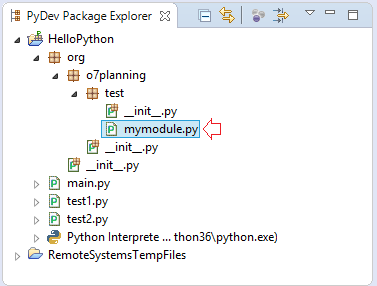
And in another module, you can enter "mymodule" to use it with the syntax:
# Import module "mymodule" in package "org.o7planning.test"
import org.o7planning.test.mymoduleOr enter a class "myclass" in the "mymodule" module:
# Import a class in module.
from org.o7planning.test.mymodule import myclass5. Examples
math is a module that is available in Python. It contains mathematical functions. To use it you need to import it. Here are some functions of this module:
Function | Description |
math.floor(x) | Return the floor of x as a float, the largest integer value less than or equal to x. |
math.fabs(x) | Return the absolute value of x. |
See more functions of math:
importExample1.py
# This will import math module
import math
# math.floor(x)
# Return the floor of x as a float,
# the largest integer value less than or equal to x.
print ("math.floor(100.12) : ", math.floor( 100.12) )
# Return the absolute value.
print ("math.fabs(-100.72) : ", math.fabs( -100.72) )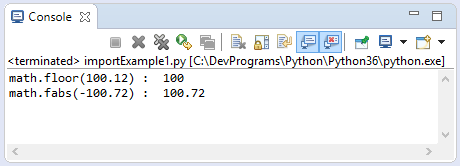
Create a module named "mymodule" and place it in the "org.o7planning.test" package. In the mymodule defines a function named sayHello.
NOTE: In this tutorial I do not introduce the details of the function. If you are beginner with Python, you do not need to worry about that.
mymodule.py
# Define a function, with one parameter
# and return a string.
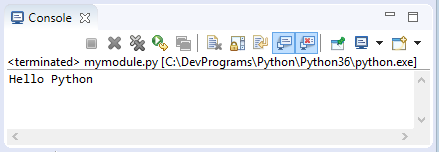
def sayHello(name) :
return "Hello "+ name
# Using sayHello function.
text = sayHello("Python")
print(text)Run mymodule:
In another module you want to use the sayHello function of "mymodule" you need to import this module, or just import the sayHello function of this module.
Import module:
importExample2.py
# Import module.
import org.o7planning.test.mymodule
# Call sayHello function of mymodule:
greeting = org.o7planning.test.mymodule.sayHello("Python")
print(greeting)Import function:
importExample3.py
# Import sayHello function.
from org.o7planning.test.mymodule import sayHello
# Call sayHello function of mymodule:
greeting = sayHello("Python")
print(greeting)Python Programming Tutorials
- Lookup Python documentation
- Branching statements in Python
- Python Function Tutorial with Examples
- Class and Object in Python
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Python
- Python Dictionary Tutorial with Examples
- Python Lists Tutorial with Examples
- Python Tuples Tutorial with Examples
- Python Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- Connect to MySQL Database in Python using PyMySQL
- Python exception handling Tutorial with Examples
- Python String Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Python
- Install Python on Windows
- Install Python on Ubuntu
- Install PyDev for Eclipse
- Conventions and Grammar versions in Python
- Python Tutorial for Beginners
- Python Loops Tutorial with Examples
Show More