Swift Structs Tutorial with Examples
1. What is Struct?
In Swift, Struct (structure) is a special type of value, it creates a variable, to store multiple values, but the values are related to each other.
For example, information about an employee include:
- Employee number
- Employee name
- Position
You can create 3 variables to store the information above of employee. However you can create a Struct to store all three information on in a single variable.
Swift uses struct keyword to declare a Struct.
Employee.swift
import Foundation
struct Employee {
var empNumber:String
var empName:String
var position:String
// Constructor.
init(empNumber:String, empName:String, position:String) {
self.empNumber = empNumber;
self.empName = empName;
self.position = position;
}
}For example, use Struct:
EmployeeTest.swift
import Foundation
func test_EmployeeStruct() {
// Create a variable from Employee struct
let john = Employee(empNumber:"E01",empName: "John",position: "CLERK")
print("Emp Number: " + john.empNumber)
print("Emp Name: " + john.empName)
print("Emp Position: " + john.position)
}Edit main.swift:
main.swift
import Foundation
test_EmployeeStruct()Running the example:
Emp Number: E01
Emp Name: John
Emp Position: CLECK2. Struct vs Class
Struct is commonly used to create an object to store the value, while the class is using more diversely.
- Struct does not allow inheritance from a class or another struct.
- But Struct allows inheritance from one or more Protocol.
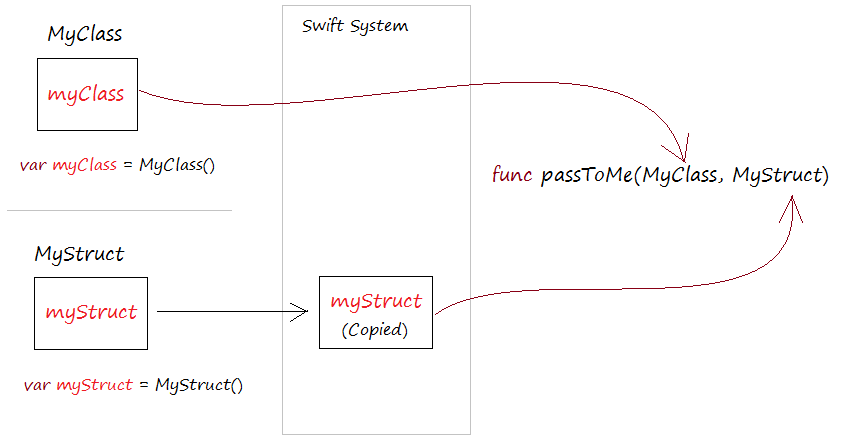
If struct appears as a parameter in a function (or method), it is passed as a value. Meanwhile, if the instance of a class appears as a parameter in a function (or method) it is passed as a reference.
StructVsClass.swift
import Foundation
// A class
class MyClass {
var name: String = "Abc"
}
// A struct
struct MyStruct {
var name: String = "Abc"
}
// A function, 2 parameters
// First parameter is a class, and second parameter is a struct.
func passToMe( myClass: MyClass, myStruct: MyStruct) {
// Change value to 'name' field.
myClass.name = "New Name"
// Can not change value to field of this struct.
// (It is a copy,its fields become constants and can not be changed.
// myStruct.name = "New Name" ***
}
func test_passToMe() {
// An object of MyClass.
var mc = MyClass()
print("mc.name = \(mc.name)") // Abc
// A value of MyStruct.
var ms = MyStruct()
print("Call passToMe function")
// Pass to passToMe() function.
// Note: The first parameter does not require a Label.
passToMe( mc, myStruct: ms)
print("mc.name = \(mc.name)") // New Name
}Running the example:
mc.name = Abc
Call passToMe function
mc.name = New Name3. Constructor of Struct
Struct can have Constructors but do not have Destructor
Here are few notes for the Constructor:
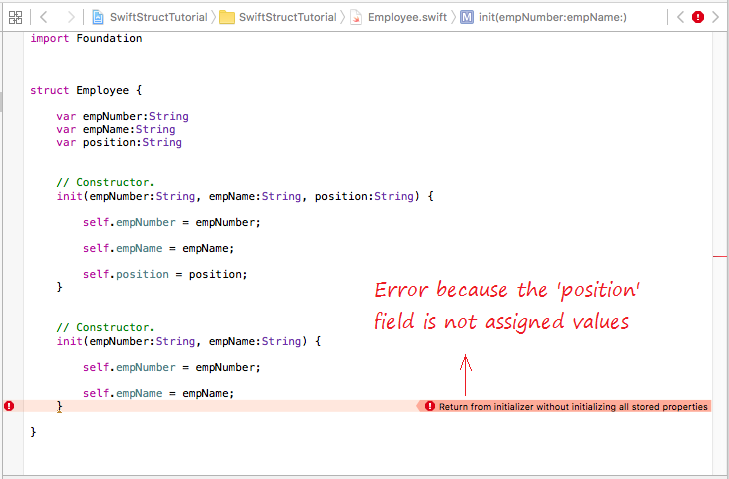
- You can write one or more constructor for struct.
- In the constructor you must assign values to all fields that don't have value.
4. Methods and properties of Struct
Struct can have methods and properties.
Book.swift
import Foundation
struct Book {
// Property
var title:String {
get {
return self.title;
}
set (value) {
self.title = value
}
}
// Property
var author:String {
get {
return self.author;
}
set(value) {
self.author = value;
}
}
// Constructor.
init( title:String, author:String) {
self.title = title;
self.author = author;
}
// Method.
func getInfo() -> String {
return "Book Title: " + self.title + ", Author: " + self.author;
}
}See more about properties at:
- Swift Properties
Swift Programming Tutorials
- Install Mac OS X 10.11 El Capitan in VMWare
- Install XCode
- Swift Tutorial for Beginners
- Swift Functions Tutorial with Examples
- Swift Closures Tutorial with Examples
- Class and Object in Swift
- Swift Enums Tutorial with Examples
- Swift Structs Tutorial with Examples
- Programming for Team using XCode and SVN
Show More