Branching statements in Python
1. Comparison operators
The common comparison operators:
Operator | Meaning | Example |
> | greater than | 5 > 4 is true |
< | less than | 4 < 5 is true |
>= | greater than or equal | 4 >= 4 is true |
<= | less than or equal | 3 <= 4 is true |
== | equal to | 1 == 1 is true |
!= | not equal to | 1 != 2 is true |
and | and | a > 4 and a < 10 |
or | or | a == 1 or a == 4 |
2. if-else statement
if is a statement which checks a certain condition in Python. For example: If a> b, then do something ....
Syntax:
if condition_1 :
# Do something
elif condition_2 :
# Do something
elif condition_N:
# Do something
else :
# Do something
The program checks the condition from top to bottom until it encounters a condition that is true, and run this block and the program does not check the remaining conditions in the branching structure.
Example (if - else):
ifElseExample.py
option = 5
if option == 1:
print("Hello")
else :
print("Bye!")Output:
Bye!Example (if - elif - else):
ifElseExample2.py
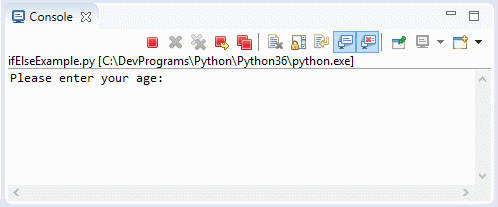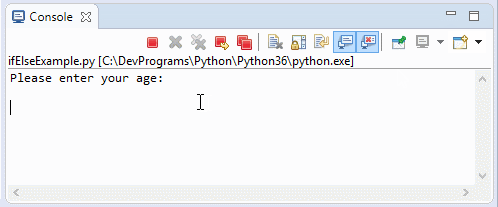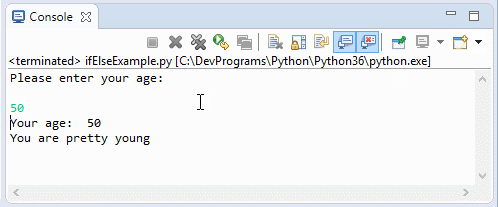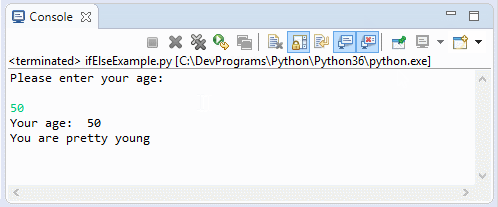
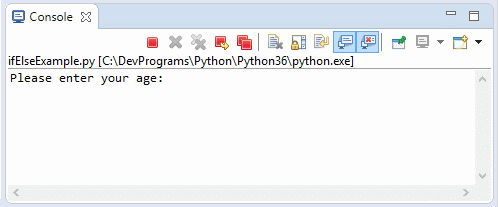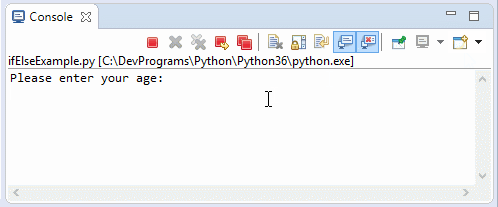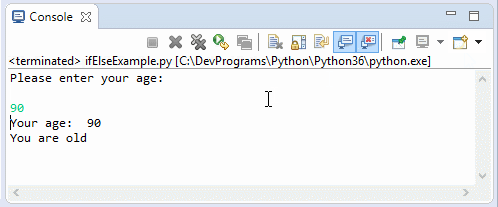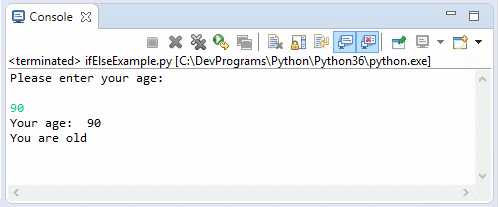
print("Please enter your age: \n")
# Declare a variable to store the user input from the keyboard.
inputStr = input()
# int(..) function convert string to integer
age = int(inputStr)
# Print out your age
print("Your age: ", age)
# If age < 80 then ..
if (age < 80) :
print("You are pretty young")
# Else if age between 80, 100 then
elif (age >= 80 and age <= 100) :
print("You are old")
# Else (Other case)
else :
print("You are verry old")Running the example:
Python Programming Tutorials
- Lookup Python documentation
- Branching statements in Python
- Python Function Tutorial with Examples
- Class and Object in Python
- Inheritance and polymorphism in Python
- Python Dictionary Tutorial with Examples
- Python Lists Tutorial with Examples
- Python Tuples Tutorial with Examples
- Python Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- Connect to MySQL Database in Python using PyMySQL
- Python exception handling Tutorial with Examples
- Python String Tutorial with Examples
- Introduction to Python
- Install Python on Windows
- Install Python on Ubuntu
- Install PyDev for Eclipse
- Conventions and Grammar versions in Python
- Python Tutorial for Beginners
- Python Loops Tutorial with Examples
Show More