Java JapaneseDate Tutorial with Examples
1. JapaneseDate
JapaneseDate is a class representing dates in the Japanese imperial calendar system, which is used mainly in this country. Although Japan now uses the ISO calendar system, the imperial calendar system is still used in cultural events and festivals.
public final class JapaneseDate
extends ChronoLocalDateImpl<JapaneseDate>
implements ChronoLocalDate, Serializable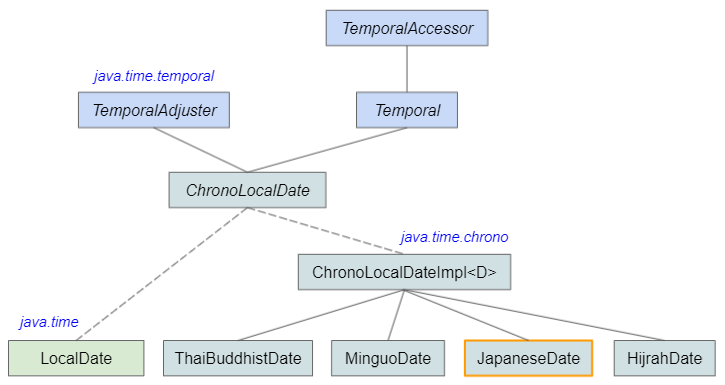
- LocalDate
- ThaiBuddhistDate
- MinguoDate
- HijrahDate
- TemporalAdjuster
- Temporal
- TemporalAccessor
- ChronoLocalDate
The Japanese imperial calendar system is similar to the ISO calendar system. The difference is that it uses the era to number the years.
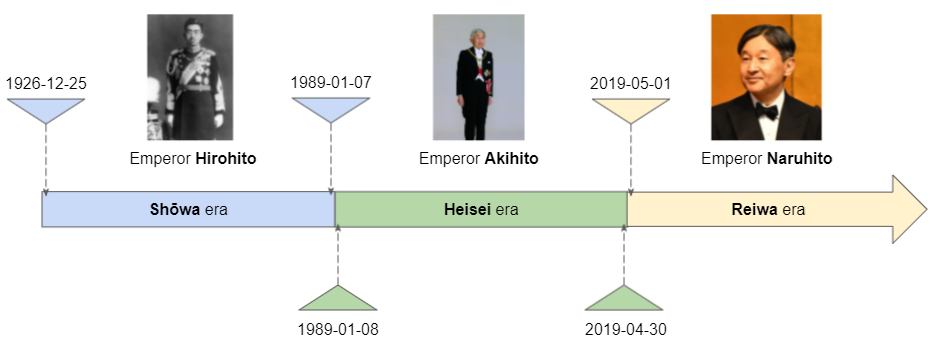
For easy understanding, see the illustration above. Emperor Akihito ruled Japan from January 8th, 1989 to April 30th, 2019. The period of his reign is known as the Heisei era. When a new era begins, the year will be numbered starting from 1, the day and month are the same as the day and month in the ISO calendar system.
JapaneseDate_Heisei_ex1.java
LocalDate isoDate_heisei_start = LocalDate.of(1989, 1, 8);
JapaneseDate jpDate_heisei_start = JapaneseDate.from(isoDate_heisei_start);
System.out.println("ISO Date Heisei era start: " + isoDate_heisei_start);
System.out.println("Japanese Date Heisei era start: " + jpDate_heisei_start);
System.out.println(" > YEAR: " + jpDate_heisei_start.get(ChronoField.YEAR));
System.out.println(" > YEAR_OF_ERA: " + jpDate_heisei_start.get(ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA));
LocalDate isoDate_heisei_end = LocalDate.of(2019, 4, 30);
JapaneseDate jpDate_heisei_end = JapaneseDate.from(isoDate_heisei_end);
System.out.println("\nISO Date Heisei era end: " + isoDate_heisei_end);
System.out.println("Japanese Date Heisei era end: " + jpDate_heisei_end);
System.out.println(" > YEAR: " + jpDate_heisei_end.get(ChronoField.YEAR));
System.out.println(" > YEAR_OF_ERA: " + jpDate_heisei_end.get(ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA));Output:
ISO Date Heisei era start: 1989-01-08
Japanese Date Heisei era start: Japanese Heisei 1-01-08
> YEAR: 1989
> YEAR_OF_ERA: 1
ISO Date Heisei era end: 2019-04-30
Japanese Date Heisei era end: Japanese Heisei 31-04-30
> YEAR: 2019
> YEAR_OF_ERA: 31April 30, 2019 Emperor Akihito officially abdicated due to health reasons, which is the last day in the Heisei era. One day later, i.e. May 1, 2020 his son Naruhito stepped on the throne and ushered in a new era called Reiwa.
We'll see what happens when we add a day to the last day of the Heisei era:
JapaneseDate_Reiwa_ex1.java
LocalDate isoDate_heisei_end = LocalDate.of(2019, 4, 30);
JapaneseDate jpDate_heisei_end = JapaneseDate.from(isoDate_heisei_end);
System.out.println("ISO Date Heisei era end: " + isoDate_heisei_end);
System.out.println("Japanese Date Heisei era end: " + jpDate_heisei_end);
// Plus 1 day to jpDate_heisei_end:
JapaneseDate jpDate_new = jpDate_heisei_end.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
System.out.println("\nAfter adding 1 day: " + jpDate_new);Output:
ISO Date Heisei era end: 2019-04-30
Japanese Date Heisei era end: Japanese Heisei 31-04-30
After adding 1 day: Japanese Reiwa 1-05-01In Java, the Japanese imperial calendar system starts with the date "Japanese Meiji 6-01-01", which is equivalent to January 1, 1873 in the ISO calendar system. Earlier dates are not supported.
JapaneseDate_supported_range_ex1.java
JapaneseDate now = JapaneseDate.now();
// Range of ISO years.
ValueRange yearRange = now.range(ChronoField.YEAR);
System.out.println(yearRange); // 1873 - 999999999
JapaneseDate jpDate = JapaneseDate.from(LocalDate.of(1873, 1, 1));
System.out.println(jpDate); // Japanese Meiji 6-01-01The article about JapaneseEra gives you a list of epochs supported by Java in the Japanese imperial calendar system:
- Era
- JapaneseEra
2. JapaneseDate Examples
The following JapaneseDateUtils class provides utility methods to help you find the first and the last date in a specified era:
JapaneseDateUtils.java
package org.o7planning.japanesedate.util;
import java.time.chrono.JapaneseDate;
import java.time.chrono.JapaneseEra;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.temporal.ValueRange;
public class JapaneseDateUtils {
public static final JapaneseDate FIRST_SUPPORTED_JP_DATE = JapaneseDate.of(JapaneseEra.MEIJI, 6, 1, 1);
public static JapaneseDate getFirstDateInSameEra(final JapaneseDate japaneseDate) {
final JapaneseEra thisEra = japaneseDate.getEra();
// Valid Japanese Year range with the same given day & month & era.
ValueRange validYearRange = japaneseDate.range(ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA); // Ex: 1-64
// Valid Min Japanese year with the same given day & month
int validMinYear = (int) validYearRange.getMinimum(); // 1
if (thisEra.equals(JapaneseEra.MEIJI)) {
if (validMinYear < 6) {
validMinYear = 6;
}
}
final JapaneseDate jpDate2 = JapaneseDate.of(thisEra, validMinYear, 12, 31);
ValueRange dayOfY2 = jpDate2.range(ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR);
// First date in the same year with jpDate2.
final JapaneseDate jpDate3 = jpDate2.minus(dayOfY2.getMaximum() - dayOfY2.getMinimum(), ChronoUnit.DAYS);
if (!jpDate3.isAfter(FIRST_SUPPORTED_JP_DATE)) {
return jpDate3;
}
final JapaneseDate jpDate4 = jpDate3.minus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
final JapaneseEra era4 = jpDate4.getEra();
if (!thisEra.equals(era4)) {
return jpDate3;
}
ValueRange dayOfY4 = jpDate4.range(ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR);
// First date in the same Era with given japaneseDate.
final JapaneseDate jpDate5 = jpDate4.minus(dayOfY4.getMaximum() - dayOfY4.getMinimum(), ChronoUnit.DAYS);
return jpDate5;
}
public static JapaneseDate getLastDateInSameEra(final JapaneseDate japaneseDate) {
final JapaneseEra thisEra = japaneseDate.getEra();
// Valid Japanese Year range with the same given day & month & era.
ValueRange validYearRange = japaneseDate.range(ChronoField.YEAR_OF_ERA); // Ex: 1-64
// Valid Max Japanese year with the same given day & month
int validMaxYear = (int) validYearRange.getMaximum(); // Ex: 64
final JapaneseDate jpDate2 = JapaneseDate.of(thisEra, validMaxYear, 1, 1);
ValueRange dayOfY2 = jpDate2.range(ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR);
// Last date in the same year with jpDate2.
final JapaneseDate jpDate3 = jpDate2.plus(dayOfY2.getMaximum() - dayOfY2.getMinimum(), ChronoUnit.DAYS);
final JapaneseDate jpDate4 = jpDate3.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
final JapaneseEra era4 = jpDate4.getEra();
if (!thisEra.equals(era4)) {
return jpDate3;
}
ValueRange dayOfY4 = jpDate4.range(ChronoField.DAY_OF_YEAR);
// Last date in the same Era with given japaneseDate.
final JapaneseDate jpDate5 = jpDate4.plus(dayOfY4.getMaximum() - dayOfY4.getMinimum(), ChronoUnit.DAYS);
return jpDate5;
}
public static JapaneseDate getFirstDateInEra(final JapaneseEra era) {
JapaneseDate jpDate = FIRST_SUPPORTED_JP_DATE;
while (true) {
JapaneseEra jpEra = jpDate.getEra();
if (era.equals(jpEra)) {
return getFirstDateInSameEra(jpDate);
}
jpDate = getLastDateInSameEra(jpDate);
jpDate = jpDate.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS); // First Date in next era.
}
}
public static JapaneseDate getLastDateInEra(final JapaneseEra era) {
JapaneseDate jpDate = FIRST_SUPPORTED_JP_DATE;
while (true) {
JapaneseEra jpEra = jpDate.getEra();
if (era.equals(jpEra)) {
return getLastDateInSameEra(jpDate);
}
jpDate = getLastDateInSameEra(jpDate);
jpDate = jpDate.plus(1, ChronoUnit.DAYS); // First Date in next era.
}
}
}Example: Find the first and the last date in the same era with a given date.
JapaneseDate_firstlast_date_ex1.java
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.of(1970, 5, 20);
JapaneseDate japanseDate = JapaneseDate.from(localDate);
System.out.printf("JP Date: %s ~ ISO Date: %s%n%n", japanseDate, LocalDate.from(localDate));
JapaneseDate firstJPDate = JapaneseDateUtils.getFirstDateInSameEra(japanseDate);
JapaneseDate lastJPDate = JapaneseDateUtils.getLastDateInSameEra(japanseDate);
System.out.printf("The first JP Date: %s ~ ISO Date: %s%n", firstJPDate, LocalDate.from(firstJPDate));
System.out.printf("The last JP Date: %s ~ ISO Date: %s%n", lastJPDate, LocalDate.from(lastJPDate));Output:
JP Date: Japanese Showa 45-05-20 ~ ISO Date: 1970-05-20
The first JP Date: Japanese Showa 1-12-25 ~ ISO Date: 1926-12-25
The last JP Date: Japanese Showa 64-01-07 ~ ISO Date: 1989-01-073. JapaneseDate methods
public static JapaneseDate now()
public static JapaneseDate now(ZoneId zone)
public static JapaneseDate now(Clock clock)
public static JapaneseDate of(JapaneseEra era, int yearOfEra, int month, int dayOfMonth)
public static JapaneseDate of(int prolepticYear, int month, int dayOfMonth)
public static JapaneseDate from(TemporalAccessor temporal)// Inherited from ChronoLocalDate interface
public JapaneseChronology getChronology()
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDate interface
public JapaneseEra getEra()
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDate interface
public int lengthOfMonth()
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDate interface
public int lengthOfYear()
// Inherited from TemporalAccessor interface
public boolean isSupported(TemporalField field)
// Inherited from TemporalAccessor interface
public ValueRange range(TemporalField field)
// Inherited from TemporalAccessor interface
public long getLong(TemporalField field)
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public JapaneseDate with(TemporalField field, long newValue)
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public JapaneseDate with(TemporalAdjuster adjuster)
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public JapaneseDate plus(TemporalAmount amount)
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public JapaneseDate minus(TemporalAmount amount)
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public JapaneseDate plus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public JapaneseDate minus(long amountToAdd, TemporalUnit unit)
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDate interface
public final ChronoLocalDateTime<JapaneseDate> atTime(LocalTime localTime)
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDate interface
public ChronoPeriod until(ChronoLocalDate endDate)
// Inherited from ChronoLocalDate interface
public long toEpochDay()
// Inherited from Temporal interface
public long until(Temporal endExclusive, TemporalUnit unit)Java Date Time Tutorials
- Java ZoneId Tutorial with Examples
- Java Temporal Tutorial with Examples
- Java Period Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAdjusters Tutorial with Examples
- Java MinguoDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAccessor Tutorial with Examples
- Java JapaneseEra Tutorial with Examples
- Java HijrahDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- What is Daylight Saving Time (DST)?
- Java LocalDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java LocalTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java LocalDateTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java ZonedDateTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java JapaneseDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Duration Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalQuery Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAdjuster Tutorial with Examples
- Java ChronoUnit Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalQueries Tutorial with Examples
Show More