Create a Multiple Languages web application with Spring MVC
1. The objective of the document
It is better to build a multilingual website because it helps your website to access to more users. The multilingual website is known as Internationalization (i18n) that is opposed to Localization (L10n).
Note: Internationalization is a word comprising 18 characters, the first character is i and the last one is n, so it is commonly abbreviated as i18n.
Spring provides extensive support for internationalization (i18n) through the use of Spring interceptors, Locale Resolvers and Resource Bundles for different locales.
In this post, I will guide you to build a simple multilingual website using Spring MVC.
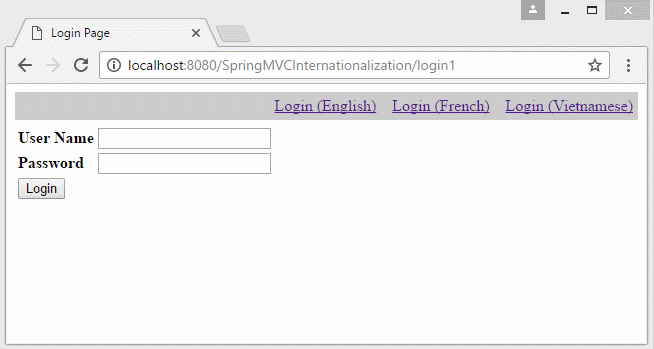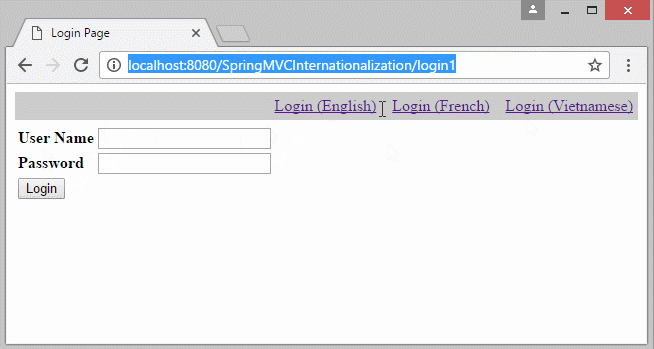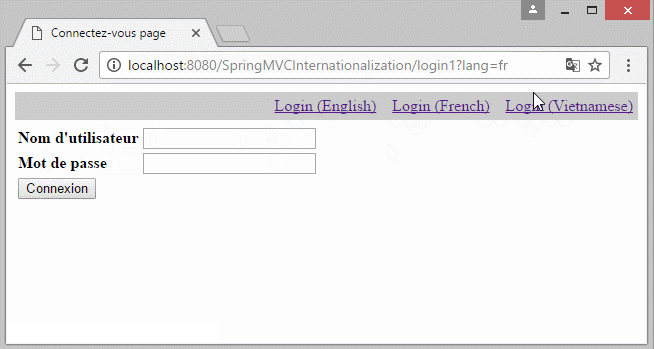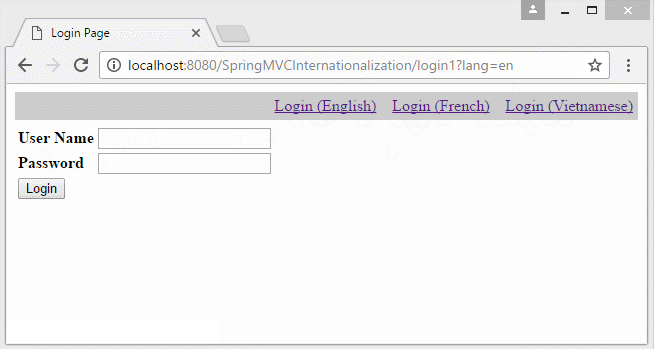
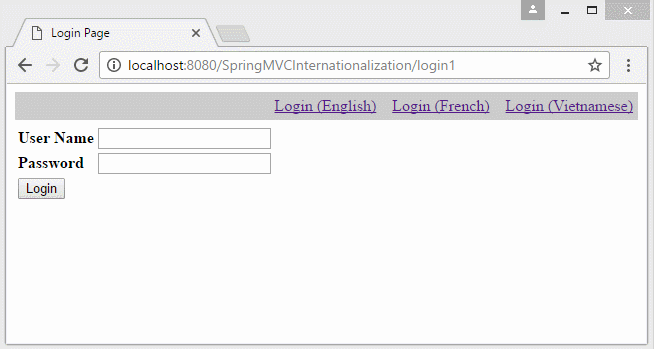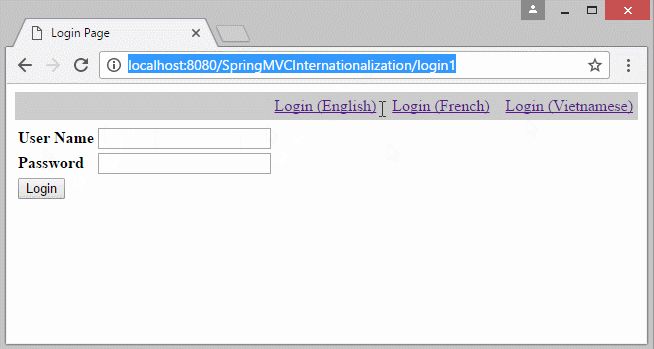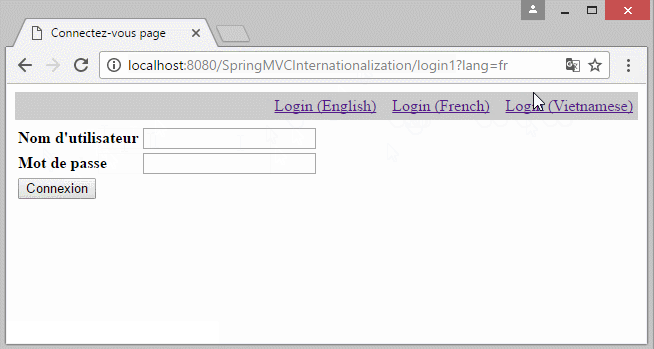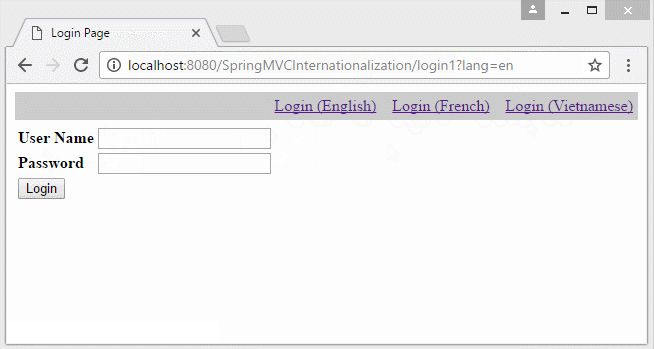
You can preview the example below:
In the example, the locale information lies on the parameter of the URL. Locale information will stored in Cookie, and the user does not reselect language in the next pages.
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCInternationalization/login1?lang=vi
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCInternationalization/login1?lang=fr
Another example of the Locale information on URL:
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCInternationalization/vi/login2
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCInternationalization/en/login2
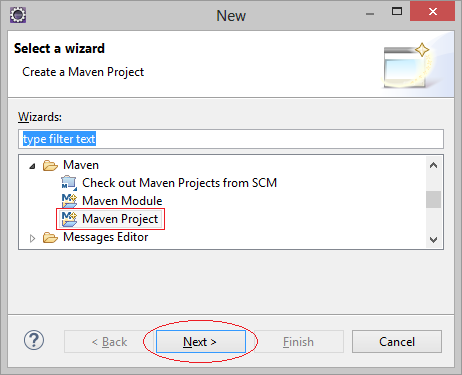
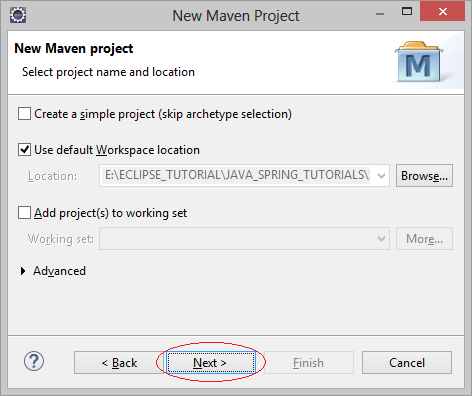
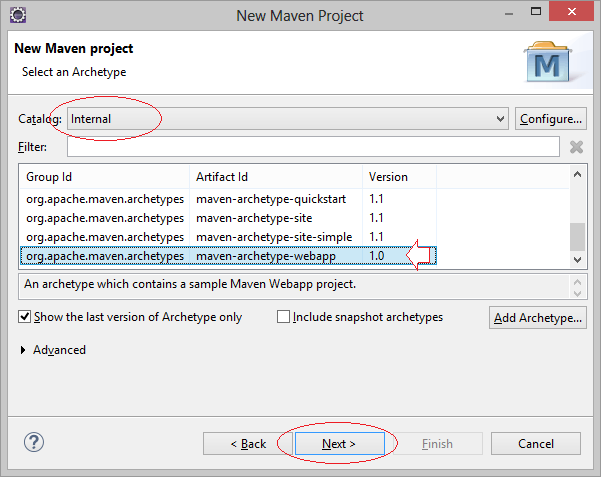
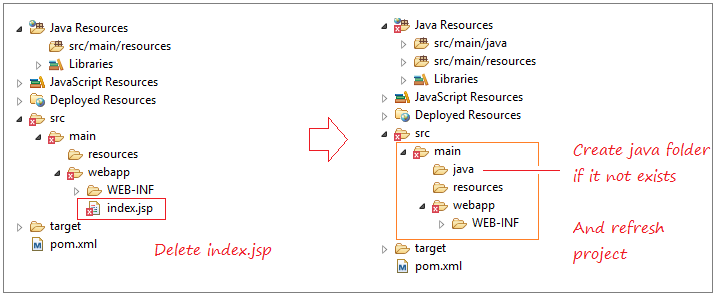
2. Create Maven Project
- File/New/Other..
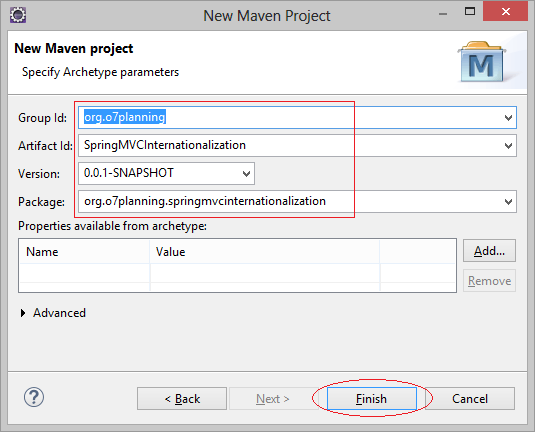
- Group Id: org.o7planning
- Artifact Id: SpringMVCInternationalization
- Package: org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization
Project is created.
Make sure that you use >= 6.
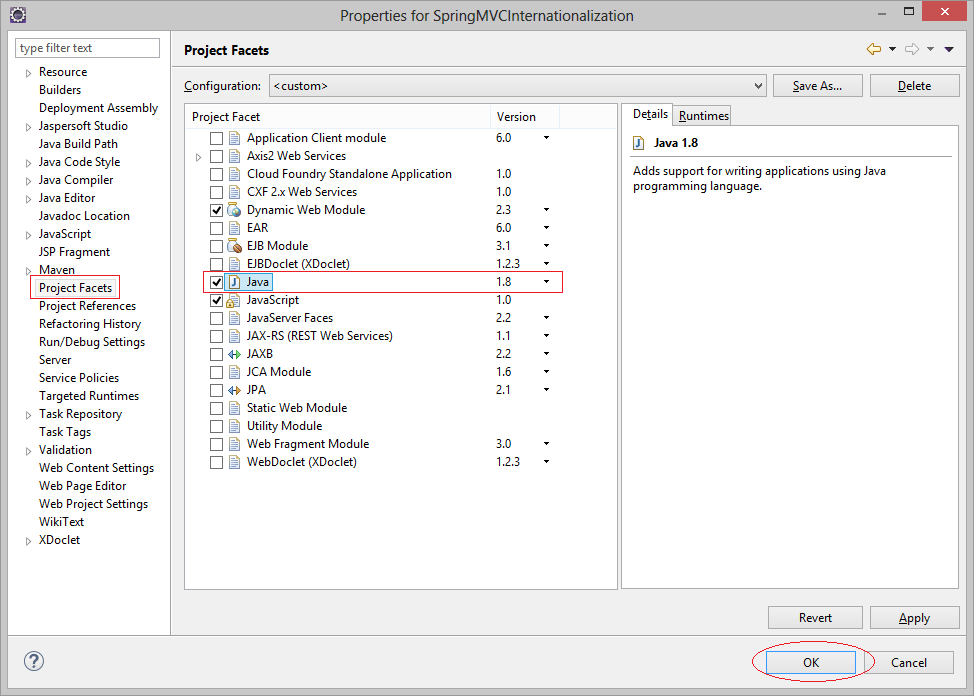
Project Properties:
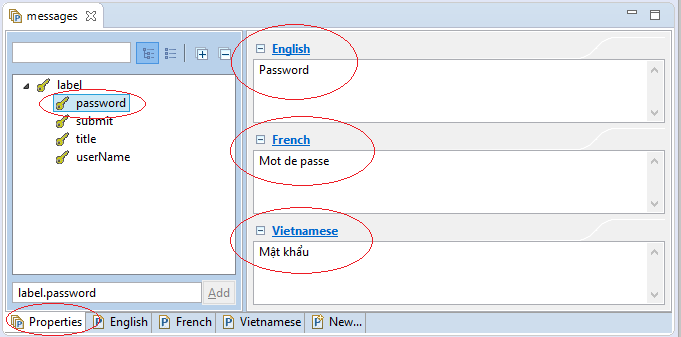
3. Message Resources
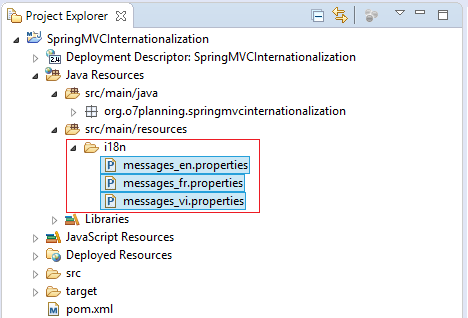
I here create 3 properties files for the languages including: English, French and Vietnamese. These files will loaded and managed by messageResource Bean.
i18n/messages_en.properties
#Generated by Eclipse Messages Editor (Eclipse Babel)
label.password = Password
label.submit = Login
label.title = Login Page
label.userName = User Namei18n/messages_fr.properties
#Generated by Eclipse Messages Editor (Eclipse Babel)
label.password = Mot de passe
label.submit = Connexion
label.title = Connectez-vous page
label.userName = Nom d'utilisateuri18n/messages_vi.properties
#Generated by Eclipse Messages Editor (Eclipse Babel)
label.password = M\u1EADt kh\u1EA9u
label.submit = \u0110\u0103ng nh\u1EADp
label.title = Trang \u0111\u0103ng nh\u1EADp
label.userName = T\u00EAn ng\u01B0\u1EDDi d\u00F9ngEclipse supports you in edit the file's information by using "Message Editor".
4. Config Spring MVC
If you are building a multilingual website, you need to use the UTF-8 encoding.
SpringWebAppInitializer.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.config;
import javax.servlet.FilterRegistration;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRegistration;
import org.springframework.web.WebApplicationInitializer;
import org.springframework.web.context.support.AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet;
public class SpringWebAppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext appContext = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
appContext.register(ApplicationContextConfig.class);
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = servletContext.addServlet("SpringDispatcher",
new DispatcherServlet(appContext));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping("/");
// UtF8 Charactor Filter.
FilterRegistration.Dynamic fr = servletContext.addFilter("encodingFilter", CharacterEncodingFilter.class);
fr.setInitParameter("encoding", "UTF-8");
fr.setInitParameter("forceEncoding", "true");
fr.addMappingForUrlPatterns(null, true, "/*");
}
}You need to declare 2 Spring BEANs including localeResolver and messageResource.
localeResolver - Specifies how to get Locale information that the user will use. CookieLocaleResolver will read the Locale information from Cookie in order to find that which languges the user used before.
messageResource - Will load the content of the properties files
localeResolver - Specifies how to get Locale information that the user will use. CookieLocaleResolver will read the Locale information from Cookie in order to find that which languges the user used before.
messageResource - Will load the content of the properties files
ApplicationContextConfig.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.config;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.CookieLocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.*")
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean(name = "viewResolver")
public InternalResourceViewResolver getViewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/pages/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
@Bean(name = "messageSource")
public MessageSource getMessageResource() {
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageResource= new ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource();
// Read i18n/messages_xxx.properties file.
// For example: i18n/messages_en.properties
messageResource.setBasename("classpath:i18n/messages");
messageResource.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
return messageResource;
}
@Bean(name = "localeResolver")
public LocaleResolver getLocaleResolver() {
CookieLocaleResolver resolver= new CookieLocaleResolver();
resolver.setCookieDomain("myAppLocaleCookie");
// 60 minutes
resolver.setCookieMaxAge(60*60);
return resolver;
}
}Before request is processed by Controller, it has to pass through Interceptors where you need to register LocaleChangeInterceptor, the Interceptor processes the Locale changes from the user.
WebMvcConfig.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
// Static Resource Config
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// Default..
}
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
LocaleChangeInterceptor localeInterceptor = new LocaleChangeInterceptor();
localeInterceptor.setParamName("lang");
registry.addInterceptor(localeInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/*");
}
}5. Controller & Views
MainController.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/login1")
public String login1(Model model) {
return "login1";
}
}
login1.jsp
<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring"%>
<%@ page session="false"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title><spring:message code="label.title" /></title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="text-align: right;padding:5px;margin:5px 0px;background:#ccc;">
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login1?lang=en">Login (English)</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login1?lang=fr">Login (French)</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/login1?lang=vi">Login (Vietnamese)</a>
</div>
<form method="post" action="">
<table>
<tr>
<td>
<strong>
<spring:message code="label.userName" />
</strong>
</td>
<td><input name="userName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<strong>
<spring:message code="label.password" />
</strong>
</td>
<td><input name="password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<spring:message code="label.submit" var="labelSubmit"></spring:message>
<input type="submit" value="${labelSubmit}" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
</html>7. Locale information on the URL
In the case that you want to build a multilingual website which the Locale information lies on URL. You need to change some configures:
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCInternationalization/vi/login2
- http://localhost:8080/SpringMVCInternationalization/en/login2
Create 2 classes - UrlLocaleInterceptor and UrlLocaleResolver.
UrlLocaleInterceptor.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.interceptor;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.RequestContextUtils;
public class UrlLocaleInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
LocaleResolver localeResolver = RequestContextUtils.getLocaleResolver(request);
if (localeResolver == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No LocaleResolver found: not in a DispatcherServlet request?");
}
// Get locale from LocaleResolver.
Locale locale = localeResolver.resolveLocale(request);
localeResolver.setLocale(request, response, locale);
return true;
}
}
UrlLocaleResolver.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.resolver;
import java.util.Locale;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
public class UrlLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
private static final String URL_LOCALE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME = "URL_LOCALE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME";
@Override
public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) {
// ==> /SpringMVCInternationalization/en/...
// ==> /SpringMVCInternationalization/fr/...
// ==> /SpringMVCInternationalization/WEB-INF/pages/...
String uri = request.getRequestURI();
System.out.println("URI=" + uri);
String prefixEn = request.getServletContext().getContextPath() + "/en/";
String prefixFr = request.getServletContext().getContextPath() + "/fr/";
String prefixVi = request.getServletContext().getContextPath() + "/vi/";
Locale locale = null;
// English
if (uri.startsWith(prefixEn)) {
locale = Locale.ENGLISH;
}
// French
else if (uri.startsWith(prefixFr)) {
locale = Locale.FRANCE;
}
// Vietnamese
else if (uri.startsWith(prefixVi)) {
locale = new Locale("vi", "VN");
}
if (locale != null) {
request.getSession().setAttribute(URL_LOCALE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME, locale);
}
if (locale == null) {
locale = (Locale) request.getSession().getAttribute(URL_LOCALE_ATTRIBUTE_NAME);
if (locale == null) {
locale = Locale.ENGLISH;
}
}
return locale;
}
@Override
public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
// Nothing
}
}Edit ApplicationContextConfig:
ApplicationContextConfig.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.config;
import org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.resolver.UrlLocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.context.MessageSource;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.*")
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean(name = "viewResolver")
public InternalResourceViewResolver getViewResolver() {
InternalResourceViewResolver viewResolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
viewResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/pages/");
viewResolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return viewResolver;
}
@Bean(name = "messageSource")
public MessageSource getMessageResource() {
ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource messageResource= new ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource();
// Read i18n/messages_xxx.properties file.
// For example: i18n/messages_en.properties
messageResource.setBasename("classpath:i18n/messages");
messageResource.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
return messageResource;
}
// To solver URL like:
// /SpringMVCInternationalization/en/login2
// /SpringMVCInternationalization/vi/login2
// /SpringMVCInternationalization/fr/login2
@Bean(name = "localeResolver")
public LocaleResolver getLocaleResolver() {
LocaleResolver resolver= new UrlLocaleResolver();
return resolver;
}
}Re-change the Interceptor configuration in WebMvcConfig:
WebMvcConfig.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.config;
import org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.interceptor.UrlLocaleInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ResourceHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// Default..
}
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
UrlLocaleInterceptor localeInterceptor = new UrlLocaleInterceptor();
registry.addInterceptor(localeInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/en/*", "/fr/*", "/vi/*");
}
}Controller:
MainController.java
package org.o7planning.springmvcinternationalization.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class MainController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/{locale:en|fr|vi}/login2")
public String login2(Model model) {
return "login2";
}
}
login2.jsp
<%@taglib uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" prefix="spring"%>
<%@ page session="false"%>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title><spring:message code="label.title" /></title>
</head>
<body>
<div style="text-align: right;padding:5px;margin:5px 0px;background:#ccc;">
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/en/login2">Login (English)</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/fr/login2">Login (French)</a>
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/vi/login2">Login (Vietnamese)</a>
</div>
<form method="post" action="">
<table>
<tr>
<td>
<strong>
<spring:message code="label.userName" />
</strong>
</td>
<td><input name="userName" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<strong>
<spring:message code="label.password" />
</strong>
</td>
<td><input name="password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">
<spring:message code="label.submit" var="labelSubmit"></spring:message>
<input type="submit" value="${labelSubmit}" />
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
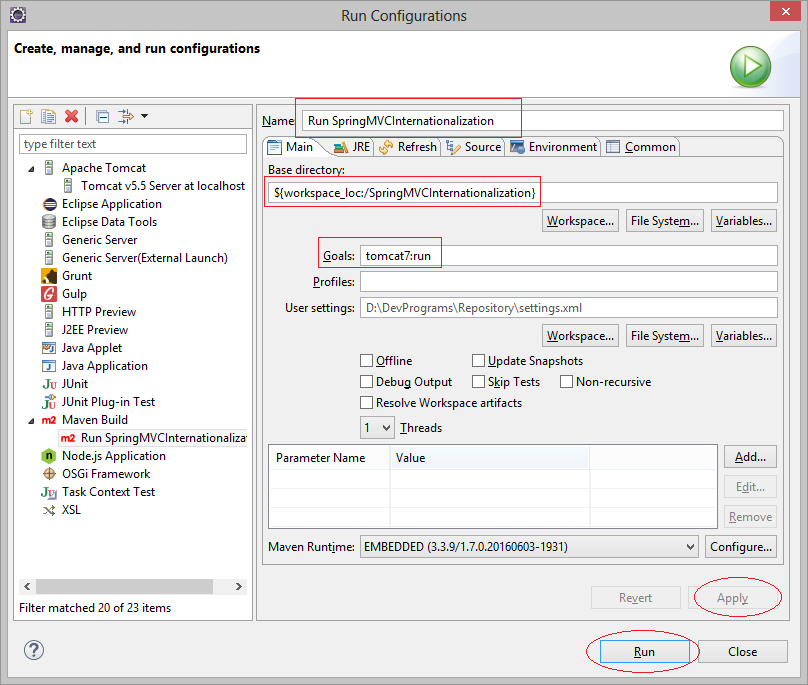
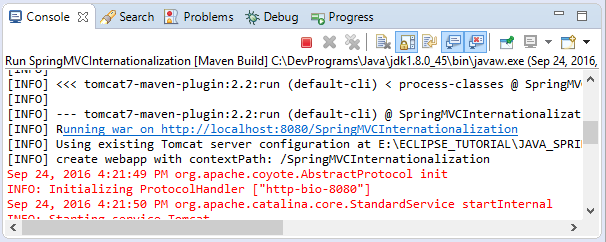
</html>Running the apps:
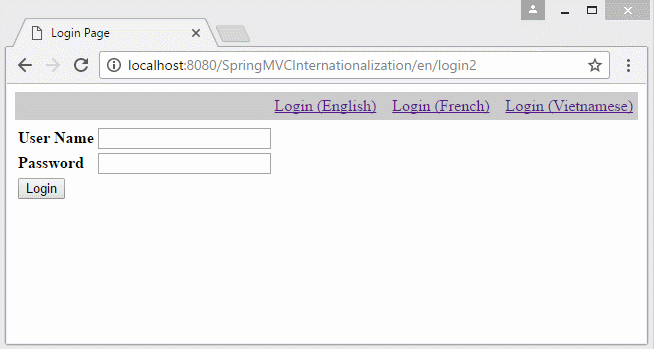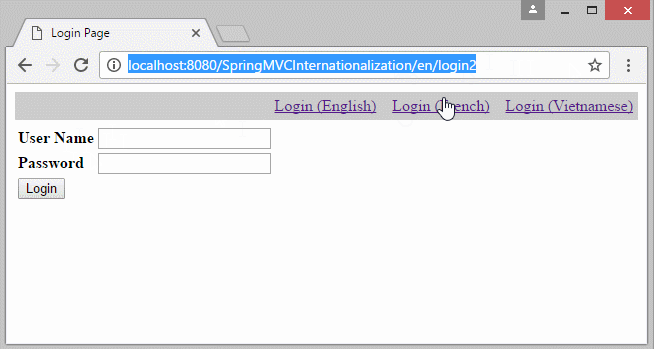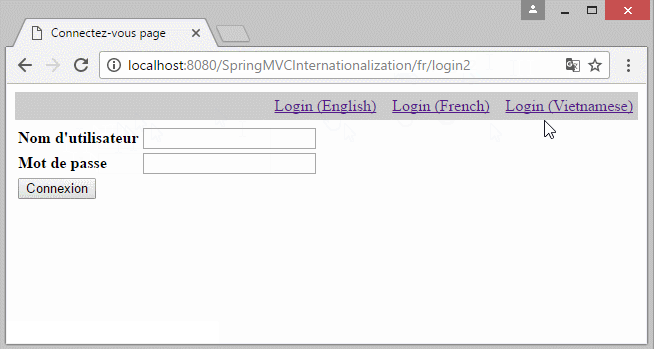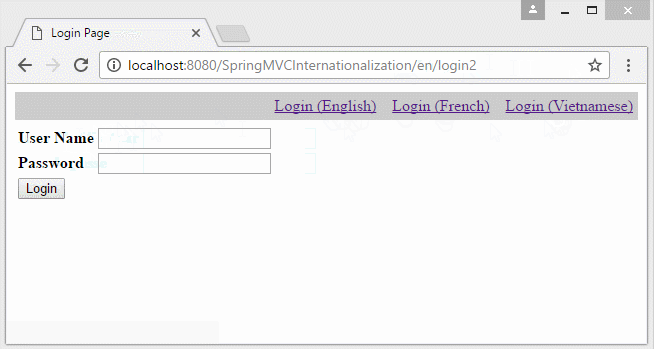
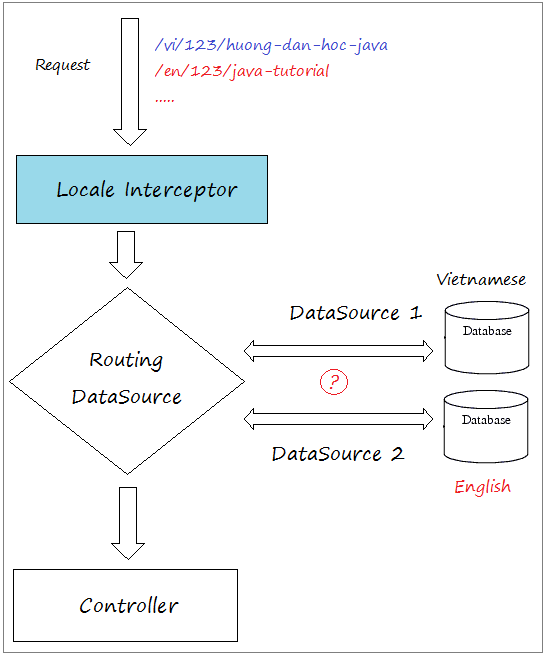
8. Multilingual websites with content stored in DB
The example of a multilingual website above is unable to satisfy you. You have the demand for a news website with multiple languages, and its content is stored in Database. A solution you can use multiple Datasources in which each datasoure is a database containing the content of a language.
You can see more at:
Spring MVC Tutorials
- Spring Tutorial for Beginners
- Install Spring Tool Suite for Eclipse
- Spring MVC Tutorial for Beginners - Hello Spring 4 MVC
- Configure Static Resources in Spring MVC
- Spring MVC Interceptors Tutorial with Examples
- Create a Multiple Languages web application with Spring MVC
- Spring MVC File Upload Tutorial with Examples
- Simple Login Java Web Application using Spring MVC, Spring Security and Spring JDBC
- Spring MVC Security with Hibernate Tutorial with Examples
- Spring MVC Security and Spring JDBC Tutorial (XML Config)
- Social Login in Spring MVC with Spring Social Security
- Spring MVC and Velocity Tutorial with Examples
- Spring MVC and FreeMarker Tutorial with Examples
- Use Template in Spring MVC with Apache Tiles
- Spring MVC and Spring JDBC Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Use Multiple DataSources in Spring MVC
- Spring MVC and Hibernate Transaction Tutorial with Examples
- Spring MVC Form Handling and Hibernate Tutorial with Examples
- Run background scheduled tasks in Spring
- Create a Java Shopping Cart Web Application using Spring MVC and Hibernate
- Simple CRUD example with Spring MVC RESTful Web Service
- Deploy Spring MVC on Oracle WebLogic Server
Show More