Understanding Spring Cloud Config Server with Example
1. The objective of the lesson
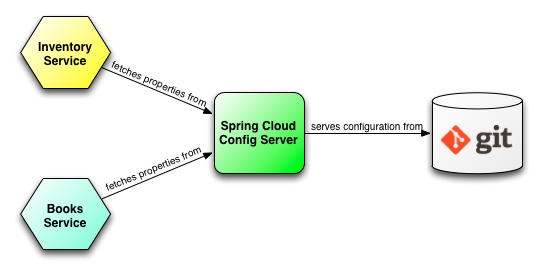
OK, this is the first step for you to build a distributed application using Spring Cloud. In this lesson, I am going to guide you for creating a service to manage configurations for other services.
The contents to be discussed in this lesson include:
- What is a Config Server? Why need a Config Server in distributed applications.
- Explain Centralized Configuration Management, and Versioned Configuration Management.
- Set up a repository to store configuration information.
- Build and Run Spring Cloud Config Server.
2. Config Server - Why?
OK, now we will discuss why you need to have a service that manages configurations for other services in a distributed application.
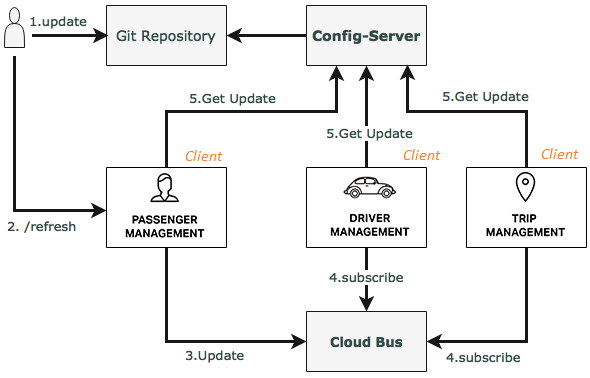
Below is the illustration of a distributed application - "Taxi Management", including three sub-applications, each of which is deployed on a server.
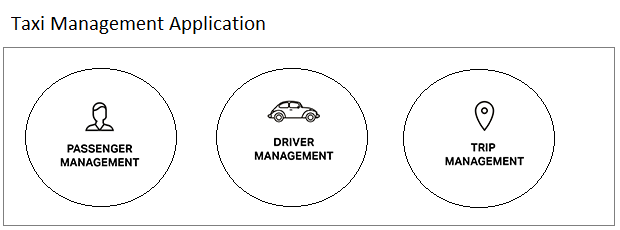
Each service (application) is a project developed by a team of developers. In a project, apart from code, it contains configurations, for example, information connected to database, information on location of data sources, etc. It will be a bad idea if You make hard code of this information in the project code. Therefore, this information is normally put in separate files, which are referred to as configuration files.
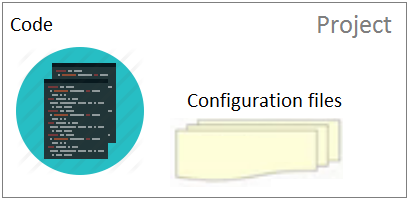
After being completed, the project will be packed and deployed onto the Server. Normally, configuration files will be packed together with the code and form a sole (file) product. Thus, if there are any changes in the configuration, you need to compile, and repack the project and re-deploy it onto the server. This is obviously a challenge in a distributed application environment.
Config Server?
The idea to solve the above problem is that a service (application) is required to manage configurations for other services. It runs independently on a server.
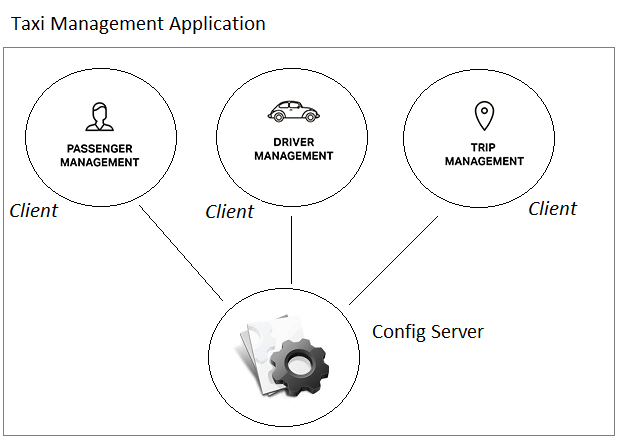
The above idea brings about the following benefits:
- TODO
- Spring Cloud Bus:
When you change a configuration file on the Config-Server, you will surely want to notify of such changes to Clients. The Spring Cloud Bus provides a mechanism for informing to Clients that "There is a change" and requires the Clients to update new information.
3. How does Config Server store data?
When you put all configuration files on the Config Server, you will ask how the Config Server stores those files.
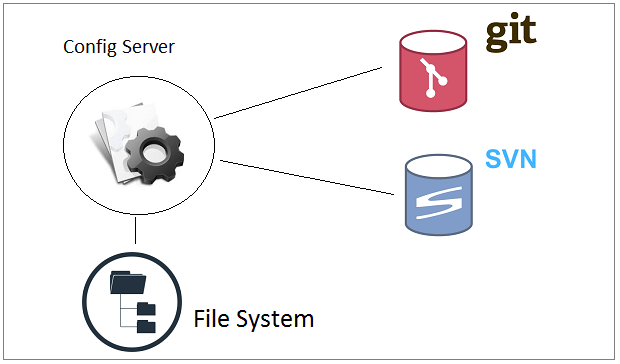
There are 2 main ways for the Config Server to store configuration files:
- Store them on the hard drive of the server as system files.
- Use GIT or SVN (Subversion).
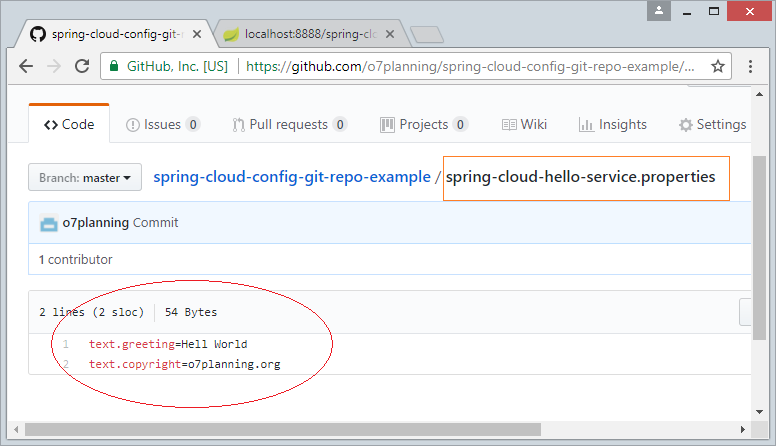
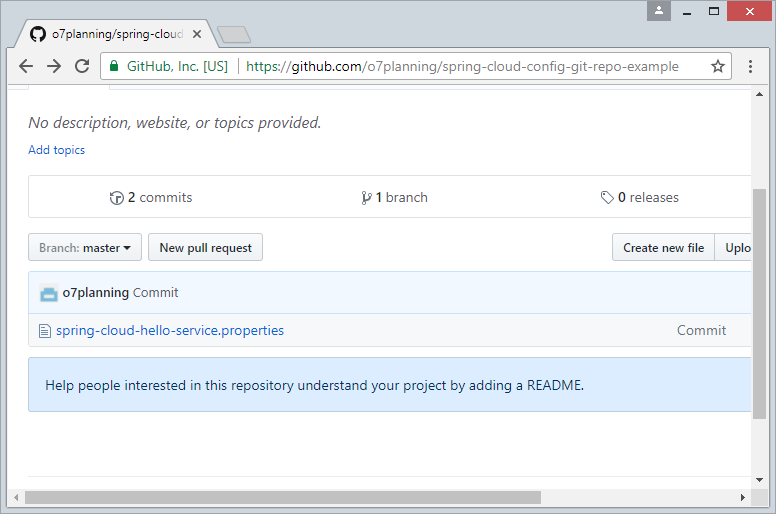
In this lesson, I am going to create a Config Server, which stores configuration files on GitHub. I have created a GitHub Repository:
4. Create Spring Boot project
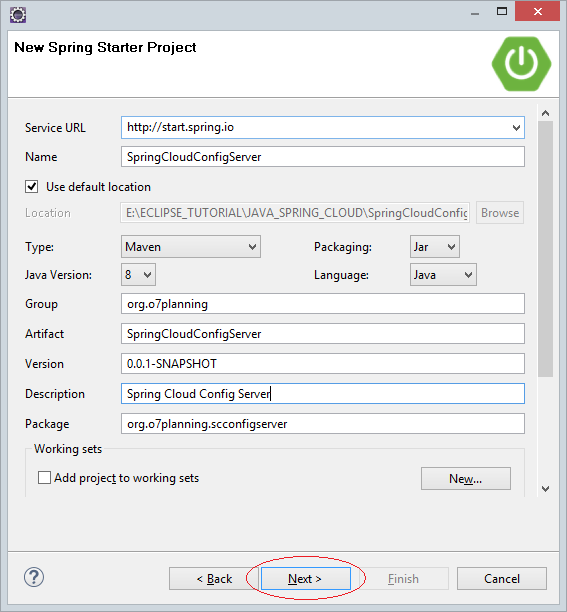
On the Eclipse, create a Spring Boot project:
Enter:
- Name: SpringCloudConfigServer
- Group: org.o7planning
- Artifact: SpringCloudConfigServer
- Description: Spring Cloud Config Server
- Package: org.o7planning.scconfigserver
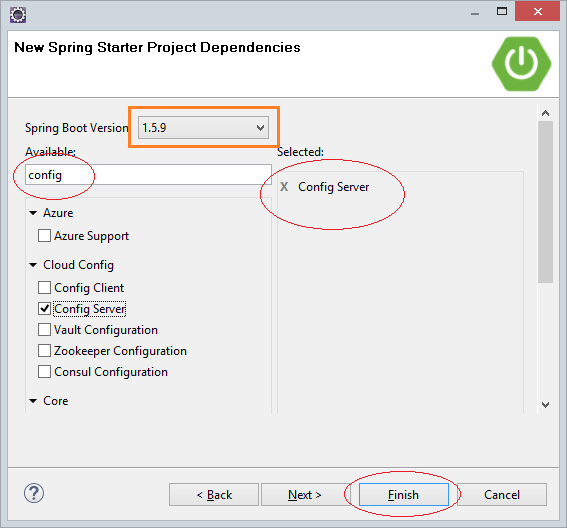
2.0.0.M..xxtrial version Spring Boot isbuggy with the Spring Cloud; therefore, we will use Spring Boot 1.5.9.
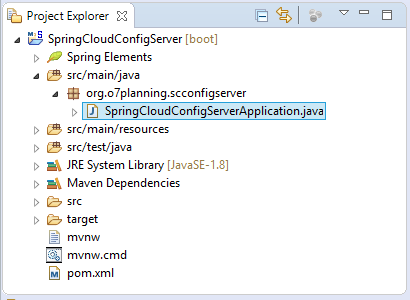
OK, the Project has been created:
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.o7planning</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringCloudConfigServer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>SpringCloudConfigServer</name>
<description>Spring Cloud Config Server</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Edgware.RELEASE</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-config-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>@EnableConfigServer
SpringCloudConfigServerApplication.java
package org.o7planning.scconfigserver;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer;
@EnableConfigServer // ==> Important!!
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringCloudConfigServerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringCloudConfigServerApplication.class, args);
}
}5. Configure Config Server
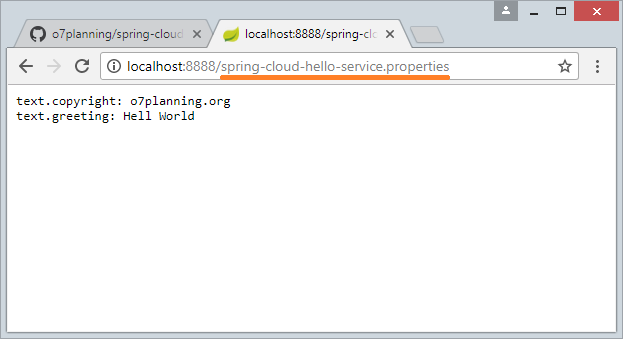
This service (application) will be deployed and run on port 8888 and store configuration files on the GitHub, so you need some configurations in the application.properties file.
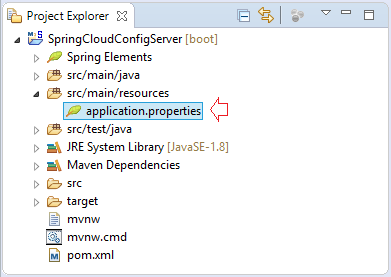
application.properties
server.port=8888
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri=https://github.com/o7planning/spring-cloud-config-git-repo-example.git
# For File System:
# spring.profiles.active=native
# spring.cloud.config.server.native.searchLocations=C:/Users/tran/Desktop/configIf Git Server (or SVN Server) requires an username/password, you need to make additional configurations. You can refer to the appendix at the end of this post.
Spring Cloud Tutorials
- What is Cloud Computing?
- Introduction to Netflix and its cloud computing technology
- Introduction to Spring Cloud
- Understanding Spring Cloud Config Server with Example
- Understanding Spring Cloud Config Client with Example
- Understanding Spring Cloud Eureka Server with Example
- Understanding Spring Cloud Discovery Eureka Client with Example
- Undertanding load balancing in Spring Cloud with Ribbon and example
Show More