Java TemporalAdjuster Tutorial with Examples
1. TemporalAdjuster
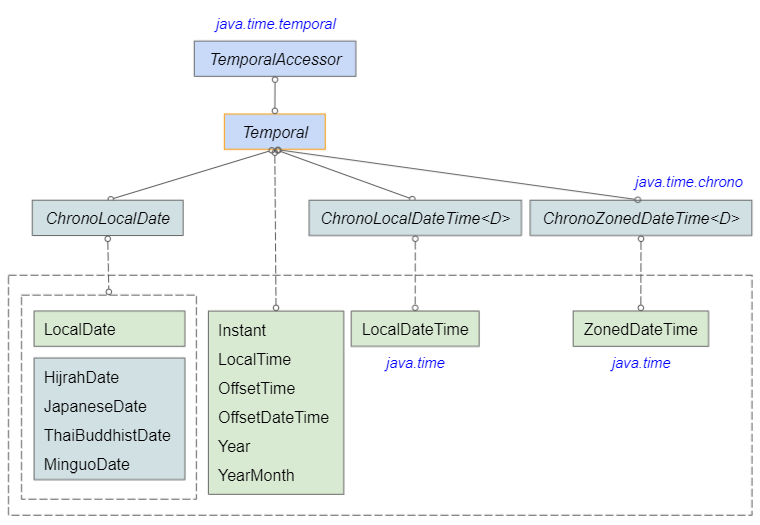
The TemporalAdjuster interface is a tool for adjusting a Temporal object to create a copy. Basically, TemporalAdjuster exists to externalize a process of adjusting Temporal objects rather than adjusting them directly.
@FunctionalInterface
public interface TemporalAdjuster {
Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal);
}Example: We create TruncateTimeAdjuster class to truncate the time (hours, minutes, seconds, nanoseconds) of a Temporal object.
Temporal | Example | Apply TruncateTimeAdjuster |
LocalDateTime | 2020-11-25 13:30:45 | 2020-11-25 00:00:00 |
ZonedDateTime | 2020-11-25 13:30:45+06:00[Asia/Bishkek] | 2020-11-25 00:00:00+06:00[Asia/Bishkek] |
LocalTime | 13:30:45 | 00:00:00 |
TruncateTimeAdjuster.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class TruncateTimeAdjuster implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
Temporal adjustedTemporal = temporal;
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.HOUR_OF_DAY, 0);
}
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.MINUTE_OF_HOUR, 0);
}
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.SECOND_OF_MINUTE, 0);
}
if (temporal.isSupported(ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND)) {
adjustedTemporal = adjustedTemporal.with(ChronoField.NANO_OF_SECOND, 0);
}
return adjustedTemporal;
}
}Using TruncateTemporalAdjuster:
TruncateTimeAdjuster_ex1.java
TruncateTimeAdjuster truncateTimeAdjuster = new TruncateTimeAdjuster();
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime adjustedLocalDateTime = (LocalDateTime) truncateTimeAdjuster.adjustInto(localDateTime);
System.out.printf("localDateTime: %s%n", localDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedLocalDateTime: %s%n%n", adjustedLocalDateTime);
// Create a Temporal object from ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime adjustedZonedDateTime = (ZonedDateTime) truncateTimeAdjuster.adjustInto(zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("zonedDateTime: %s%n", zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedZonedDateTime: %s%n%n", adjustedZonedDateTime);
// Create a Temporal object from OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime = OffsetDateTime.now();
OffsetDateTime adjustedOffsetDateTime = (OffsetDateTime) truncateTimeAdjuster.adjustInto(offsetDateTime);
System.out.printf("offsetDateTime: %s%n", offsetDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedOffsetDateTime: %s%n", adjustedOffsetDateTime);Output:
localDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:30:09.309188
adjustedLocalDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:00
zonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:30:09.322306+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
adjustedZonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:00+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
offsetDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:30:09.323143+06:00
adjustedOffsetDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:00+06:00There are many classes in the Java Date Time API that implement the TemporalAdjuster interface, which means they are capable of adjusting other Temporal objects:
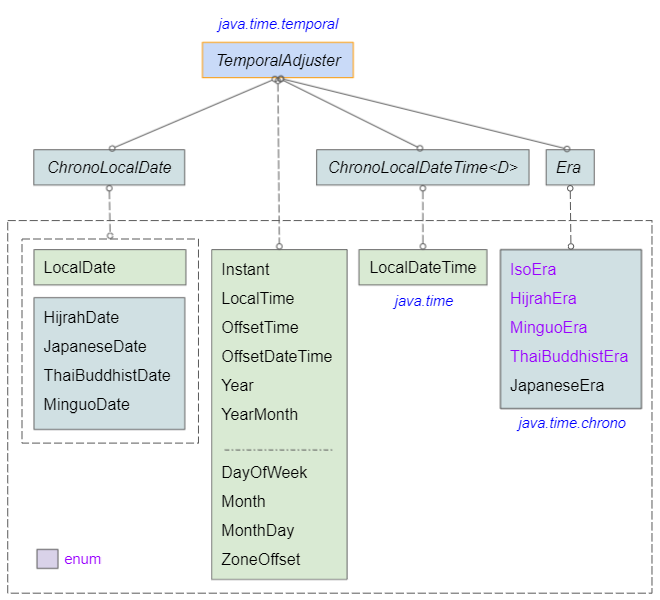
- IsoEra
- MinguoEra
- LocalDateTime
- LocalTime
- ZoneOffset
- HijrahEra
- MonthDay
- Month
- DayOfWeek
- LocalDate
- JapaneseEra
- YearMonth
- OffsetTime
- Instant
- Era
- Year
- OffsetDateTime
- ThaiBuddhistEra
- ChronoLocalDate
- ThaiBuddhistDate
- MinguoDate
- JapaneseDate
- HijrahDate
- ChronoLocalDateTime
- TemporalAdjusters
There are two ways to adjust a Temporal object, in which the second approach is recommended.
// these two lines are equivalent, but the second approach is recommended
adjustedTemporal = thisAdjuster.adjustInto(temporal); // (1)
adjustedTemporal = temporal.with(thisAdjuster); // (2)2. Basic Examples
Example: Adjust all given Temporal objects to May 2000, other fields remain unchanged.
TemporalAdjuster_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.YearMonth;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class TemporalAdjuster_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = YearMonth.of(2020, 5); // May 2020.
// Create a Temporal object from ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime adjustedZonedDateTime = (ZonedDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("zonedDateTime: %s%n", zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedZonedDateTime: %s%n%n", adjustedZonedDateTime);
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate adjustedLocalDate = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate);
System.out.printf("localDate: %s%n", localDate);
System.out.printf("adjustedLocalDate: %s%n", adjustedLocalDate);
}
}Output:
zonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T00:51:07.837210+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
adjustedZonedDateTime: 2020-05-05T00:51:07.837210+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
localDate: 2021-07-05
adjustedLocalDate: 2020-05-05Example: Adjust the zone-offset for the given OffsetDateTime objects to +15;
TemporalAdjuster_ex2.java
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = ZoneOffset.ofHours(15);
// Create a Temporal object from OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime1 = OffsetDateTime.now();
OffsetDateTime adjustedOffsetDateTime1 = (OffsetDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(offsetDateTime1);
System.out.printf("offsetDateTime1: %s%n", offsetDateTime1);
System.out.printf("adjustedOffsetDateTime1: %s%n%n", adjustedOffsetDateTime1);
// Create a Temporal object from OffsetDateTime
OffsetDateTime offsetDateTime2 = OffsetDateTime.parse("2000-01-01T01:00+01:00");
OffsetDateTime adjustedOffsetDateTime2 = (OffsetDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(offsetDateTime2);
System.out.printf("offsetDateTime2: %s%n", offsetDateTime2);
System.out.printf("adjustedOffsetDateTime2: %s%n%n", adjustedOffsetDateTime2);Output:
offsetDateTime1: 2021-07-05T01:15:48.372665+06:00
adjustedOffsetDateTime1: 2021-07-05T01:15:48.372665+15:00
offsetDateTime2: 2000-01-01T01:00+01:00
adjustedOffsetDateTime2: 2000-01-01T01:00+15:00- OffsetDateTime
- ZonedDateTime
- LocalDate
3. Custom TemporalAdjuster Examples
Assume that the working days of the week are from Monday to Friday. We write NextWorkingDayAdjuster class to find the next working day after the given date.
NextWorkingDayAdjuster.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.DayOfWeek;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextWorkingDayAdjuster implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
int field = temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_WEEK);
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = DayOfWeek.of(field);
int daysToAdd = 1;
if (DayOfWeek.FRIDAY.equals(dayOfWeek)) {
daysToAdd = 3;
} else if (DayOfWeek.SATURDAY.equals(dayOfWeek)) {
daysToAdd = 2;
}
return temporal.plus(daysToAdd, ChronoUnit.DAYS);
}
}For example, using the NextWorkingDayAdjuster class:
NextWorkingDayAdjuster_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextWorkingDayAdjuster_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = new NextWorkingDayAdjuster();
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.now();
LocalDate nextWorkingDay = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate);
System.out.printf("localDate: %s%n", localDate);
System.out.printf("nextWorkingDay: %s%n", nextWorkingDay);
System.out.println(" ----- ");
// Create a Temporal object from ZonedDateTime
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = ZonedDateTime.now();
ZonedDateTime adjustedZonedDateTime = (ZonedDateTime) adjuster.adjustInto(zonedDateTime);
nextWorkingDay = adjustedZonedDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.printf("zonedDateTime: %s%n", zonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("adjustedZonedDateTime: %s%n", adjustedZonedDateTime);
System.out.printf("nextWorkingDay: %s%n", nextWorkingDay);
}
}Output:
localDate: 2021-07-05
nextWorkingDay: 2021-07-06
-----
zonedDateTime: 2021-07-05T01:34:09.112648+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
adjustedZonedDateTime: 2021-07-06T01:34:09.112648+06:00[Asia/Bishkek]
nextWorkingDay: 2021-07-06Example: Write the NextChristmasAdjuster class to find the next Christmas date:
NextChristmasAdjuster.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoField;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextChristmasAdjuster implements TemporalAdjuster {
@Override
public Temporal adjustInto(Temporal temporal) {
int month = temporal.get(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR);
int day = temporal.get(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH);
if(month == 12 && day > 25) {
temporal = temporal.plus(Period.ofYears(1));
}
return temporal.with(ChronoField.MONTH_OF_YEAR, 12).with(ChronoField.DAY_OF_MONTH, 25);
}
}Using the NextChristmasAdjuster class:
NextChristmasAdjuster_ex1.java
package org.o7planning.temporaladjuster.ex;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjuster;
public class NextChristmasAdjuster_ex1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemporalAdjuster adjuster = new NextChristmasAdjuster();
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2021, 7, 5);
LocalDate nextChristmasDay = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate1);
System.out.printf("localDate1: %s%n", localDate1);
System.out.printf("nextChristmasDay: %s%n", nextChristmasDay);
System.out.println(" ----- ");
// Create a Temporal object from LocalDate
LocalDate localDate2 = LocalDate.of(2021, 12, 26);
nextChristmasDay = (LocalDate) adjuster.adjustInto(localDate2);
System.out.printf("localDate2: %s%n", localDate2);
System.out.printf("nextChristmasDay: %s%n", nextChristmasDay);
}
}Output:
localDate1: 2021-07-05
nextChristmasDay: 2021-12-25
-----
localDate2: 2021-12-26
nextChristmasDay: 2022-12-25- ChronoField
- Temporal
- ZonedDateTime
- DayOfWeek
4. TemporalAdjusters Examples
The TemporalAdjusters class provides static methods to obtain standard TemporalAdjuster(s). These include:
- Finding the first or last day of the month.
- Finding the first day of next month.
- Finding the first or last day of the year.
- Finding the first day of next year.
- Finding the first or last "day-of-week" within a month, such as "first Wednesday in June".
- Finding the next or previous "day-of-week", such as "next Thursday".
Java Date Time Tutorials
- Java ZoneId Tutorial with Examples
- Java Temporal Tutorial with Examples
- Java Period Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAdjusters Tutorial with Examples
- Java MinguoDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAccessor Tutorial with Examples
- Java JapaneseEra Tutorial with Examples
- Java HijrahDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Date Time Tutorial with Examples
- What is Daylight Saving Time (DST)?
- Java LocalDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java LocalTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java LocalDateTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java ZonedDateTime Tutorial with Examples
- Java JapaneseDate Tutorial with Examples
- Java Duration Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalQuery Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalAdjuster Tutorial with Examples
- Java ChronoUnit Tutorial with Examples
- Java TemporalQueries Tutorial with Examples
Show More