Pagination in Java Hibernate
1. What is Pagination?
Pagination is a technique for splitting a list of multiple records into sublists. For example, you search with a keyword on Google and receives tens of thousands of results. However, every Google page displays only 10 results for you. Other results will show on next pages.
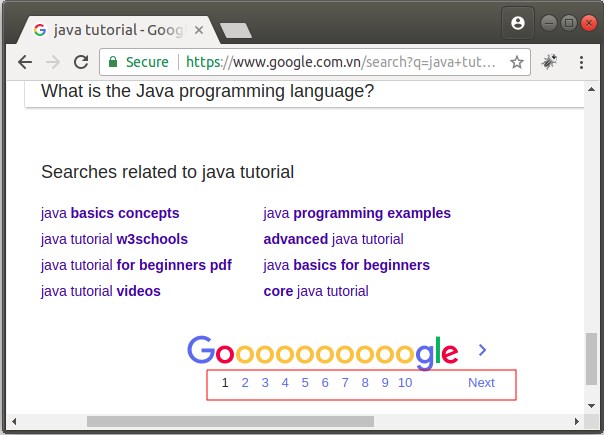
In the Java application using Hibernate, a query statement can return a list of records, and you ask the question that what is done to take only part of the list (the records from position N1 to position N2), and get information on total records and total pages.
Hibernate vs JPA
Hibernate and JPA are two identical technologies. If you know about the Hibernate, you can work with the JPA easily and vice versa. However, they also have some differences. One of such differences is that the Hibernate provides better pagination techniques than the JPA does. In this lesson, I am going to guiding you for using the pagination technique of Hibernate 5. It is noted that this technique is not supported by the JPA.
2. Pagination with Hibernate
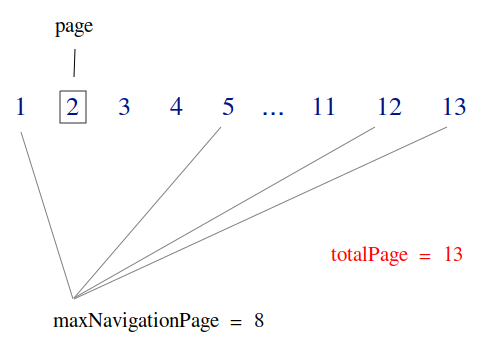
All things you need to do are to create a Query object, and provide page, maxResult, maxNavigationResult parameters to create a PaginationResult object.
The PaginationResult is a utility class that helps you implement a query and returns a list of records suitable for the above parameters.
The PaginationResult is a utility class that helps you implement a query and returns a list of records suitable for the above parameters.
PaginationResult.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.pagination;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.ScrollMode;
import org.hibernate.ScrollableResults;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
public class PaginationResult<E> {
private int totalRecords;
private int currentPage;
private List<E> list;
private int maxResult;
private int totalPages;
private int maxNavigationPage;
private List<Integer> navigationPages;
// @page: 1, 2, ..
public PaginationResult(Query<E> query, int page, int maxResult, int maxNavigationPage) {
final int pageIndex = page - 1 < 0 ? 0 : page - 1;
int fromRecordIndex = pageIndex * maxResult;
int maxRecordIndex = fromRecordIndex + maxResult;
ScrollableResults resultScroll = query.scroll(ScrollMode.SCROLL_INSENSITIVE );
List<E> results = new ArrayList<E>();
boolean hasResult = resultScroll.first();
if (hasResult) {
// Scroll to position:
hasResult = resultScroll.scroll(fromRecordIndex);
if (hasResult) {
do {
E record = (E) resultScroll.get(0);
results.add(record);
} while (resultScroll.next()//
&& resultScroll.getRowNumber() >= fromRecordIndex
&& resultScroll.getRowNumber() < maxRecordIndex);
}
// Go to Last record.
resultScroll.last();
}
// Total Records
this.totalRecords = resultScroll.getRowNumber() + 1;
this.currentPage = pageIndex + 1;
this.list = results;
this.maxResult = maxResult;
if (this.totalRecords % this.maxResult == 0) {
this.totalPages = this.totalRecords / this.maxResult;
} else {
this.totalPages = (this.totalRecords / this.maxResult) + 1;
}
this.maxNavigationPage = maxNavigationPage;
if (maxNavigationPage < totalPages) {
this.maxNavigationPage = maxNavigationPage;
}
resultScroll.close();
this.calcNavigationPages();
}
private void calcNavigationPages() {
this.navigationPages = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int current = this.currentPage > this.totalPages ? this.totalPages : this.currentPage;
int begin = current - this.maxNavigationPage / 2;
int end = current + this.maxNavigationPage / 2;
// The first page
navigationPages.add(1);
if (begin > 2) {
// Using for '...'
navigationPages.add(-1);
}
for (int i = begin; i < end; i++) {
if (i > 1 && i < this.totalPages) {
navigationPages.add(i);
}
}
if (end < this.totalPages - 2) {
// Using for '...'
navigationPages.add(-1);
}
// The last page.
navigationPages.add(this.totalPages);
}
public int getTotalPages() {
return totalPages;
}
public int getTotalRecords() {
return totalRecords;
}
public int getCurrentPage() {
return currentPage;
}
public List<E> getList() {
return list;
}
public int getMaxResult() {
return maxResult;
}
public List<Integer> getNavigationPages() {
return navigationPages;
}
}Example:
Employee.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.entities;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.Lob;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.Temporal;
import javax.persistence.TemporalType;
import javax.persistence.UniqueConstraint;
@Entity
@Table(name = "EMPLOYEE", //
uniqueConstraints = { @UniqueConstraint(columnNames = { "EMP_NO" }) })
public class Employee {
@Id
@Column(name = "EMP_ID")
private Long empId;
@Column(name = "EMP_NO", length = 20, nullable = false)
private String empNo;
@Column(name = "EMP_NAME", length = 50, nullable = false)
private String empName;
@Column(name = "JOB", length = 30, nullable = false)
private String job;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "MNG_ID")
private Employee manager;
@Column(name = "HIRE_DATE", nullable = false)
@Temporal(TemporalType.DATE)
private Date hideDate;
@Column(name = "SALARY", nullable = false)
private Float salary;
@Lob
@Column(name = "IMAGE", length = Integer.MAX_VALUE, nullable = true)
private byte[] image;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY)
@JoinColumn(name = "DEPT_ID", nullable = false)
private Department department;
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "empId")
private Set<Employee> employees = new HashSet<Employee>(0);
// Getter & Setter
}Department.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.entities;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.UniqueConstraint;
@Entity
@Table(name = "DEPARTMENT", //
uniqueConstraints = { @UniqueConstraint(columnNames = { "DEPT_NO" }) })
public class Department {
@Id
@Column(name = "DEPT_ID")
private Integer deptId;
@Column(name = "DEPT_NO", length = 20, nullable = false)
private String deptNo;
@Column(name = "DEPT_NAME", nullable = false)
private String deptName;
@Column(name = "LOCATION")
private String location;
@OneToMany(fetch = FetchType.LAZY, mappedBy = "department")
private Set<Employee> employees = new HashSet<Employee>(0);
public Department() {
}
// Getter & Setter
}EmployeeInfo.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.beans;
public class EmployeeInfo {
private Long empId;
private String empNo;
private String empName;
private String deptNo;
private String deptName;
public EmployeeInfo() {
}
// This constructor is used by Hibernate Query.
public EmployeeInfo(Long empId, String empNo, String empName, String deptNo, String deptName) {
this.empId = empId;
this.empNo = empNo;
this.empName = empName;
this.deptNo = deptNo;
this.deptName = deptName;
}
// Getter & Setter
}Example:
PaginationExample1.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.pagination;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.HibernateUtils;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.entities.Employee;
public class PaginationExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Have sessionFactory object...
SessionFactory factory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
Session session = factory.getCurrentSession();
String sql = "Select e from " + Employee.class.getName() + " e " //
+ " Where e.empId > :empId ";
Query<Employee> query = session.createQuery(sql, Employee.class);
query.setParameter("empId", 100);
int page = 1;
int maxResult = 20;
int maxNavigationResult = 10;
PaginationResult<Employee> result = new PaginationResult<Employee>(query, page, maxResult, maxNavigationResult);
// Result:
List<Employee> emps = result.getList();
int totalPages = result.getTotalRecords();
int totalRecords = result.getTotalRecords();
// 1 2 3 4 5 ... 11 12 13
List<Integer> navPages = result.getNavigationPages();
}
}Example:
PaginationExample2.java
package org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.pagination;
import java.util.List;
import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.query.Query;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.HibernateUtils;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.beans.EmployeeInfo;
import org.o7planning.tutorial.hibernate.entities.Employee;
public class PaginationExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Get sessionFactory object...
SessionFactory factory = HibernateUtils.getSessionFactory();
Session session = factory.getCurrentSession();
String sql = "Select new " + EmployeeInfo.class.getName() //
+ " (e.empId,e.empNo,e.empName,d.deptNo,d.deptName) " //
+ " from " + Employee.class.getName() + " e " //
+ " Join e.department d " //
+ " Order by e.empNo ";
Query<EmployeeInfo> query = session.createQuery(sql, EmployeeInfo.class);
int page = 1;
int maxResult = 20;
int maxNavigationResult = 10;
PaginationResult<EmployeeInfo> result
= new PaginationResult<EmployeeInfo>(query, page, maxResult, maxNavigationResult);
// Result:
List<EmployeeInfo> emps = result.getList();
int totalPages = result.getTotalRecords();
int totalRecords = result.getTotalRecords();
// 1 2 3 4 5 ... 11 12 13
List<Integer> navPages = result.getNavigationPages();
}
}And example .... of a JSP code snippet using PaginationResult:
JSP Pagination
<c:if test="${paginationProducts.totalPages > 1}">
<div class="page-navigator">
<c:forEach items="${paginationProducts.navigationPages}" var = "page">
<c:if test="${page != -1 }">
<a href="productList?page=${page}" class="nav-item">${page}</a>
</c:if>
<c:if test="${page == -1 }">
<span class="nav-item"> ... </span>
</c:if>
</c:forEach>
</div>
</c:if>